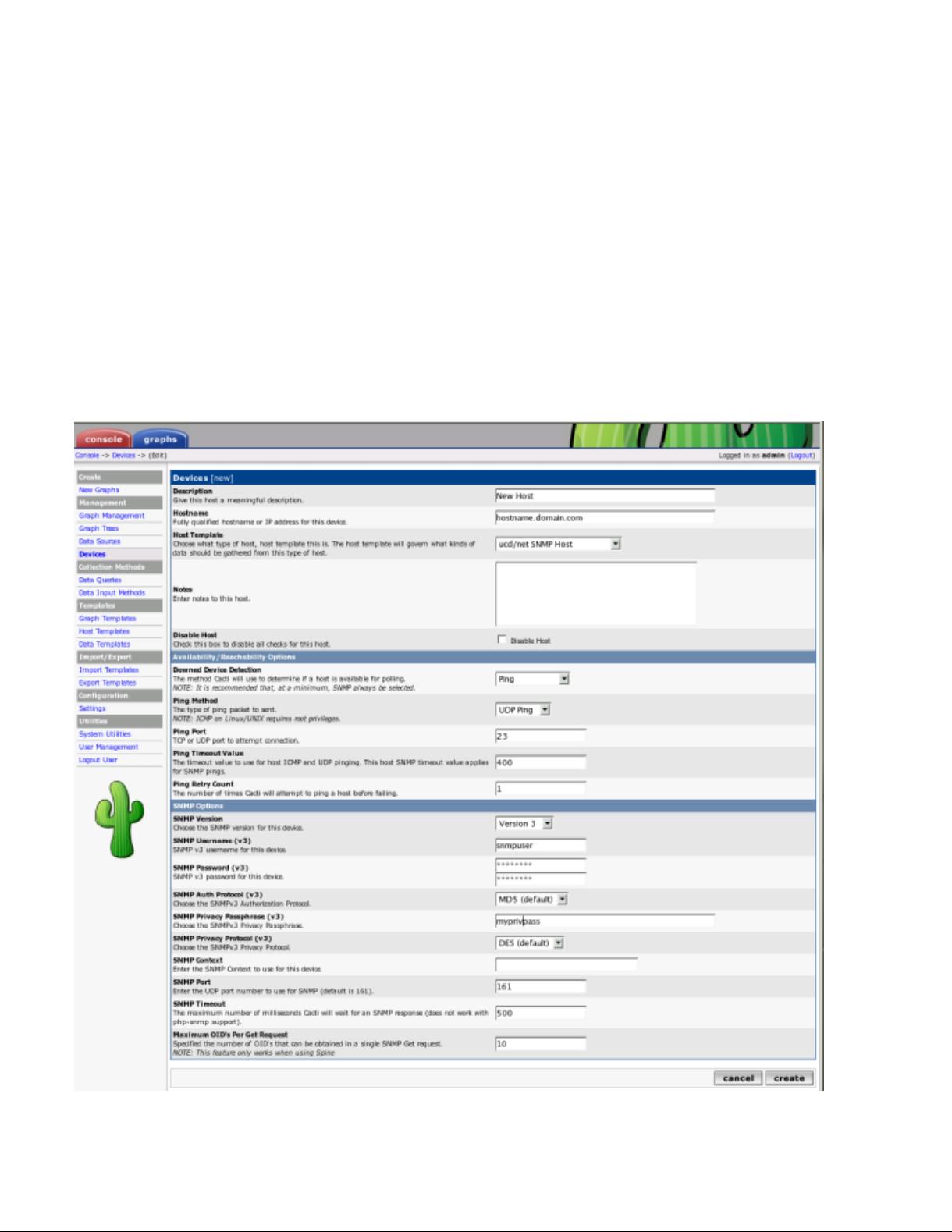
Chapter 7. How to Graph Your Network
Field Description
SNMP Username The username of an SNMP V3 createUser statement or equivalent
SNMP Password The authpassphrase of an SNMP V3 createUser statement or equivalent
SNMP Auth Protocol The authentication type of an SNMP V3 createUser statement or equivalent.
Select either MD5 or SHA. This entry defaults to MD5.
SNMP Privacy Passphrase The privacy passphrase of an SNMP V3 createUser statement or equivalent.
SNMP Privacy Protocol The privacy protocol of an SNMP V3 createUser statement or equivalent. Select
either DES or AES. This entry defaults to DES.
SNMP Context When using the View-Based Access Control Model (VACM), it is possible to specify an
SNMP Context when mapping a community name to a security name with a com2sec
directive, with the group directive and the access directive. This allows for defining
special access models. If using such a parameter with your target’s SNMP
configuration, specify the context name to be used to access that target here.
After saving your new device, you should be redirected back to the same edit form with some additional information.
If you configured SNMP for this host by providing a valid community string, you should see various statistics listed at
the top of the page. If you see "SNMP error" instead, this indicates an SNMP problem between Cacti and your device.
Towards the bottom of the page there will be two addition boxes, Associated Data Queries, and Associated Graph Tem-
plates. If you selected a host template on the previous page, there will probably be a few items in each box. If there is
nothing listed in either box, you will need to associate at least one data query or graph template with your new device
or you will not be able to create graphs in the next step. If no available graph template or data query applies to your
device, you can check the Cacti templates repository or create your own if nothing currently exists.
