"Meta分析与循证医学:统计学基础解析"
版权申诉
8 浏览量
更新于2024-02-22
收藏 2.73MB PPT 举报
Meta-analysis is a statistical technique used in evidence-based medicine to combine the results of multiple studies on a particular topic. The goal of meta-analysis is to provide a more precise estimate of the effect of a treatment or intervention by synthesizing data from various studies.
Meta-analysis involves collecting data from individual studies, analyzing the data using statistical methods, and then summarizing the results. By pooling data from multiple studies, meta-analysis can increase the statistical power to detect differences or effects that may not be apparent in individual studies.
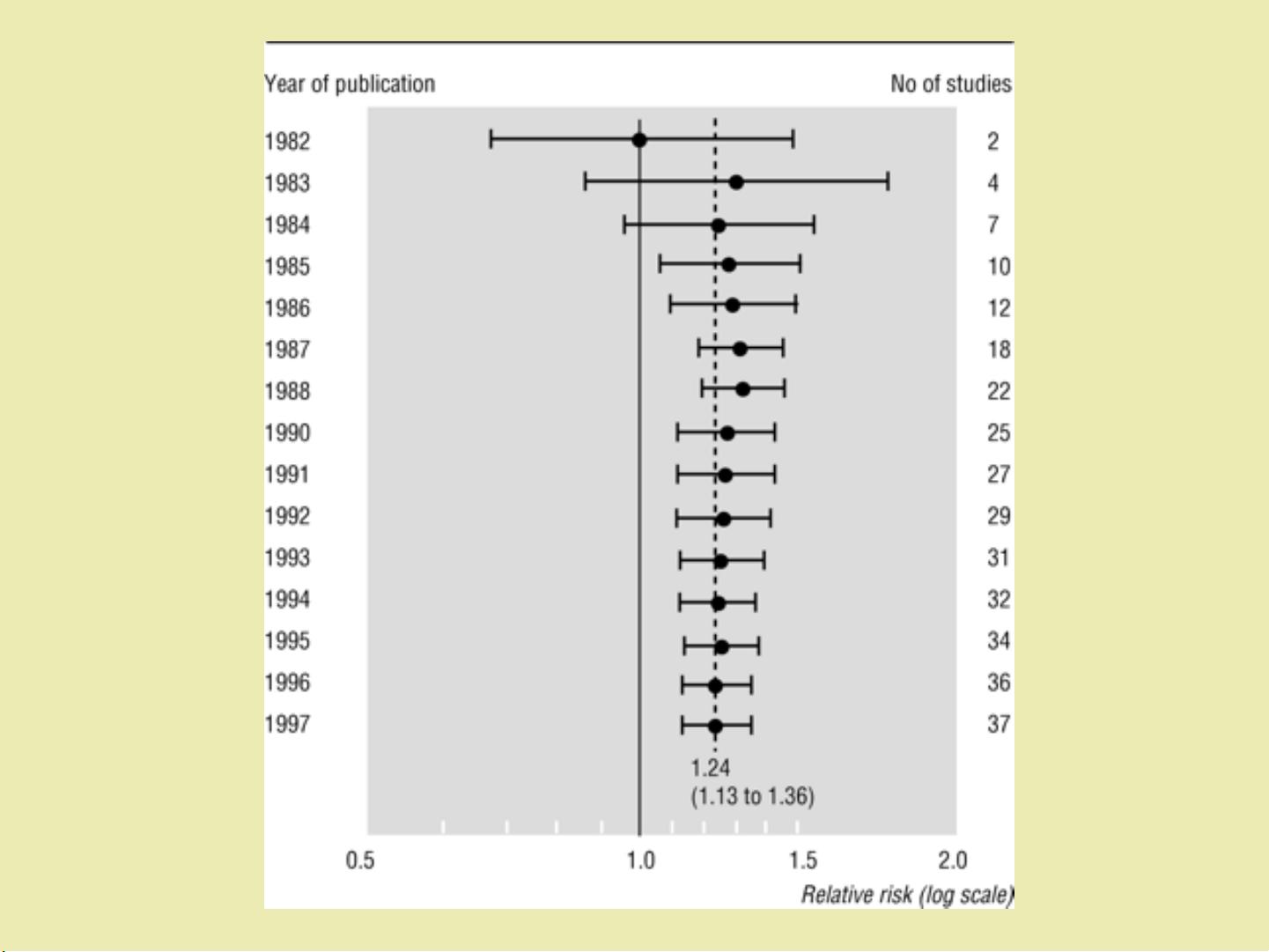
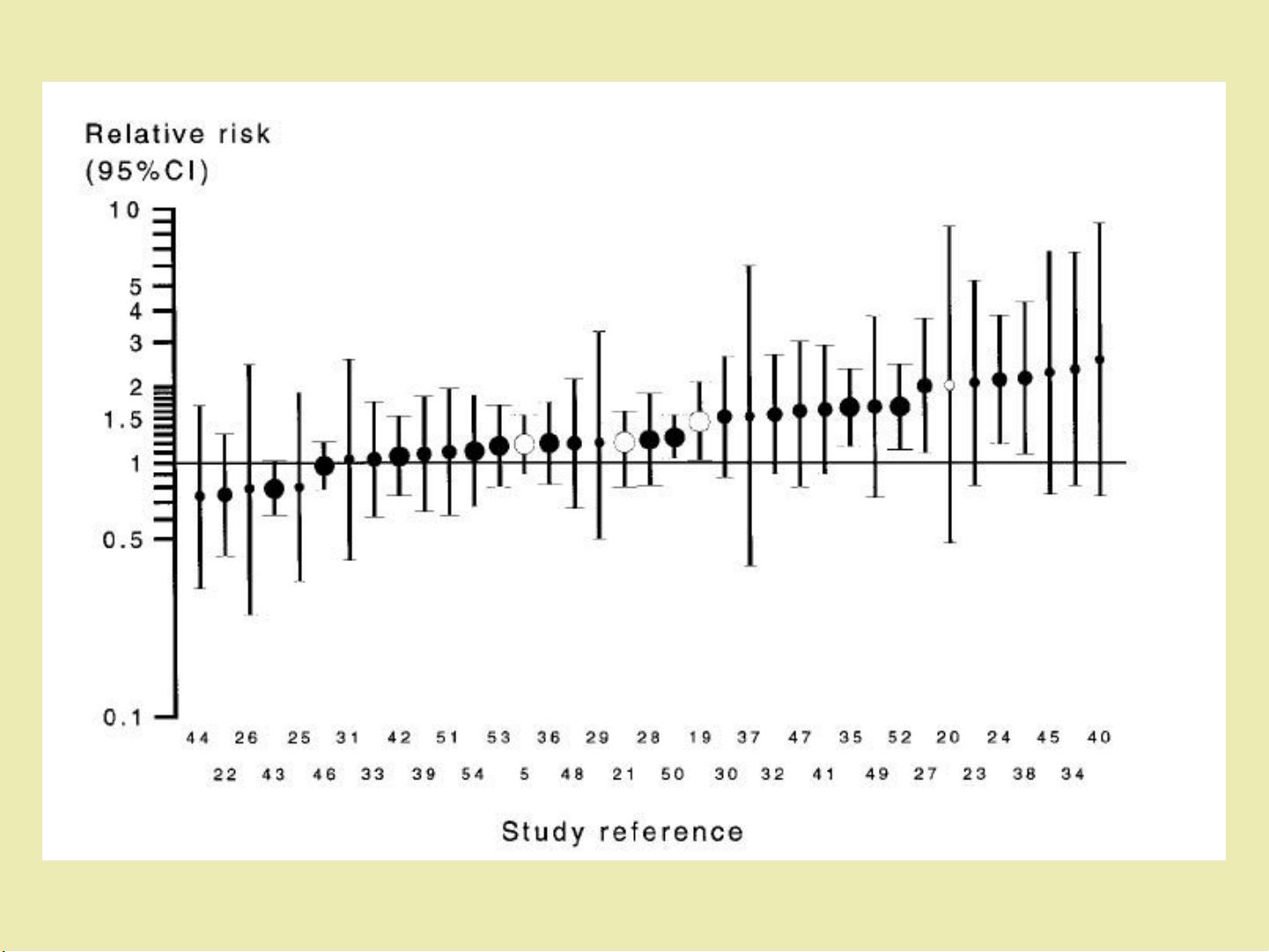
One of the key principles of meta-analysis is the concept of heterogeneity, which refers to the variability in the results of individual studies. A meta-analysis must account for this heterogeneity and use appropriate statistical methods to assess and quantify it.
