(c)2000 (c)2001 by SD Group (MEI,SanDisk,Toshiba)
20
Date: April 2001
SD-Memory Card Specifications / Part 1. Physical Layer Specification; Version 1.01
SD Memory Card System Concept
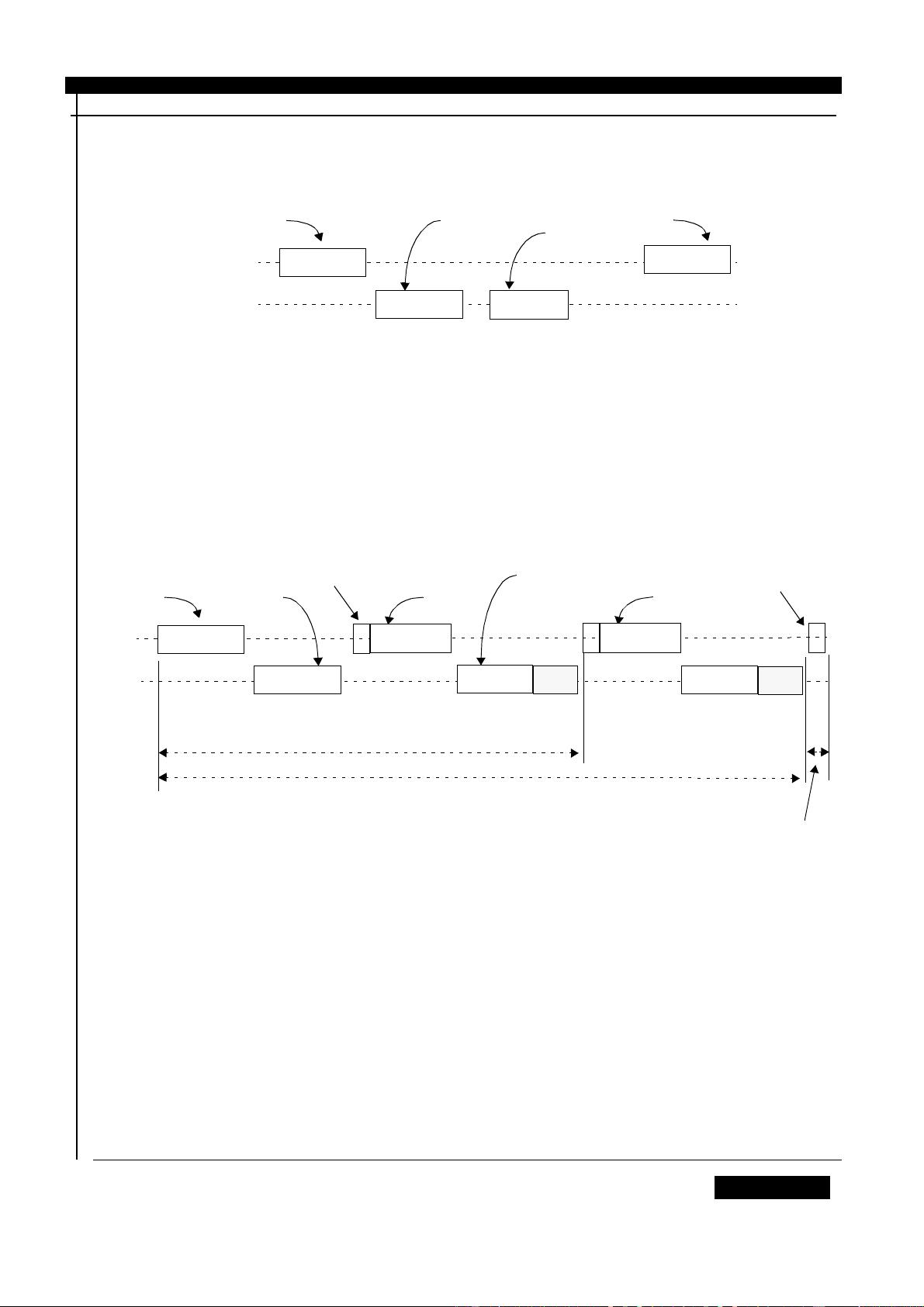
The only difference (as opposed to addition) between the SD Memory Card and the MultiMediaCard
is the bus topology and initialization protocol. While the MultiMediaCard stack is connected on the
same bus and being identified using synchronous transmission of Open-drain outputs, each SD
Memory Card has an independent point-to-point connection to the host, and the cards are identified
serially, one at a time (refer to Table 4 for a command set comparison between SD Memory Card
and MultiMediaCard. Detailed description of the SD Memory card protocol commands can be found
in Chapter 4).
The initializing procedure in the SD protocol is defined to successfully identify either a MultiMedi-
aCard or a SD Memory Card, which ever is currently connected on the bus. After card detection, the
host executes the initializing procedure and ends up with an identified card of a known type.
Once the card is initialized the application can determine the card capabilities by querying the vari-
ous configuration registers, and decide whether or not to use it.
The physical dimension of the SD Memory Card is thicker than MultiMediaCard (2.1mm vs. 1.4mm;
refer to Chapter 9) but it is defined in such a way that a MultiMediaCard can be inserted into SD
Memory Card socket. Note that because of the small differences between the mechanical definition
of the pads layout of MultiMediaCard it is required that the SD Host will set its own DAT1-DAT3 lines
to be in Input Mode (Tri-State) while they are not in use.
