Functional Description Vweb Proprietary and Confidential
Vwe
b
Corp.
- PROPR
I
ET
ARY
Ha
r
d
wa
r
e Re
fe
r
e
n
c
e
Ma
n
ua
l
-
PR
EL
I
MINA
RY
VW2010 Hardware Description PRELIMINARY
page 6 May 13, 2003
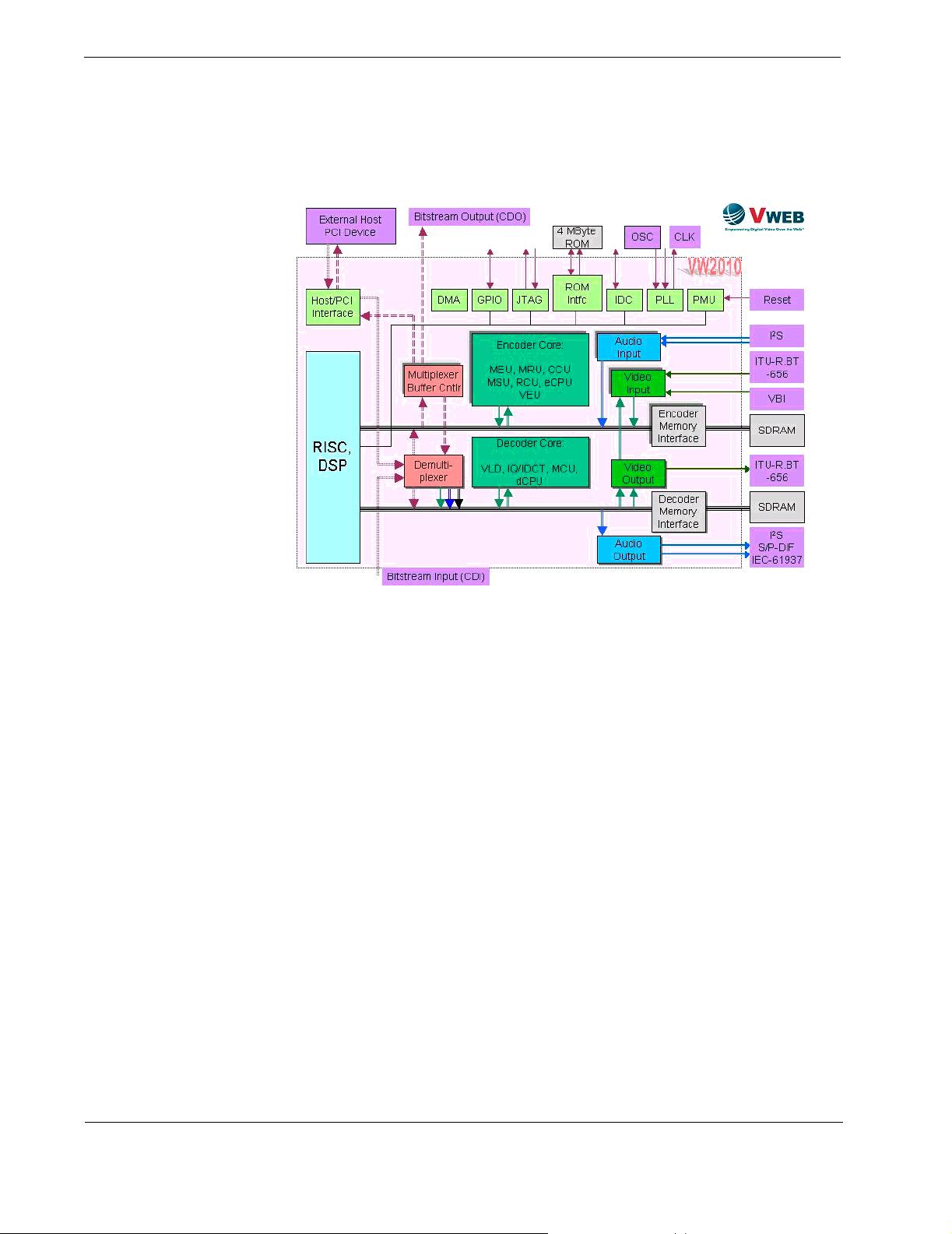
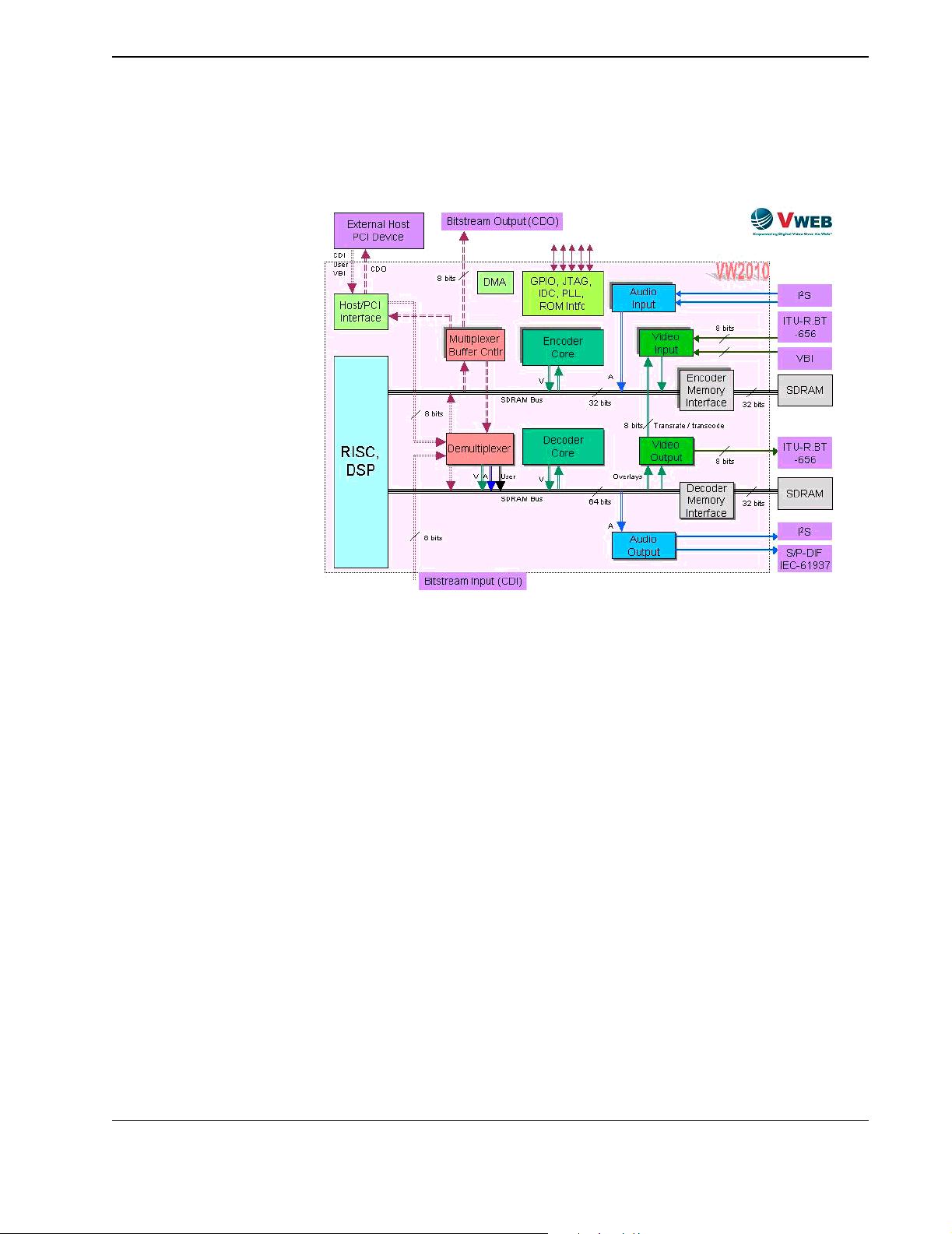
In the RISC, the compressed video from the encoder core modules is optionally com-
bined with compressed audio, and with user data, if any; then the data is multiplexed
and/or processed for network delivery. The resulting compressed data stream (CDO
bitstream) is sent to the multiplexer buffer controller (BUF) via the encoder SDRAM
bus.
By this time the CDO is a regular MPEG bitstream (SS, PS, TS, ES or PES, depending
on how the encoder was set up). For the sake of generality, in this document this MPEG
bitstream is still called CDO.
Compressed Data
Output Paths (CDO)
Under control by the RISC, the multiplexer buffer controller (BUF) sets up the appro-
priate buffers and FIFOs, and routes the CDO bitstream to the host/PCI interface
unit's output port, or directly to the dedicated 8-bit parallel or 1-bit serial CDO output
port.
Compressed Data
Input Paths (CDI)
Multiplexed / combined / compressed data input bitstream (CDI), as well as user data
and VBI, can be input on one of the input ports: on the host/PCI port, or on the ded-
icated 8-bit parallel / 1-bit serial CDI input port. From these ports, the data is internally
routed to the demultiplexer (DEMUX), which directly stores the data in the decoder or
encoder SDRAM via the corresponding high speed SDRAM bus (without demultiplex-
ing at this time).
There is no separate compressed audio input path. It is assumed the CDI bistream may
