8 Rec. ITU-T G.989.3 (05/2021)
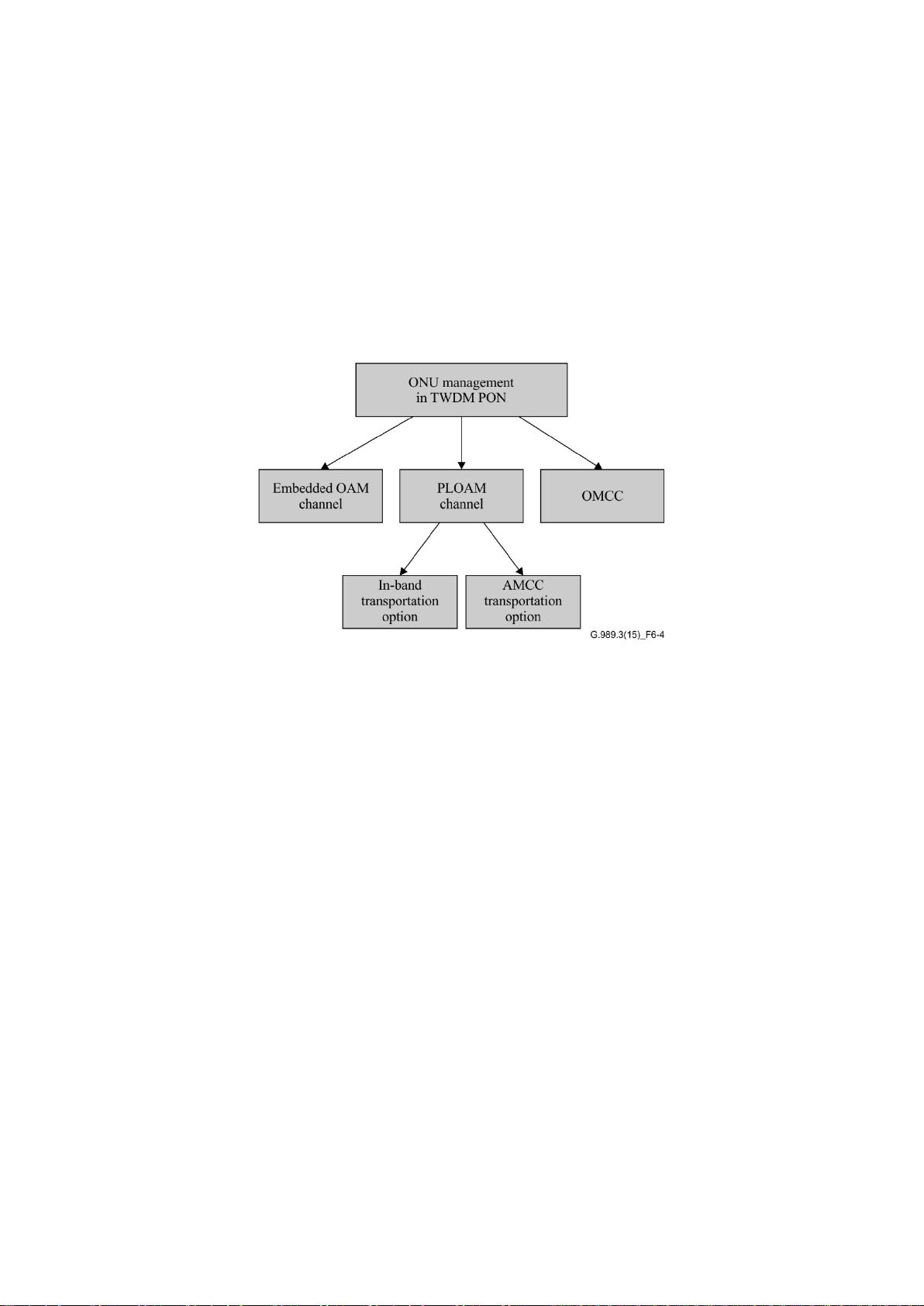
6.1.3.2 TWDM TC framing sublayer
The TWDM TC framing sublayer is responsible for the construction and parsing of the overhead
fields that support the necessary PON management functionality. The TWDM TC framing sublayer
formats are devised so that the frames, bursts and their elements are aligned to 4-byte word
boundaries, whenever possible.
