R15+38.300 NG-RAN技术详解:架构、协议与物理层
需积分: 11 7 浏览量
更新于2024-07-18
收藏 2MB PDF 举报
R15+38.300+无线接入网(NG-RAN)概述和总体描述是3GPP(Third Generation Partnership Project,第三代合作伙伴计划)为5G标准制定的重要技术规范,它关注的是下一代无线接入网的设计和实现。该规范的版本为3GPPTS38.300V15.2.0,发布于2018年6月,详细阐述了NR(New Radio)技术及其与现有NG-RAN(Next-Generation Radio Access Network)的衔接。
主要内容包括以下几个方面:
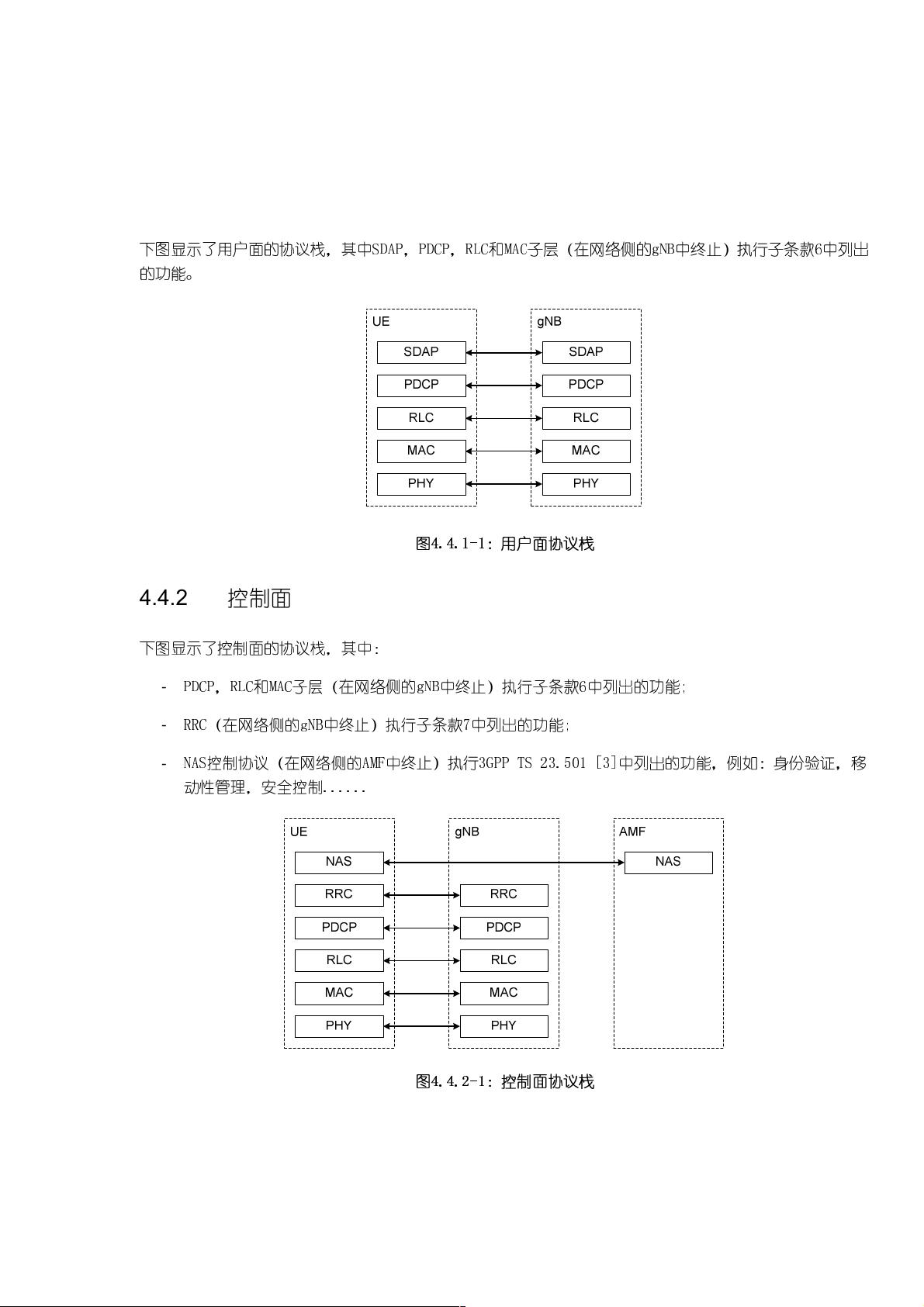
1. **整体架构和功能划分**:NG-RAN的架构分为整体架构和功能模块,其中NG接口负责用户面和控制面的通信,包括NG用户面和NG控制面;Xn接口用于连接多个NG-RAN节点,包含Xn用户面和Xn控制面。无线协议架构区分了用户面和控制面,支持多RAT(Radio Access Technology,无线接入技术)双连接。
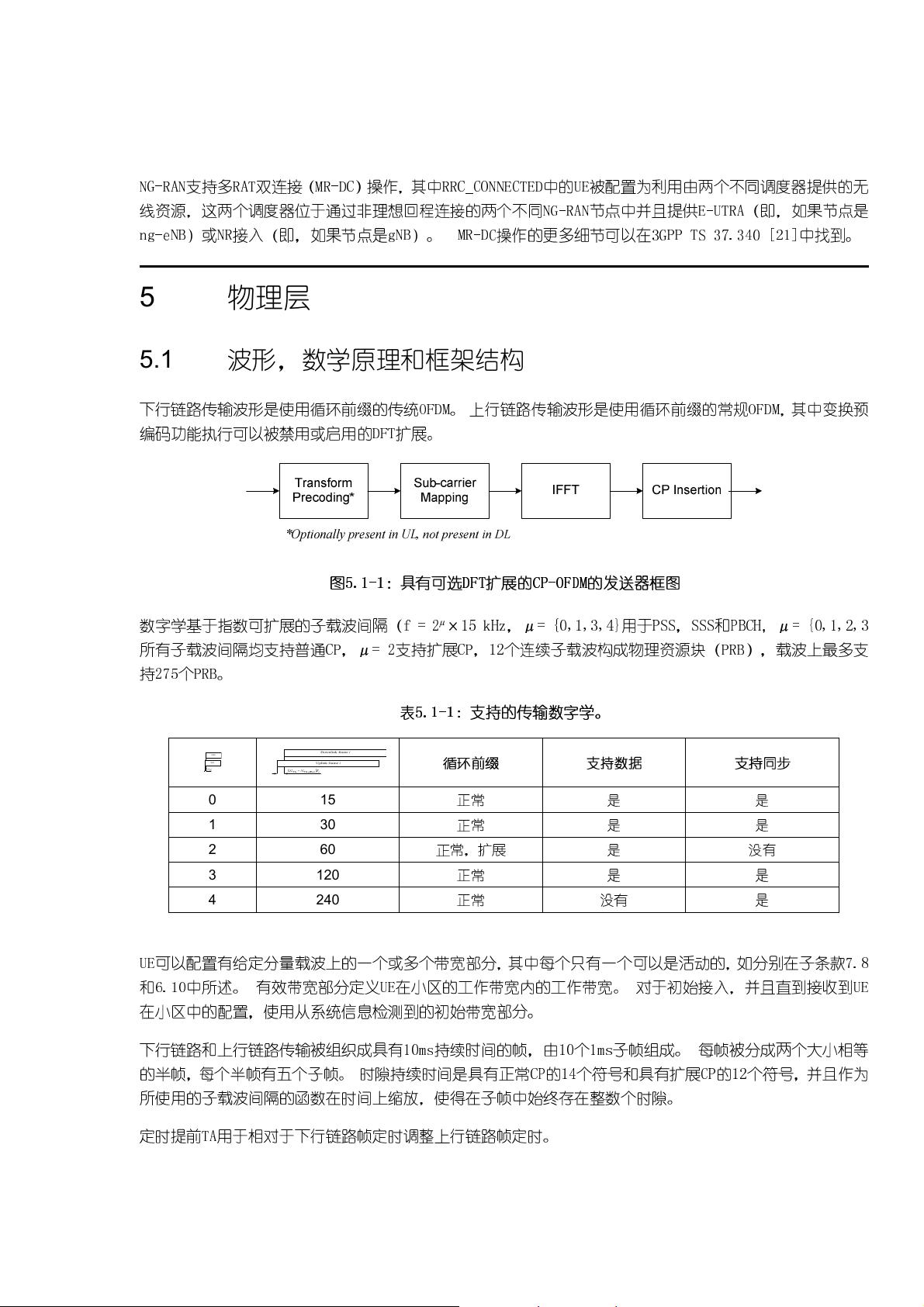
2. **物理层**:物理层是无线通信的基础,涉及波形、数学原理和框架结构。下行部分讨论了传输方案、物理下行链路共享信道的处理、控制信道、同步信号和PBCH(Physical Broadcast Channel,物理广播信道)等,以及链路适配、功率控制、小区搜索、HARQ( Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request,混合自动重传请求)等关键过程。上行链路同样涵盖了传输方案、控制信道、随机接入、功率控制和时序控制,以及HARQ机制。
