COL 12(11), 110602(2014) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS November 10, 2014
1671-7694/2014/110602(6) 110602-1 © 2014 Chinese Optics Letters
Compared with wavelength division multiplexing
(WDM)
[1]
networks, elastic optical networks (EONs)
[2]
based on the optical orthogonal frequency division
multiplexing (O-OFDM) technique
[3]
can signicantly
improve spectrum utilization, while more complex con-
straints on the routing and spectrum allocation (RSA)
problem keep them from being operated in a totally
elastic way. There is a new kind of constraint called
spectrum continuity constraint (SCC) in RSA prob-
lem
[4]
, consisting of two major parts. The rst one is
almost the same as the conventional weakly connected
component (WCC), that is, it must be assigned the
same spectrum range on all the physical links (p-links)
the optical channel (OC) traverses, which is called spec-
trum consistency constraint. The second one stemming
from EON is called spectrum contiguity constraint,
meaning that the frequency units taken by one OC
must be contiguous. The latter would cause spectrum
fragments and decrease the performance of networks.
Virtual topology design scheme with energy eiciency for
IP over elastic optical networks
Yiming Yu (于一鸣)
*
, Yongli Zhao (赵永利), Jie Zhang (张 杰), Hui Li (李 慧),
Yuefeng Ji (纪越峰), and Wanyi Gu (顾畹仪)
State Key Laboratory of Information Photonics and Optical Communications,
Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Beijing 100876, China
*
Corresponding author: tony_yu@bupt.edu.cn
Received February 25, 2014; accepted July 25, 2014; posted online October 27, 2014
The rapid growth of the Internet raises the importance of resource planning of Internet protocol (IP) over
elastic optical networks (EONs), which is a challenging task due to more complex and obscure physical
