An Introductory Resource Guide for Implementing the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Security Rule
3. A Framework for Managing Risk
The HIPAA Security Rule is all about implementing effective risk management to
adequately and effectively protect EPHI. The assessment, analysis, and management of
risk provides the foundation of a covered entity’s Security Rule compliance efforts,
serving as tools to develop and maintain a covered entity’s strategy to protect the
confidentiality, integrity, and availability of EPHI.
All EPHI created, received, maintained, or transmitted by a covered entity is subject to
the Security Rule. Covered entities are required to implement reasonable and appropriate
security measures to protect against reasonably anticipated threats or vulnerabilities to the
security of EPHI. Under the Security Rule, covered entities are required to evaluate risks
and vulnerabilities in their environments and to implement security controls to address
those risks and vulnerabilities.
The selection and specification of security controls can be accomplished as part of an
organization-wide information security program that involves the management of
organizational risk - that is, the risk to information, individuals, and the organization as a
whole. The management of risk is a key element in the organization's information
security program and provides an effective framework for selecting the appropriate
security controls for an information system - the security controls necessary to protect
individuals and the operations and assets of the organization.
This section describes a process of managing risk to organizational missions and business
functions that arise from the operation and use of information systems by discussing each
phase of the NIST Risk Management Framework
7
and providing a mapping of this
framework to complementary requirements of the HIPAA Security Rule.
3.1. NIST Risk Management Framework (RMF)
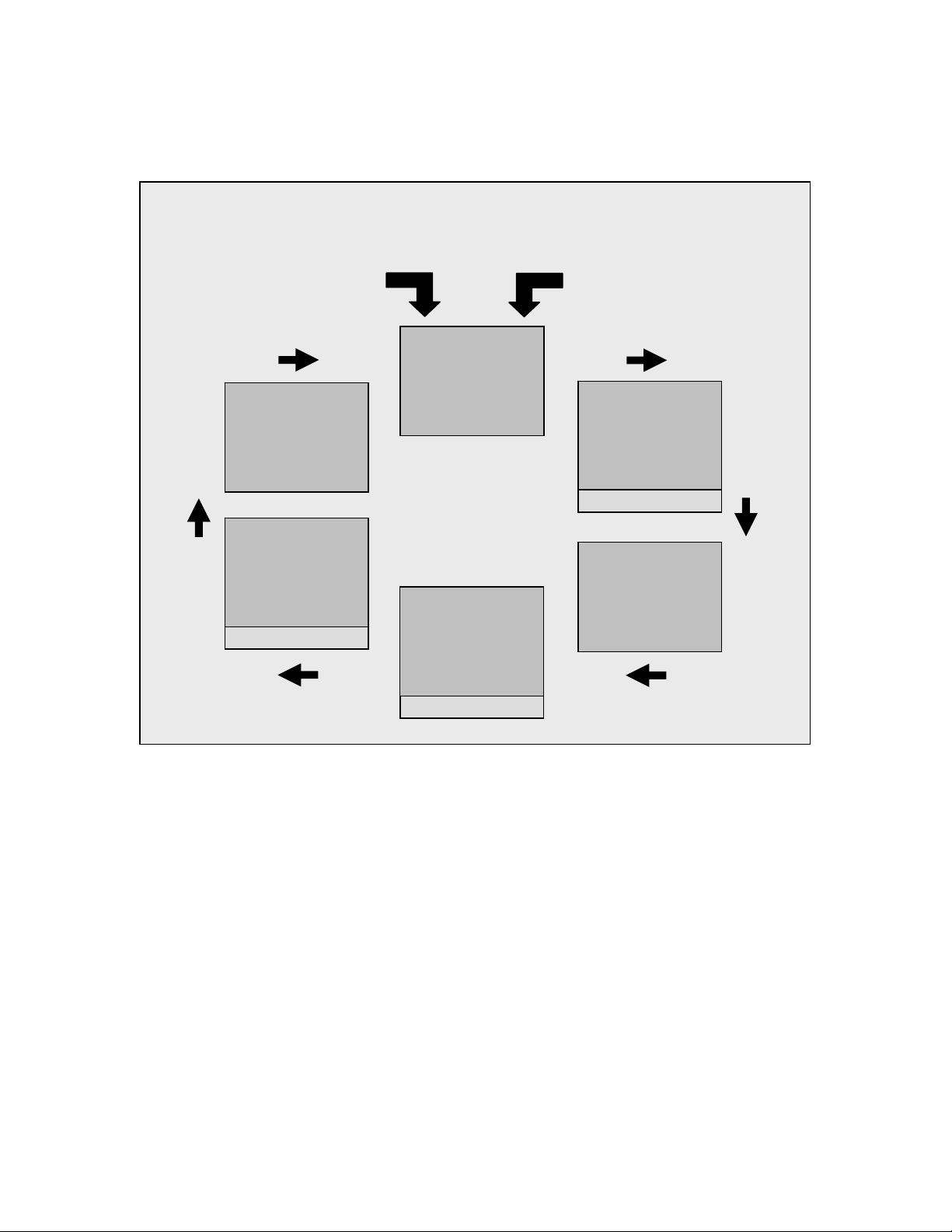
The NIST RMF, illustrated in Figure 2, provides the covered entity with a disciplined,
structured, extensible, and repeatable process for achieving risk-based protection related
to the operation and use of information systems and the protection of EPHI. It represents
an information security life cycle that facilitates continuous monitoring and improvement
in the security state of the information systems within the organization.
The activities that compose the NIST RMF are paramount to an effective information
security program and can be applied to both new and legacy information systems within
the context of a system development life cycle. A risk-based approach to security control
selection and specification considers effectiveness, efficiency, and constraints due to
applicable laws, directives, Executive Orders, policies, standards, or regulations.
The flexible nature of the NIST RMF allows other communities of interest (e.g., state,
local, and tribal governments and private sector entities) to use the framework voluntarily
either with the NIST security standards and guidelines or with industry-specific standards
and guidelines. The RMF provides organizations with the flexibility needed to apply the
right security controls to the right information systems at the right time to adequately
7
NIST Special Publication 800-39, Managing Risk from Information Systems: An Organizational Perspective, (Second
Public Draft), April 2008.
10