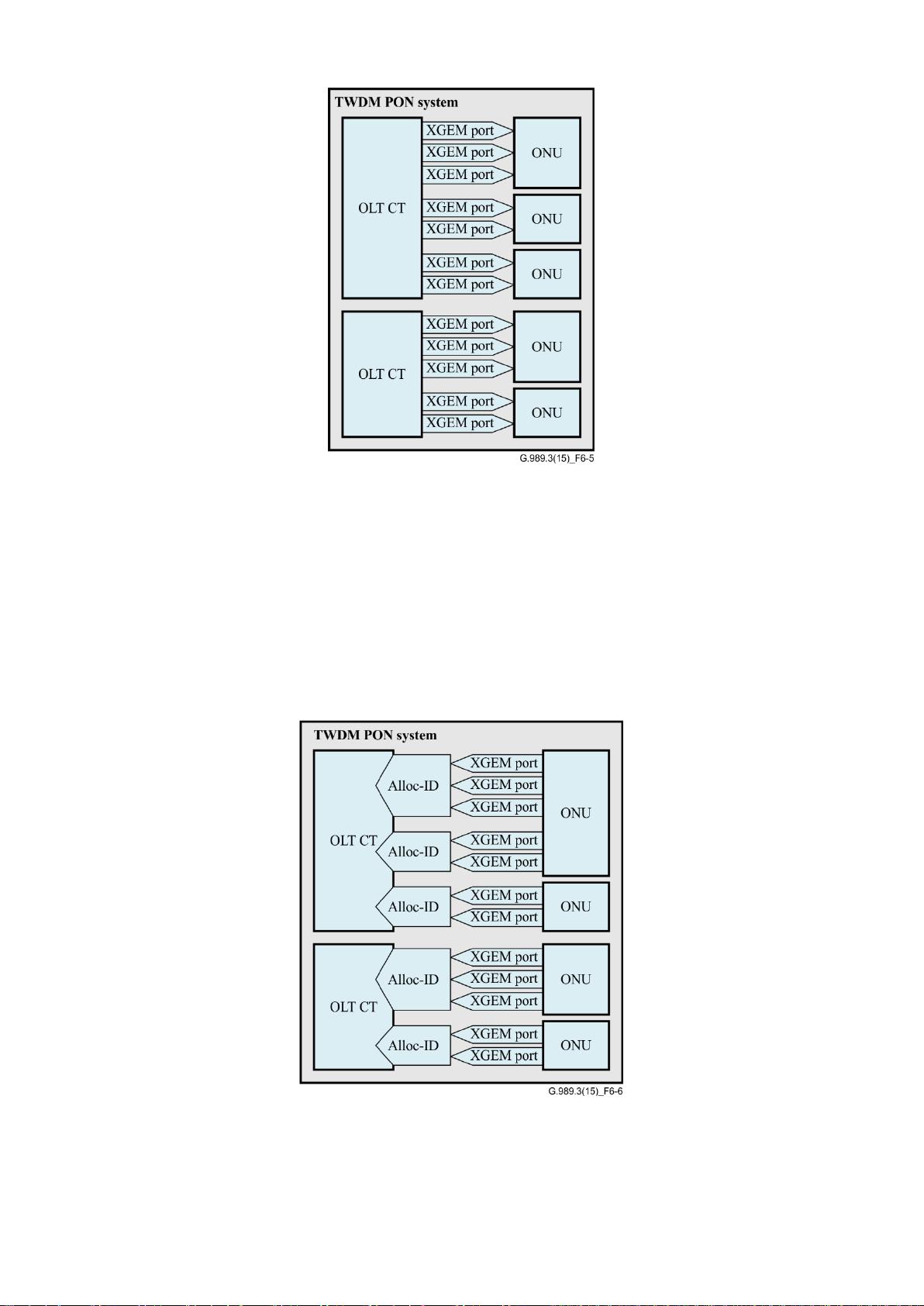
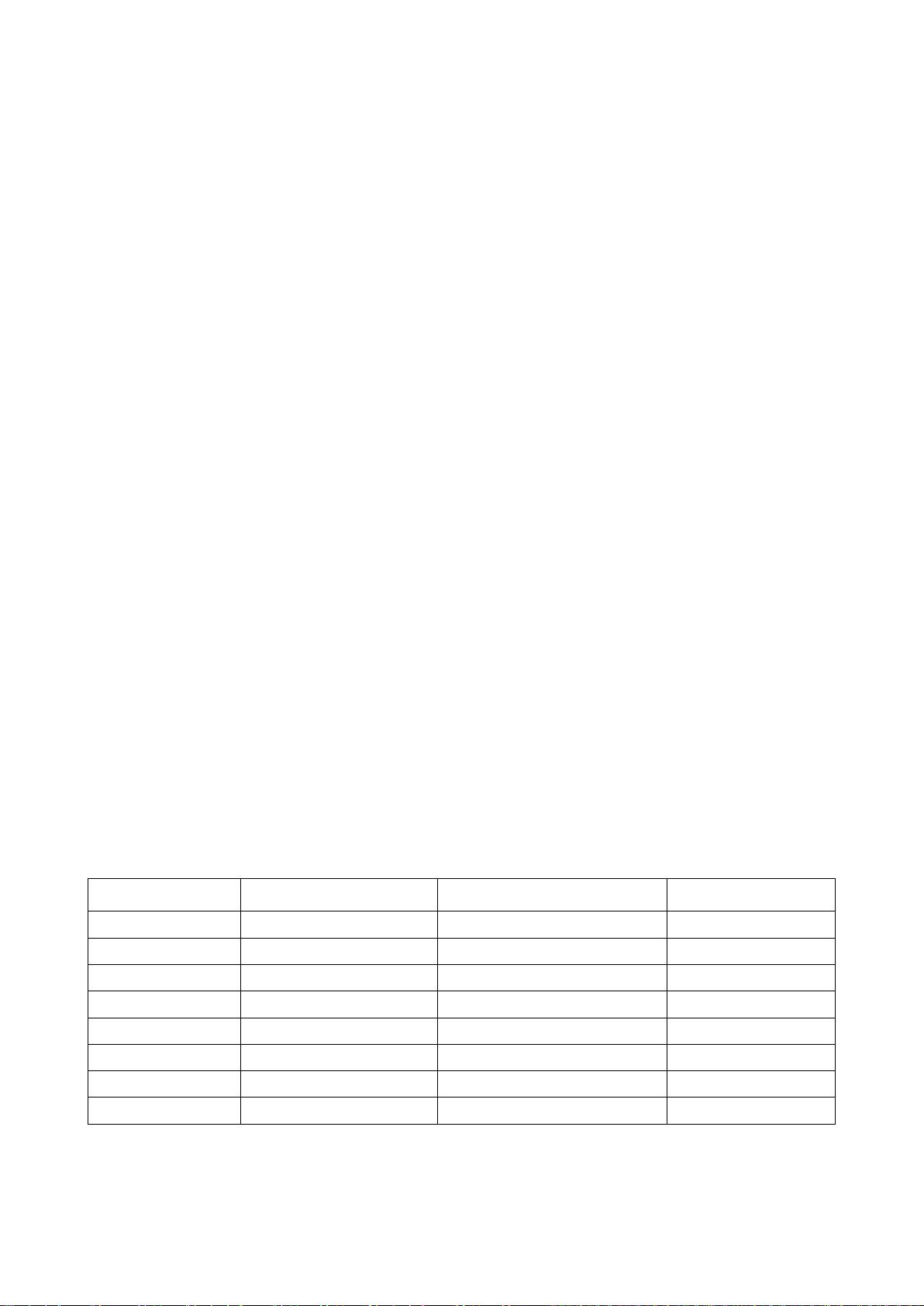
On the transmitter side, the TWDM TC framing sublayer accepts multiple series of XGEM frames
forming the FS payload from the TWDM TC service adaptation sublayer, and constructs the
downstream FS frame or upstream FS burst by providing the overhead fields for the embedded
operation, administration and maintenance (OAM) and the physical layer operation, administration
and maintenance (PLOAM) messaging channel. The size of each downstream FS frame payload is
obtained by subtracting the variable size of the upstream bandwidth management overhead and the
PLOAM channel load from the fixed size of the downstream FS frame. In the upstream direction, a
FS burst multiplexes FS payloads associated with multiple Alloc-IDs, the size of each payload being
determined based on the incoming bandwidth management information.
On the receiver side, the TWDM TC framing sublayer accepts the FS frames or FS bursts, parses the
FS overhead fields, extracts the incoming embedded management and PLOAM messaging flows, and
delivers the FS payloads to the TWDM TC service adaptation sublayer. The incoming PLOAM
messages are delivered to the PLOAM processor. The embedded OAM information to the extent
pertaining to upstream bandwidth management (BWmap parsing) and dynamic bandwidth
assignment (DBA) signalling is processed within the framing sublayer itself, providing partial control
over the PHY adaptation sublayer (upstream PHY burst timing and profile control). The rest of the
embedded OAM information is delivered to the appropriate TWDM TC functional entities outside of
the framing sublayer, such as ONU electrical power management and performance monitoring
blocks.
See clause 8.1.1 for the details of downstream FS frame format specification, including BWmap
