An Efficient Hardware-oriented Algorithm of Spatial Motion Vector
Prediction for AVS HD Video Encoder
Minghui Yang
1, 2
, Xiaodong Xie
2
1
Peking University Shenzhen Graduate School, 518055 Shenzhen, P. R. China
2
National Engineering Laboratory for Video Technology, Peking University
100871 Beijing, P. R. China
{mhyang, xdxie}@jdl.ac.cn
Keywords: spatial motion vector, hardware pipeline, AVS.
Abstract. Motion Vector Prediction (MVP) plays an important role in improving coding efficiency
in HEVC, H.264/AVC and AVS video coding standard. MVP is implemented by exploiting
redundancy of adjacent-block optimal coding information under the constraint that MVP must be
performed in a serial way. The constraint prevents parallel processing and MB pipeline based on
LevelC+. In multi-stage pipeline, to some extent, adjacent-block best mode-decision information
can hardly be obtained. In this paper, we propose a new hardware-oriented method to improve the
coding performance at a cost of few hardware resources. When adjacent block is not available,
spatial motion vector prediction (SMVP) for integer motion estimation (IME) and fraction motion
estimation (FME) will take the IME best mode information and FME best mode information of left
block as best information to derive PMV (Predicted Motion Vector) for current macro-block or
block. Experimental results shows that the method we propose can achieve a better performance
than the existing methods by 0.1db for the cases with intense movement and a non-degrading
performance for flat cases.
I. Introduction
AVS video standard is developed by the audio video coding standard working group of China,
which was approved by the Chinese science and technology department of Ministry of Information
Industry in June 2002 and has been accepted as an option by ITU-TFGIPTV for IPTV applications