Three different card detect mechanisms are defined for the SD Memory Card (e.g. mechanical
insertion which can be sensed using the WP switch, Electrical insertion which can be sensed using
the pull-up resistor on DAT3 and periodical attempts to initialize the card). Since some of these
methods may be not relevant (or behave differently) for the MultiMediaCard, it is recommended not
to depend on the preemptive card detects methods only. The host should implement a polling
mechanism or allow the operator to request card identification.
I/O Mode not supported supported
(optional)
I/O (Interrupt) mode is not sup-
ported in SD Memory Card.
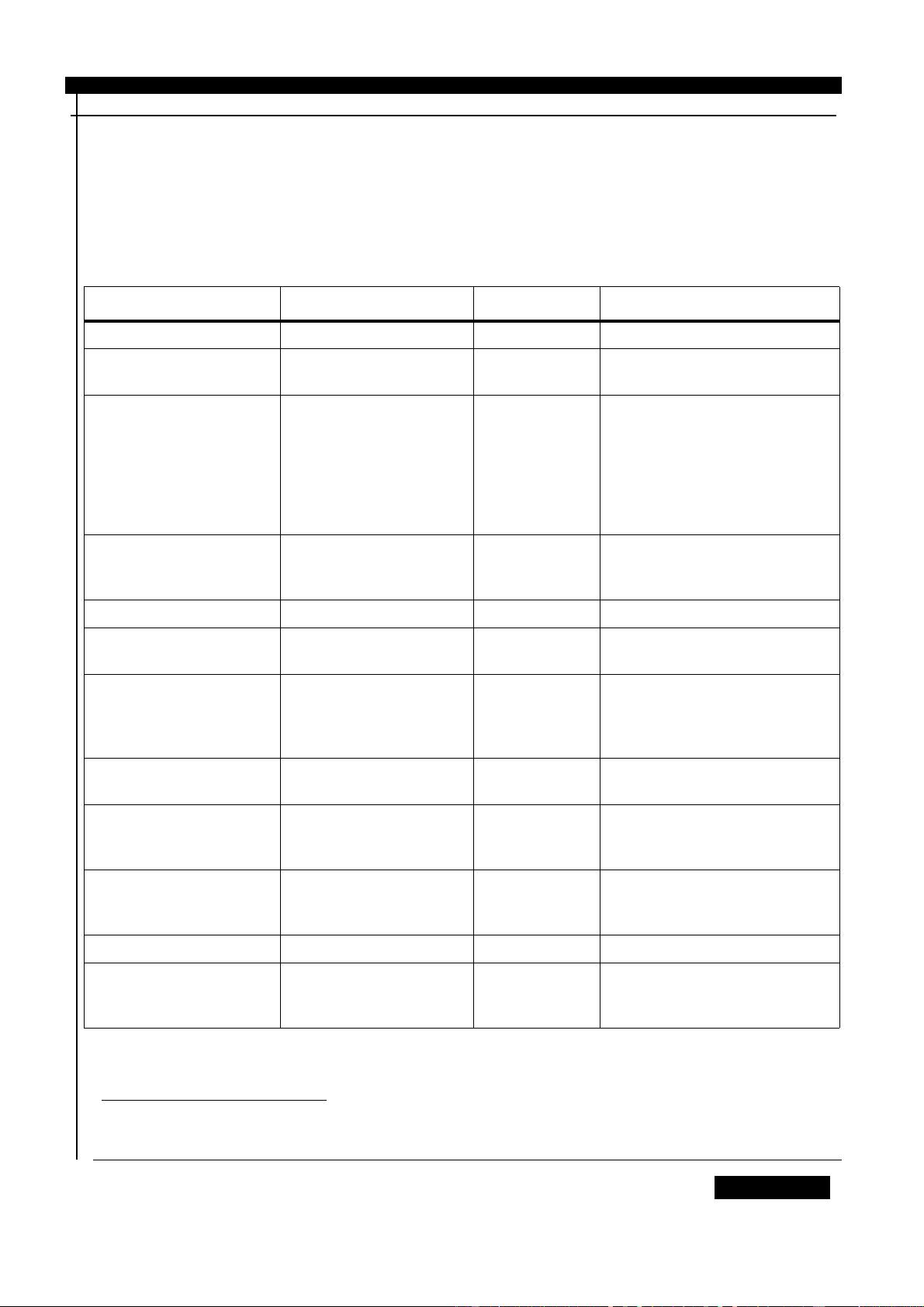
Class CMD
SD Memory
Card
MultiMedia
Card
Comment
Class 0 CMD0 CMD0
(Mandatory)
CMD0 Same command.
CMD1 Reserved CMD1 In SD Memory Card ACMD41 is used instead of CMD1
CMD2 CMD2
(Mandatory)
CMD2 Similar command except buffer type used to transmit
to response of the card. (SD Memory Card: push-pull,
MultiMediaCard: open-drain)
CMD3 CMD3
(Mandatory)
CMD3 In both protocols this command is used to assign a
logical address to the card. While In MultiMediaCard
the host assigned the address, in SD memory Card it
is the responsibility of the card.
CMD
4-10
CMD4-10
(Mandatory)
CMD4-10 Same commands.
Table 4: Commands comparison table.
SD Memory Card MultiMediaCard Comments
Table 3: Differences between SD Memory Card and MultiMediaCard Feature set