Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -Kilo -
OpenStack Installation Guide for
Ubuntu 14.04
May 10, 2016 kilo
13
Table2.1.Passwords
Password name Description
Database password (no variable used) Root password for the database
ADMIN_PASS Password of user admin
CEILOMETER_DBPASS Database password for the Telemetry service
CEILOMETER_PASS Password of Telemetry service user ceilometer
CINDER_DBPASS Database password for the Block Storage service
CINDER_PASS Password of Block Storage service user cinder
DASH_DBPASS Database password for the dashboard
DEMO_PASS Password of user demo
GLANCE_DBPASS Database password for Image service
GLANCE_PASS Password of Image service user glance
HEAT_DBPASS Database password for the Orchestration service
HEAT_DOMAIN_PASS Password of Orchestration domain
HEAT_PASS Password of Orchestration service user heat
KEYSTONE_DBPASS Database password of Identity service
NEUTRON_DBPASS Database password for the Networking service
NEUTRON_PASS Password of Networking service user neutron
NOVA_DBPASS Database password for Compute service
NOVA_PASS Password of Compute service user nova
RABBIT_PASS Password of user guest of RabbitMQ
SAHARA_DBPASS Database password of Data processing service
SWIFT_PASS Password of Object Storage service user swift
TROVE_DBPASS Database password of Database service
TROVE_PASS Password of Database service user trove
OpenStack and supporting services require administrative privileges during installation and
operation. In some cases, services perform modifications to the host that can interfere with
deployment automation tools such as Ansible, Chef, and Puppet. For example, some Open-
Stack services add a root wrapper to sudo that can interfere with security policies. See the
Cloud Administrator Guide for more information. Also, the Networking service assumes de-
fault values for kernel network parameters and modifies firewall rules. To avoid most issues
during your initial installation, we recommend using a stock deployment of a supported dis-
tribution on your hosts. However, if you choose to automate deployment of your hosts, re-
view the configuration and policies applied to them before proceeding further.
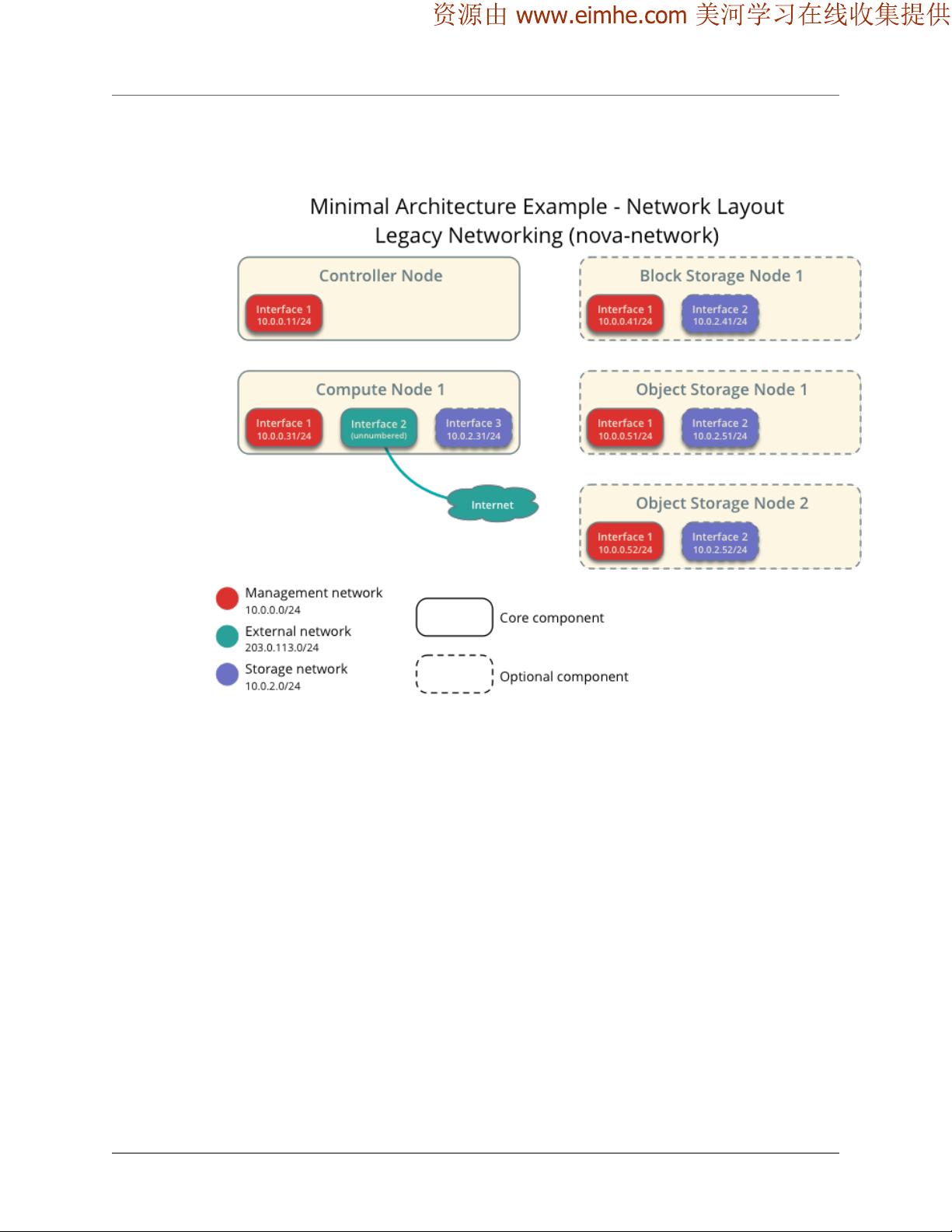
Networking
After installing the operating system on each node for the architecture that you choose to
deploy, you must configure the network interfaces. We recommend that you disable any
automated network management tools and manually edit the appropriate configuration
files for your distribution. For more information on how to configure networking on your
distribution, see the documentation.
All nodes require Internet access for administrative purposes such as package installation,
security updates, DNS, and NTP. In most cases, nodes should obtain Internet access through
the management network interface. To highlight the importance of network separation,
the example architectures use private address space for the management network and as-