[1]. The AVS-P2 is one part of AVS-video, which targets to high-definition (HD) digital video
broadcasting and high-density storage media and achieves comparable performance with
H.264/AVC with lower cost [1]. MVP is an important tool in AVS like in HEVC and H.264 /AVC.
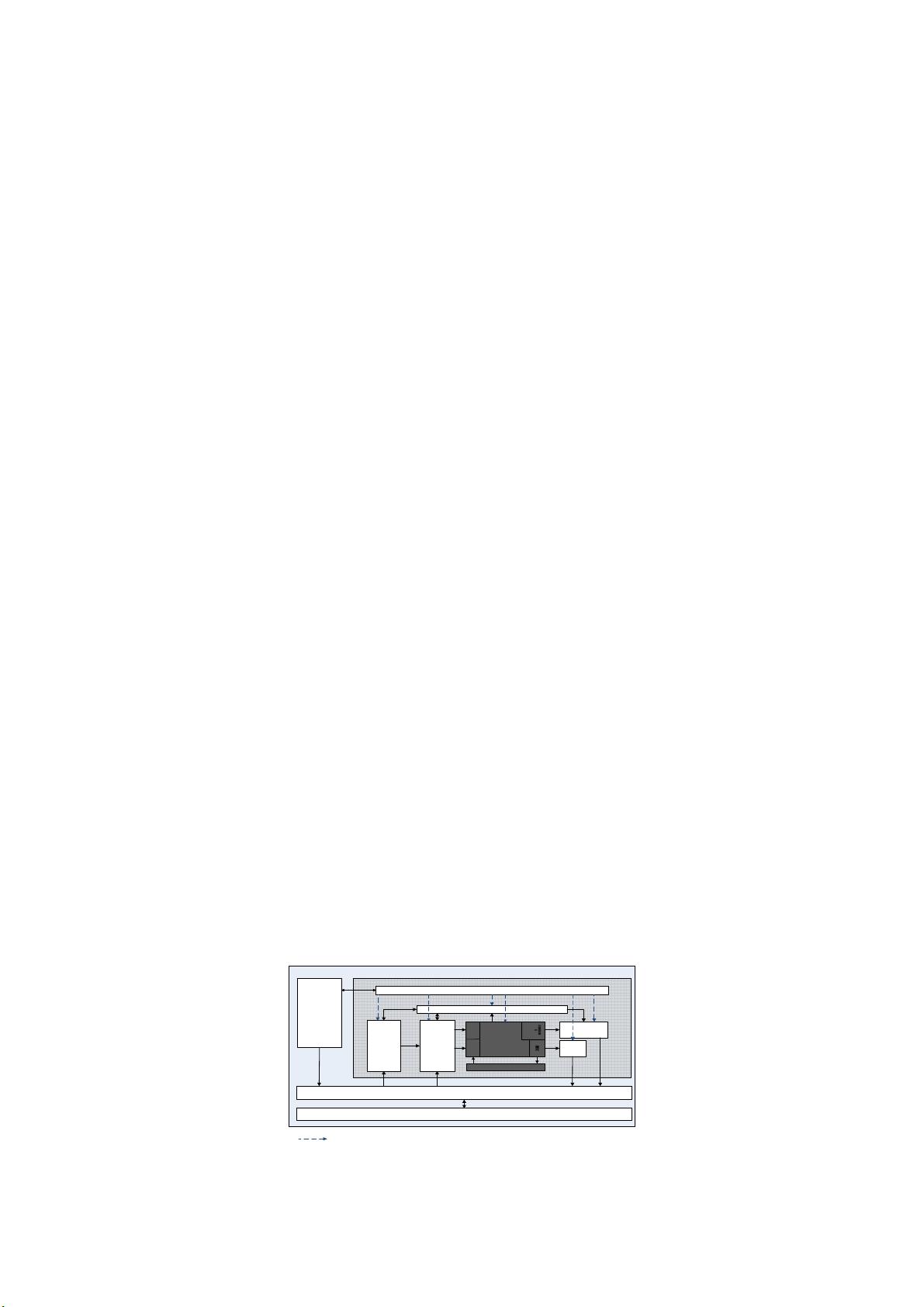
In a popular multi-stage MB-pipelined hardware structure (Fig.1), it is exploited in several stages
such as IME, FME, MD, BG. SMVP which need best mode decision (MD) information (mainly
including reference index and motion vector) of the adjacent MBs (including left, top-left, top and
top-right MBs), which impedes the coding pipeline. In a popular coding order called n-stitched
zigzag scan [2], sometimes it doesn’t satisfy those data dependencies.
SDRAM
SDRAMSDRAM
SDRAM
DRAM
DRAMDRAM
DRAM-
--
-CTRL
CTRLCTRL
CTRL
MB
MBMB
MB_
__
_CTRL
CTRLCTRL
CTRL
MB
MBMB
MB_
__
_LEVEL
LEVELLEVEL
LEVEL_
__
_ENCODING
ENCODINGENCODING
ENCODING
MVP
MVPMVP
MVP
IME
IMEIME
IME FME
FMEFME
FME
BG
BGBG
BG
DBK
DBKDBK
DBK
INTRA
INTRAINTRA
INTRA -
--
-P RED
PREDPRED
PRED
ORG
ORGORG
ORG
PRED
PREDPRED
PRED
INTRA
INTRAINTRA
INTRA-
--
-
INTER MD
INTER MDINTER MD
INTER MD
C
O
D
E
N
U
M
C
O
D
E
N
U
M
C
O
D
E
N
U
M
C
O
D
E
N
U
M
S
S
S
S
R
E
C
R
E
C
R
E
C
R
E
C
FIRMWARE
FIRMWAREFIRMWARE
FIRMWARE
FRAME
FRAMEFRAME
FRAME_
__
_LEVEL
LEVELLEVEL
LEVEL_
__
_ENCODING
ENCODINGENCODING
ENCODING
Local bus
DBK: Dblocking MB_CTRL: control MB-staged work flow and data flow
BG:Binary Generation
MD: Mode Decision
Fig. 1. AVS MB-staged pipeline engine.
Applied Mechanics and Materials Vols. 556-562 (2014) pp 4365-4371
© (2014) Trans Tech Publications, Switzerland
doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.556-562.4365
All rights reserved. No part of contents of this paper may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means without the written permission of TTP,
www.ttp.net. (ID: 222.29.140.213-17/05/14,10:27:34)









