学习与了解能谱仪的结构原理及使用的PPT教案
版权申诉
44 浏览量
更新于2024-02-29
收藏 782KB PPTX 举报
X-ray Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) is a fundamental electron microscopy technique with compositional analysis capabilities. The method relies on the generation of characteristic X-rays when inner-shell electrons are displaced and jump to higher energy levels, releasing excess energy in the form of X-rays. These characteristic X-rays have unique energy levels specific to each element, allowing for elemental identification and quantification based on their energy values and intensity in the spectrum.
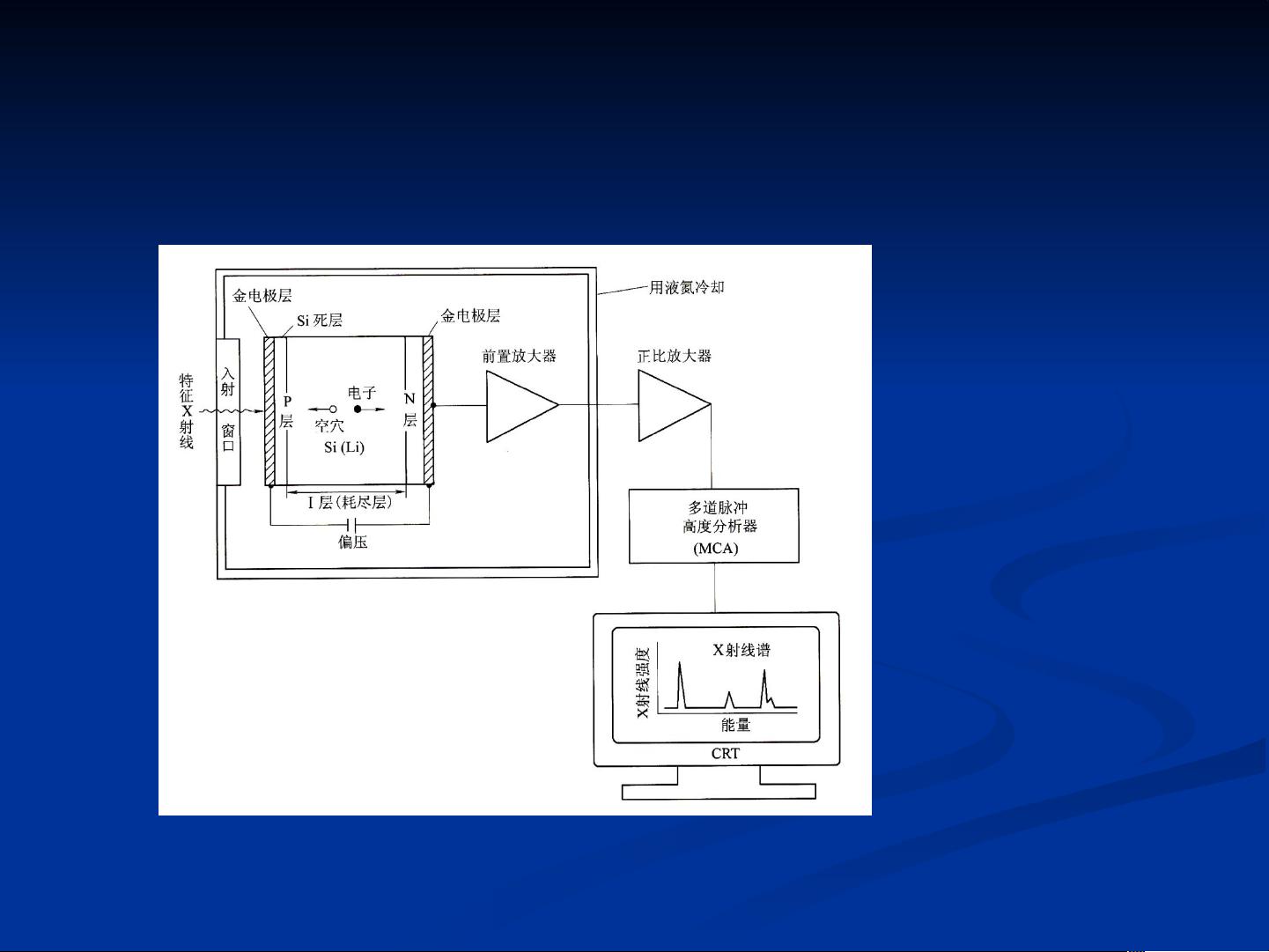
In the context of the Sirion 200 field emission scanning electron microscope with the GENESIS60E X-ray spectrometer attachment, the structure and working principles of the X-ray spectrometer are explored. The X-ray detector plays a crucial role in converting the emitted X-rays into electronic signals for analysis. Various types of X-ray detectors, such as silicon drift detectors or silicon PIN diodes, can be used for energy dispersive X-ray analysis.
Understanding the construction and operation of the X-ray spectrometer is essential for accurate elemental analysis. By selecting appropriate analytical parameters and methods, such as peak identification and background subtraction, researchers can achieve reliable results in micro-area compositional analysis. The ability to interpret and analyze X-ray energy dispersive spectra enables researchers to identify elements present in a sample and quantify their concentrations accurately.
Overall, mastering the principles and usage of X-ray spectrometers is essential for researchers in various scientific fields, including materials science, geology, and biology. By combining theoretical knowledge with practical applications, researchers can leverage X-ray energy dispersive spectroscopy for detailed elemental analysis and mapping in diverse research projects. Through continuous learning and experimentation, researchers can unlock the full potential of X-ray spectrometers for advancing scientific research and discovery.
点击了解资源详情
点击了解资源详情
点击了解资源详情
2021-10-05 上传
2021-10-11 上传
2021-10-02 上传
2021-10-03 上传
2021-10-05 上传
2021-10-05 上传
woshifafuge
- 粉丝: 8
- 资源: 58万+
最新资源
- JavaScript实现的高效pomodoro时钟教程
- CMake 3.25.3版本发布:程序员必备构建工具
- 直流无刷电机控制技术项目源码集合
- Ak Kamal电子安全客户端加载器-CRX插件介绍
- 揭露流氓软件:月息背后的秘密
- 京东自动抢购茅台脚本指南:如何设置eid与fp参数
- 动态格式化Matlab轴刻度标签 - ticklabelformat实用教程
- DSTUHack2021后端接口与Go语言实现解析
- CMake 3.25.2版本Linux软件包发布
- Node.js网络数据抓取技术深入解析
- QRSorteios-crx扩展:优化税务文件扫描流程
- 掌握JavaScript中的算法技巧
- Rails+React打造MF员工租房解决方案
- Utsanjan:自学成才的UI/UX设计师与技术博客作者
- CMake 3.25.2版本发布,支持Windows x86_64架构
- AR_RENTAL平台:HTML技术在增强现实领域的应用