constraints of it. Compared with network cost, the power consumption may eventually become the barrier to
the expansion of the Internet. We present an energy-eicient virtual topology design (VTD) scheme for IP
over EON. We explicitly explain and analyze the mixed integer linear programming model and the heuristic
algorithm for this scheme. Numerical results show that the proposed VTD scheme can signicantly save
power consumption.
OCIS codes: 060.1155, 060.4251, 060.4256.
doi: 10.3788/COL201412.110602.
To surmount this constraint, several solutions, such as
split-spectrum approach
[5,6]
, have been studied and pro-
posed.
An alternative solution is the Internet protocol (IP)
over EON approach which diverts the problem to exi-
ble IP packet streams
[7]
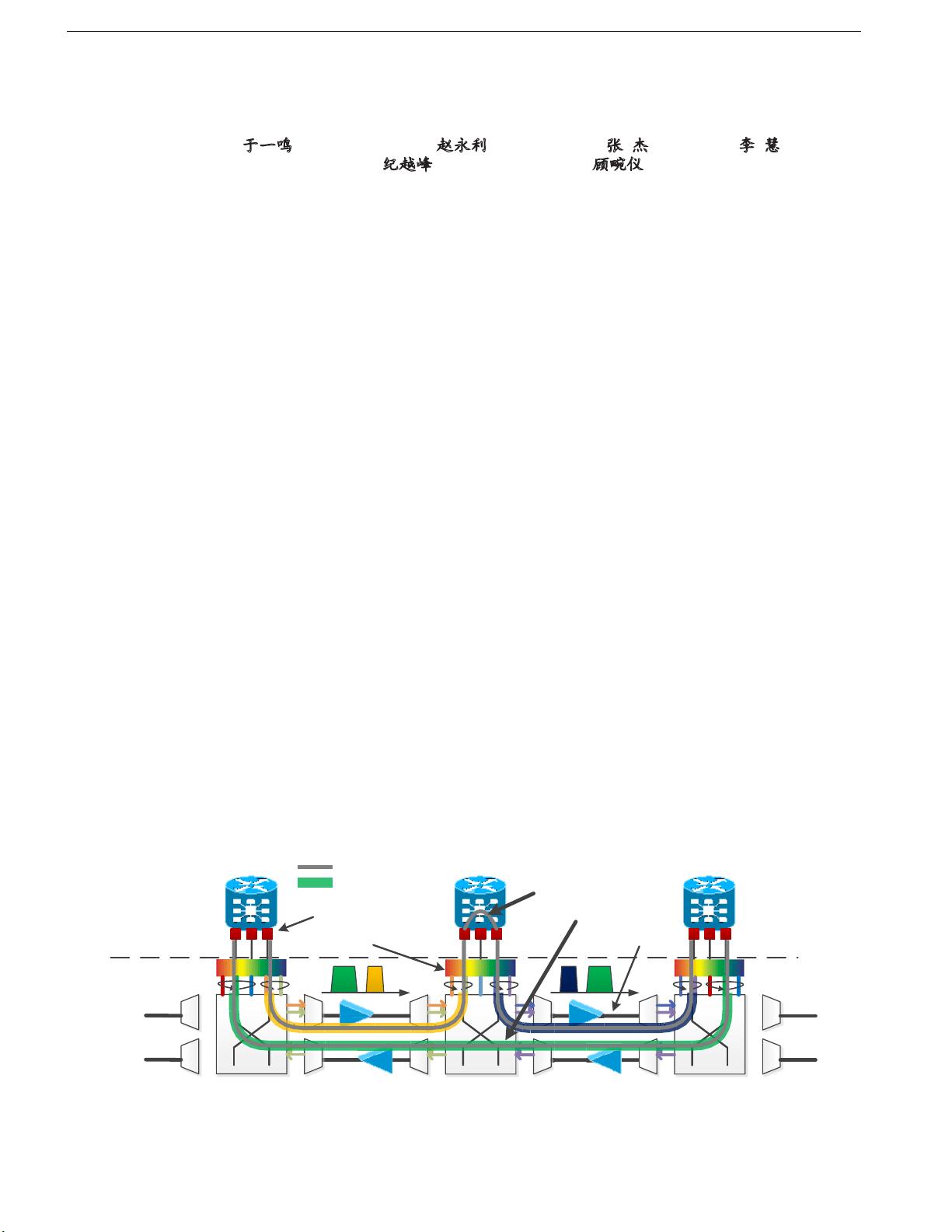
. As shown in Fig. 1, the IP over
EON is composed of two major layers: the overlay IP
(virtual) layer and the underlay optical (physical) layer.
In the IP layer, core IP routers with aggregated data
traic are connected to elastic optical switch nodes via
xed line-rate add/drop ports. The optical layer pro-
vides OCs with elastic capacity for connections between
IP routers. For each OC which may traverse several
optical nodes, a pair of elastic transponders is deployed
at the two ends for data transmission. Additionally,
erbium-doped ber ampliers (EDFAs) are deployed on
ber links to regenerate optical signals.
Due to the multi-layer nature of IP over EON, virtual
topology design (VTD) is an inevitable and important
sŝƌƚƵĂů>ĂLJĞƌ
WŚLJƐŝĐĂů>ĂLJĞƌ
/WƉŽƌƚƐ;
/W
Ϳ
sͲdƌĂŶƐƉŽŶĚĞƌƐ;
dZ
Ϳ&Ɛ;
Ϳ
ůĂƐƚŝĐKƉƚŝĐĂůEŽĚĞ ůĂƐƚŝĐKƉƚŝĐĂůEŽĚĞ ůĂƐƚŝĐKƉƚŝĐĂůEŽĚĞ
/WZŽƵƚĞƌ/WZŽƵƚĞƌ /WZŽƵƚĞƌ
KƉƚŝĐĂůLJƉĂƐƐ
/WLJƉĂƐƐ
KƉƚŝĐĂůŚĂŶŶĞů
/WŽŶŶĞĐƚŝŽŶ
sͲKy
sͲKy
sͲKy
sĂŶĚǁŝĚƚŚͲsĂƌŝĂďůĞ
Fig. 1. Architecture of an IP over EON.