3. **第2层(MAC和RLC子层)**:MAC子层主要负责数据的复用和传输,包括逻辑信道的管理、映射到传输信道、HARQ等功能。RLC子层则处理分段和重组数据,支持两种传输模式,并提供ARQ(Automatic Repeat Request,自动重传请求)服务。PDCP子层负责数据的头压缩和解压缩,以及提供安全服务。
4. **载波聚合**:为了提高数据速率,5G引入了载波聚合技术,允许在不同频率带宽上同时传输数据,增强上行链路能力。
整个文档详细介绍了NG-RAN的体系结构、关键技术细节和协议流程,为5G网络的设计、部署和优化提供了重要依据。通过理解和应用这些规范,可以确保5G无线接入网的高效、可靠和兼容性。
221 浏览量
136 浏览量
270 浏览量
270 浏览量
221 浏览量
609 浏览量
2024-10-30 上传
2021-04-19 上传
371 浏览量
milanllor
- 粉丝: 5
最新资源
- 网页自动刷新工具 v1.1 - 自定义时间间隔与关机
- pt-1.4协程源码深度解析
- EP4CE6E22C8芯片三相正弦波发生器设计与实现
- 高效处理超大XML文件的查看工具介绍
- 64K极限挑战:国际程序设计大赛优秀3D作品展
- ENVI软件全面应用教程指南
- 学生档案管理系统设计与开发
- 网络伪书:社区驱动的在线音乐制图平台
- Lettuce 5.0.3中文API文档完整包下载指南
- 雅虎通Yahoo! Messenger v0.8.115即时聊天功能详解
- 将Android手机转变为IP监控摄像机
- PLSQL入门教程:变量声明与程序交互
- 掌握.NET三层架构:实例学习与源码解析
- WPF中Devexpress GridControl分组功能实例分析
- H3Viewer: VS2010专用高效帮助文档查看工具
- STM32CubeMX LED与按键初始化及外部中断处理教程