MSP430G2231:1.8V-3.6V超低功耗微控制器手册
MSP430G2231是一款由TI公司提供的混合信号微控制器,它在低功耗、高性能和多功能性方面表现出色。该芯片的主要特点包括:
1. **电源范围**:MSP430G2231支持极宽的电压范围,从1.8伏到3.6伏,适应各种应用环境。
2. **16位定时器A**:集成有两组捕获/比较寄存器,提供了高精度的时间和计数功能,这对于需要精确时间控制的应用来说非常有用。
3. **超低功耗设计**:在活跃模式下,如在1MHz时钟下,SPI接口消耗仅为220微安,而在待机模式下,功耗降到了只有0.5微安,甚至在Off模式下,如果保持RAM,仅需0.1微安,非常适合电池供电设备。
4. **多模式电源管理**:提供五个不同的电源节省模式,包括自动扫描、样保持、超快速唤醒等,能够在不同场景下显著降低能耗。
5. **高级通信接口**:内置通用串行接口(USI),支持SPI和I2C通信,且在活跃模式下的功耗表现良好。
6. **布朗out检测器**:确保系统在电压波动时仍能正常工作,保护敏感电路免受电压下降的影响。
7. **10位A/D转换器**:具有200ksps采样率,内部带有参考源、样保持功能和自动扫描,有助于高效的数据采集。
8. **高级架构与安全特性**:基于16位RISC架构,指令周期可编程,提供代码保护功能,通过安全熔丝实现固件保护。
9. **基本时钟配置**:支持内部频率高达16MHz,配合内置的校准频率接口,以及低功耗低频振荡器。
10. **封装形式**:MSP430G2231提供14引脚塑料小型外形薄片封装,便于集成和散热。
11. **软件支持**:支持串行在线编程,无需额外的编程电压,方便开发者进行调试和固件更新。
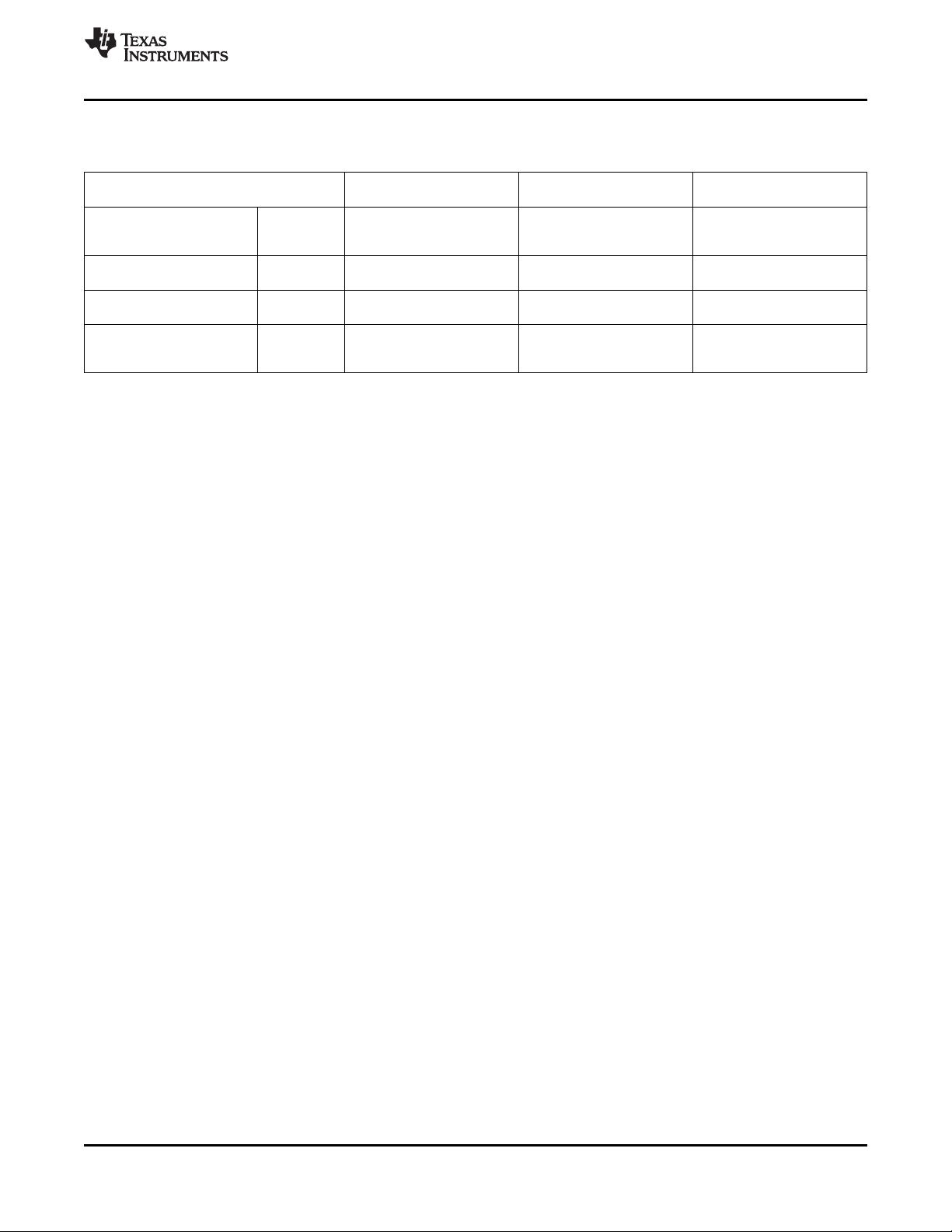
12. **家族成员详情**:图表(Table 1)中列出了MSP430G2x21和MSP430G2x31系列的其他成员及其特性对比,用户可以根据具体需求选择最适合的产品。
MSP430G2231芯片是一款适用于能源效率要求高的应用的高性能微控制器,无论是工业自动化、物联网(IoT)设备还是消费电子,都能找到其独特的价值。
2017-10-25 上传
2012-02-10 上传
2015-04-23 上传
2012-04-23 上传
点击了解资源详情
点击了解资源详情
2021-08-19 上传
2014-03-15 上传
2012-08-19 上传
bai7819
- 粉丝: 1
- 资源: 3
最新资源
- ayotidur
- Exsty-crx插件
- Language-zone
- SCATTERBAR3:创建一个 3-D 条形图,其中条形放置在用户指定的 XY 位置。-matlab开发
- TensorFlow2实战-系列教程14:Resnet实战
- [新闻文章]小虫新闻管理系统V1.0_xcnewsv1.0.rar
- AzureDiagnosticsPipeline:此存储库具有构建Azure诊断DevOps管道的源,以将诊断设置应用于Azure资源(动态)
- 蛇:基于控制台的蛇游戏
- TurboCStudy,c语言编译的源码,c语言项目
- Biorhythm:你的一周过得怎么样?-matlab开发
- koa-template-project:Koa模板项目
- 简洁棕色线条响应式html5模板5598.zip
- Coin Master Free Spins Loader-crx插件
- 苹果手机
- click-and-meet-calendar-generator:生成可打印的日历,以根据德国的COVID-19规则管理“点击并开会”约会
- -123r