contain or may consist of tagged video, audio or user data components.
Decoder Paths Decoder processing begins in the RISC. It selects buffers and FIFOs for use by the
demultiplexer (DEMUX). The DEMUX retrieves the CDI from SDRAM, extracts
video, audio and user data from the CDI, and places each type of data into their sepa-
rated buffers and FIFOs. The data flow between the decoder modules the takes place
via the decoder SDRAM, as follows.
The demultiplexer (DEMUX) extracts video data from the CDI bitstream, and sends
it to the video decoder core via the decoder SDRAM. The video decoder core modules
retrieve this data from SDRAM as needed. The video decoding core modules read and
write to the SDRAM the intermediate and final results of the MPEG-1, -2, -4 or H.263
decoding / decompressing / filtering calculations. The decoder core sends the resulting
video data to the video output unit (VOU) via SDRAM. The VOU completes the con-
version of the video data to the ITU.R-BT.656 format. The VOU also contains a graph-
ics module, which, under user control, can generate multiple graphics overlays to be
superimposed on the video.
The DEMUX extracts user data from the CDI bitstream, and sends it to the decoder
SDRAM, for further processing by the RISC. In the RISC, user data is converted to
Closed Caption or Teletext data, and sent back into SDRAM as VBI data to be mixed
with the video data in the VOU.
The DEMUX extracts audio data from the CDI bitstream, and sends it to the decoder
SDRAM. The audio is decompressed using the DSP extensions within the RISC, and
put back into SDRAM. The audio output unit (AOU) retrieves this data from SDRAM
and converts it to I
2
S or S/P-DIF format.