7.1.1. A Word About SNMP
The SNMP version that you choose can have a great effect on how SNMP works for you in Cacti. Version 1 should be
used for everything unless you have reason to choose otherwise. If you plan on utilizing (and your device supports)
high-speed (64-bit) counters, you must select version 2. Starting with Cacti 0.8.7, version 3 is fully implemented.
The way in which Cacti retrieves SNMP information from a host has an effect on which SNMP-related options are
supported. Currently there are three types of SNMP retrieval methods in Cacti and are outlined below.
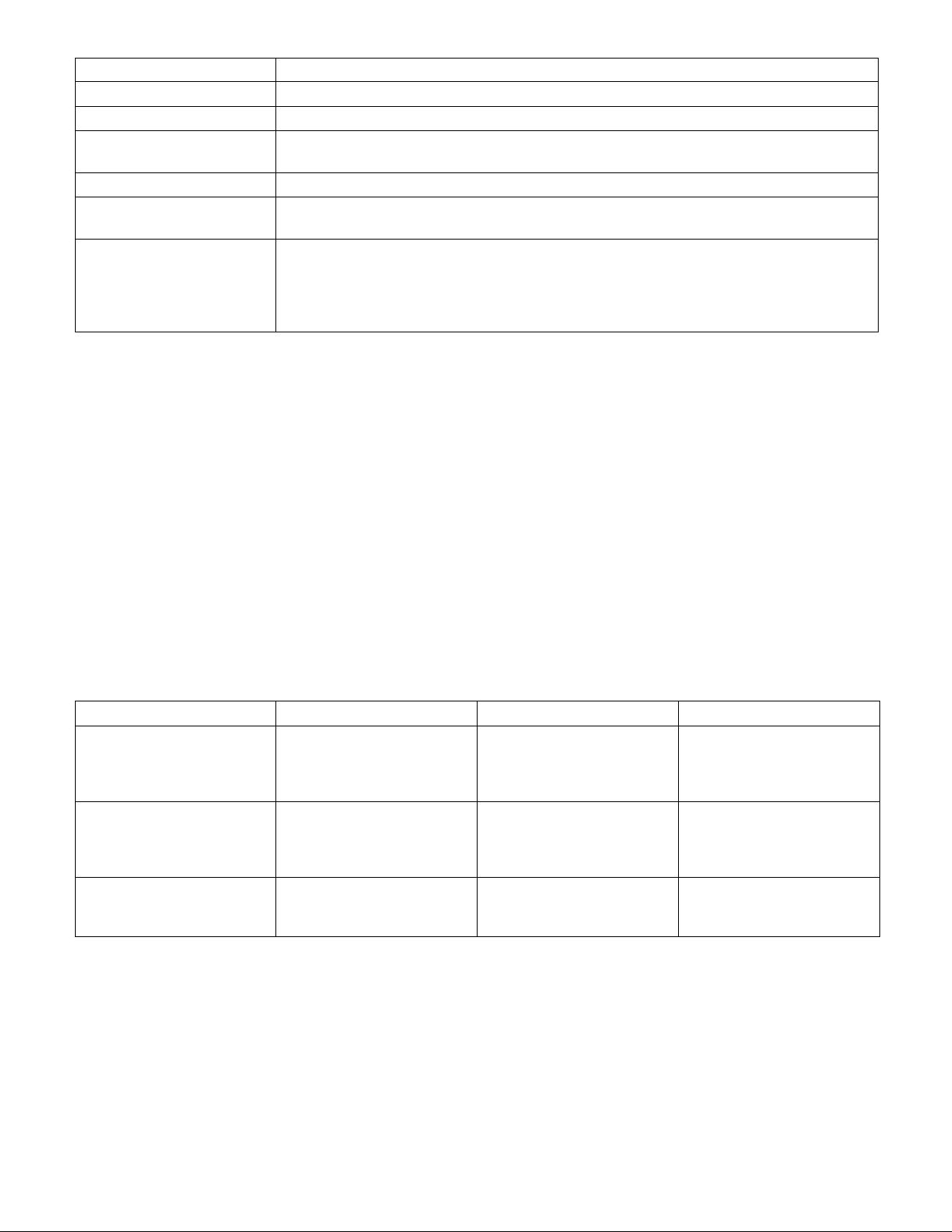
Table 7-2. SNMP Retrieval Types
Type Description Supported Options Places Used
External SNMP Calls the net-snmp
snmpwalk and snmpget
binaries that are installed
on your system.
All SNMP options Web interface and PHP
poller (poller.php)
Internal SNMP (php-snmp) Uses PHP’s SNMP
functions which are linked
against net-snmp or
ucd-snmp at compile time.
Version 1 Only
(Community and Port)
Web interface and PHP
poller (poller.php)
Spine SNMP Links directly against
net-snmp or ucd-snmp and
calls the API directly.
All SNMP options C-Based Poller (Spine)
7.1.2. SNMP V3 Options Explained
SNMP supports authentication and encryption features when using SNMP protocol version 3 known as View-Based
Access Control Model (VACM). This requires, that the target device in question supports and is configured for SNMP
V3 use. In general, configuration of V3 options is target type dependant. The following is cited from man snmpd.conf
concerning user definitions
[ SNMPv3 Users
createUser [-e ENGINEID] username (MD5|SHA) authpassphrase [DES|AES] [privpassphrase]
MD5 and SHA are the authentication types to use. DES and AES are the privacy
protocols to use. If the privacy passphrase is not specified, it is assumed
to be the same as the authentication passphrase. Note that the users created will
15