kth rule, h
k
denotes rule weight, and d
i
denotes
attribute weight.
A BRB model is composed of a number of belief rules
as shown in (1). When the input data are available, the
evidential reasoning (ER) approach [26], [27], [28] is used
to aggregate the belief rules to generate the results of the
final assessment [13].
3. Background of the ER Rule
As the inference tool of the BRB model, the ER rule can
deal with multiple items of uncertain information and
integrate qualitative knowledge with quantitative data.
Assume that there are some basic attributes of a general
attribute in a two-level hierarchy. The ER rule can
integrate these basic attributes to obtain an evaluation of
the general attribute in terms of assessment grades. The
ER rule fi rst uses the initial weights of the basic attributes
given by experts and converts them into a basic
probability mass. The basic combination principle of the
ER rule is introduced in (12)–(19).
III. DAG-BRB Model for Network Intrusion
Detection
1. Framework of the DAG-BRB Model
As mentioned above, network intrusion detection is a
complex multi-classification problem. Its practical
applications have shown that the detection rate is
particularly low, and certain special types of attacks
cannot be detected. This is because meaning of network
data is lo st after reducing their number of dimensions
using PCA, and this is more evident in complex multi-
classification problems. Another reason is that the
differences between normal data and those used for
network attacks are minor.
To solve the above problems, a DAG-BRB model is
proposed where PCA is used to reduce the number of
dimensions of the input network data, and the
referenced values of the antecedent attributes are used
as the parameters to be optimized. Several BRB
models are then combined by using a directed acyclic
graph (DAG) structure, where a single BRB model is
mainly used to distinguish two types of network
attacks. The framework of the DAG-BRB model is
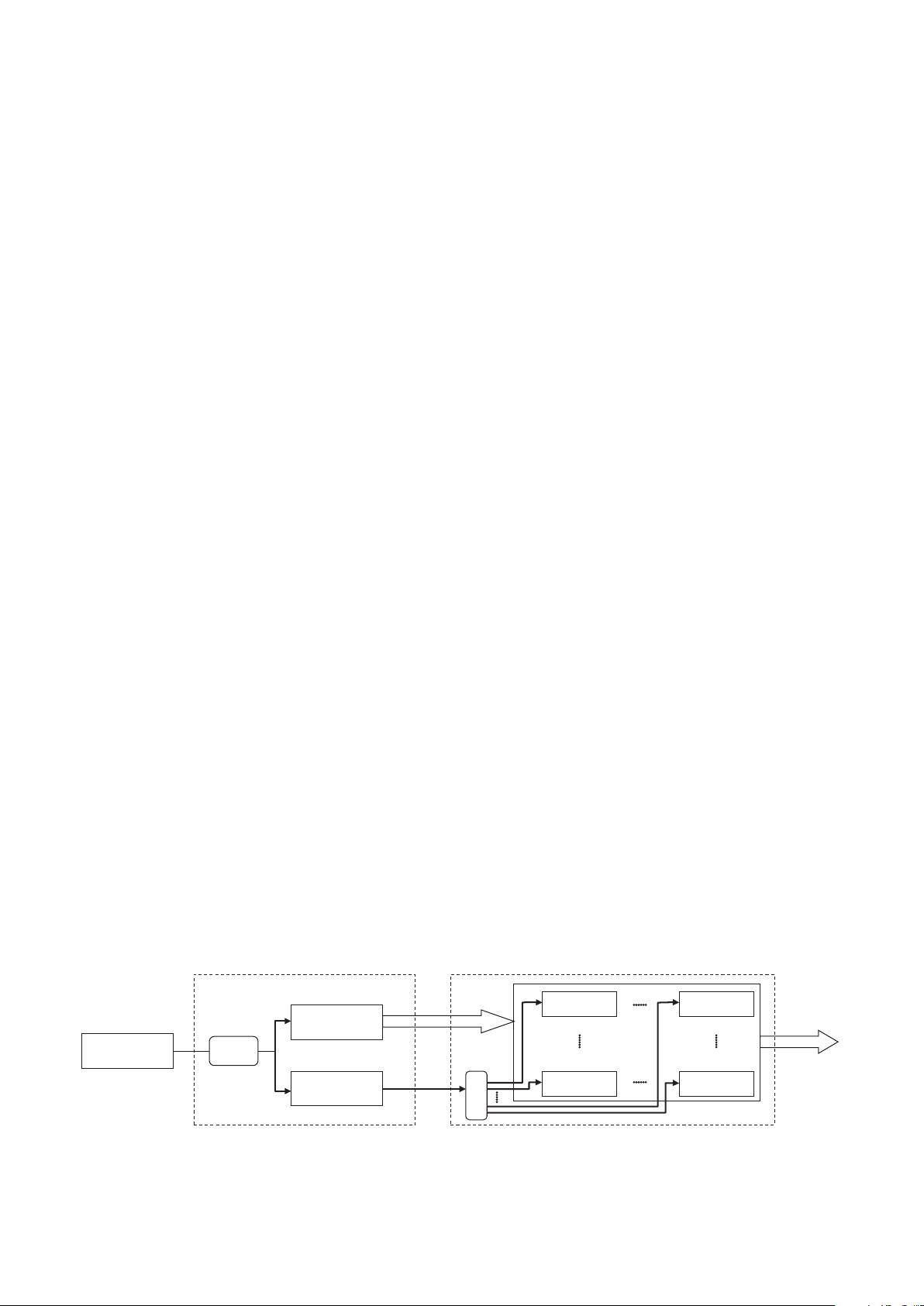
shown in Fig. 1.
In Fig. 1, the network dataset contains the attributes and
the labels of network data, such as the IP address, the TCP
fields, and the connection time. It is necessary to remove
unrelated data. Thus, the network’s dataset is first
processed using PCA.
In this paper, the outputs processed by PCA contain only
five attributes. The dataset is then divided into a testing
dataset and a training dataset. In the sorter operation, the
training dataset is divided into 10 subsets. Each contains
only two classes of network attacks. Every BRB model
needs to be trained by using the corresponding subset. For
example, a subset containing normal data and DoS attack
data, called the Normal-DoS BRB model, is used to train
the BRB model by using the constrained CMA-ES
algorithm and the ER approach. The detailed structure of
these BRB models is described below.
2. Combination BRB Model Based on DAG
In Fig. 1, several BRB models are used to form a
combination BRB model, as shown in Fig. 2, where ev ery
node in the combination model is a BRB model that only
distinguishes two types of network attacks. When all BRB
models have been trained by using the corresponding
training subset, the testing dataset is entered into the
combination BRB model as shown in Fig. 2. The detailed
procedure is as follows:
Step 1. The testing dataset is first placed in the top node
(Normal-U2R BRB model), they are determined to be
normal data or U2R attack data.
Step 2. The testing data are entered into the other BRB
model in the second layer according to type. If the testing
data are normal, they are entered into the Normal-R2L
Dataset
Testing dataset
Training dataset
PCA
Sorter
BRB model
BRB model
BRB model
BRB model
Result
Fig. 1. Framework of the DAG-BRB model.
594 ETRI Journal, Vol. 39, No. 4, August 2017
https://doi.org/10.4218/etrij.17.0116.0305

 我的内容管理
展开
我的内容管理
展开
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助 


 信息提交成功
信息提交成功