QCA与MTK嵌入式Linux系统在线升级断电恢复策略解析
20 浏览量
更新于2024-08-31
收藏 391KB PDF 举报
本文主要探讨了QCA和MTK平台上的嵌入式Linux系统如何实现在线升级时的断电自动恢复方案。QCA平台采用Fail-Safe Boot机制,而MTK平台则使用Dual Image Boot策略。
QCA Fail-Safe Boot方案:
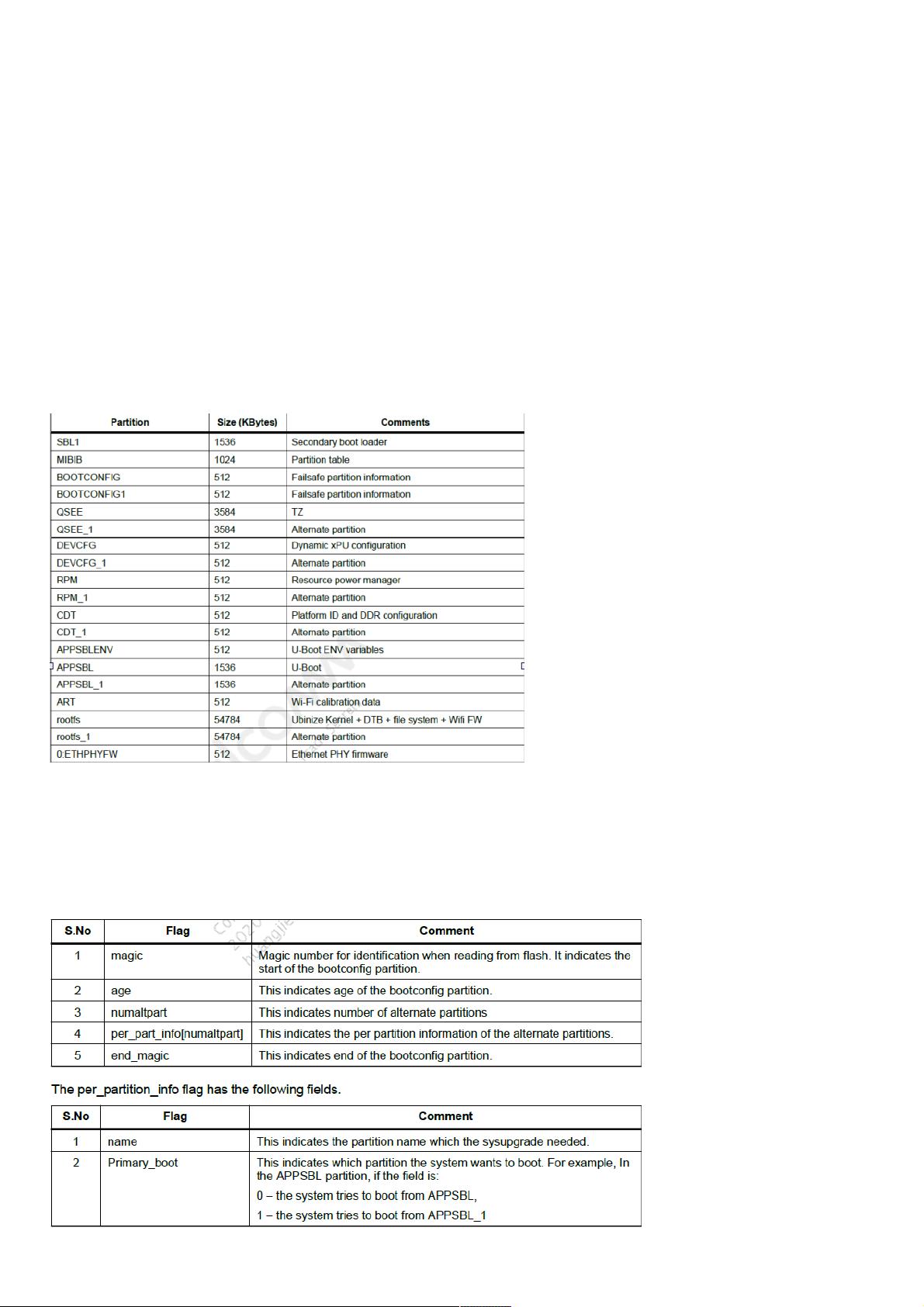
在QCA平台上,为了应对固件升级中断电可能导致的启动问题,设计了Fail-Safe Boot机制。由于NorFlash的成本较高且容量相对较小,大多数使用双Image备份功能的系统选择NandFlash作为存储介质。Fail-Safe Boot的核心在于创建备用分区来确保系统即使在升级失败后也能正常运行。系统主要分区包括:
- SBL1:二级引导程序,用于判断设备应从主分区还是备用分区启动。
- MIBIB:系统分区表信息,记录分区布局。
- BOOTCONFIG和BOOTCONFIG1:故障保护分区,存储主引导标志和分区名称等关键信息,用于判断当前系统的健康状态。
当系统升级时,新固件会首先写入备用分区。如果升级成功,系统会在下次启动时切换到新分区。若升级过程中断电,系统会依据Fail-Safe Boot策略,从健康的主分区启动,保证设备的正常运行。
MTK Dual Image Boot方案:
MTK平台的Dual Image Boot机制有所不同,它在Flash中同时保存两个完整的系统映像,通常称为Image A和Image B。系统每次启动都会从当前激活的映像启动。在线升级时,新固件会写入非活动映像。如果升级成功,下次启动会切换到新映像。如果升级中断,设备将继续从原来的映像启动,避免因升级失败导致设备无法工作。
两种方案的对比:
QCA的Fail-Safe Boot依赖于故障保护分区的信息来决定启动哪个分区,而MTK的Dual Image Boot则是基于两个完整映像的切换。QCA方案可能需要更复杂的逻辑来判断分区状态,而MTK方案则更加直观,只需比较两个映像的状态。不过,MTK方案可能需要更大的存储空间,因为需要存储两份完整的系统映像。