parsing, and clause 8.1.2 for the details of upstream FS burst format specification, including DBA
signalling.
6.1.3.3 TWDM TC PHY adaptation sublayer
The TWDM TC PHY adaptation sublayer encompasses the functions that modify the bitstream
modulating the optical transmitter with the goal to improve the detection, reception and delineation
properties of the signal transmitted over the optical medium.
On the transmitter side, the TWDM TC PHY adaptation sublayer accepts the FS frames (in the
downstream direction) or FS bursts (in the upstream direction) from the framing sublayer, optionally
performs forward error correction (FEC) encoding, performs scrambling of the content, prepends the
physical synchronization block appropriate for downstream (PSBd) or upstream (PSBu) transmission
and provides timing alignment of the resulting bitstream.
On the receiver side, the TWDM TC PHY adaptation sublayer performs physical synchronization
and delineation of the incoming bitstream, descrambles the content of the PHY frame or PHY burst,
optionally performs FEC decoding, delivering the resulting FS frames (in the downstream direction)
or FS bursts (in the upstream direction) to the TWDM TC framing sublayer.
The details of the PSBd and PSBu overhead fields are specified in clauses 10.1.1.1 and 10.1.2.1,
respectively.
The use of FEC improves the effective sensitivity and overload characteristics of the optical receiver
by introducing redundancy in the transmitted bitstream and allowing the receiver to operate at a higher
bit error ratio (BER) level. FEC is specified in detail in clause 10.1.3.
Bitstream scrambling randomizes the transmission and helps to meet the specified consecutive
identical digits (CID) tolerance. The TWDM PON scrambling method is specified in clause 10.1.4.