总结:
QCA和MTK的在线升级断电恢复策略各有优缺点。QCA方案节省了存储空间,但恢复逻辑相对复杂;MTK方案虽然占用更多空间,但恢复过程简单明了。在实际应用中,选择哪种方案取决于设备的存储资源、成本考虑以及对恢复复杂性的容忍度。无论选择哪种方案,其目标都是确保嵌入式Linux设备在升级过程中遇到意外情况时仍能保持稳定运行,提高系统的可靠性和用户体验。
2010-06-09 上传
2017-06-02 上传
2020-05-27 上传
213 浏览量
2021-04-20 上传
2018-12-03 上传
2020-06-22 上传
weixin_38703895
- 粉丝: 4
- 资源: 910
最新资源
- iirc:IRC服务器,如果我没记错的话
- Environment-Friend:一个旨在向大众传播废物管理意识的网站。 与与用户交互的聊天机器人集成
- bitbucket-companion-crx插件
- 笨蛋
- matlab二值化处理的代码-LAUCalTagWidget:BradAtcheson的CalTag摄像机校准方案的实时实施。这项工作得到了G
- 毕业设计&课设-基于MATLAB的FIR滤波器设计.zip
- 带C和Shell的操作系统:具有Shell和C编程的操作系统
- anti-csrf:功能齐全的反CSRF库
- pex:用于生成 .pex(Python EXecutable)文件的库和工具
- 盖斯玛斯
- Frogger_VG_Programming:一个Frogger克隆游戏机,用于练习为GAME 3150 05 SP2021进行编码@ Webster U
- ignite-challenge01
- 赫德梅塔卡普
- Check Adblocker-crx插件
- -COMP1521-计算机系统-基础知识:有关低级别系统内容的第一年课程
- 毕业设计&课设-该团队的直接模拟蒙特卡罗工作和模拟环境的脚本和数据。.zip