Meta-analysis also requires careful consideration of the quality of the included studies, as well as potential biases that may affect the results. By taking these factors into account, meta-analysis can provide a more reliable and comprehensive summary of the available evidence on a particular topic.
Overall, meta-analysis is a powerful tool in evidence-based medicine that can help clinicians make informed decisions based on the best available evidence. It allows for a more systematic and objective evaluation of the effectiveness of treatments and interventions, ultimately improving patient care and outcomes.
2021-10-07 上传
2021-10-07 上传
2023-07-30 上传
2022-10-20 上传
2024-05-08 上传
2021-10-07 上传
智慧安全方案
- 粉丝: 3836
- 资源: 59万+
最新资源
- express-simple-template:是一个简单的模板,用于日志记录和测试bdd
- flopbox:通过 HTTP 传输文件,只需将您的文件翻过来
- 待办事项清单:待办事项清单
- 界面专业的VC++流量监控程序
- 这是一个仅供个人学习的电商项目(Spring Cloud 2+MySql+JPA+Redis+ Golang+Gin.zip
- 物联网湿度和温度显示-项目开发
- blog-template
- AndreyC101-GAME2005-F2020-FinalTest-101255069:GAME2005-游戏物理决赛
- meteor-mailchimp-custom:自定义和添加的表单字段操作
- 这是我在学习java时候写的一个最最简单的小爬虫,用来爬知乎的标题,然后存储的在mysql.zip
- VC++ TCP 方式实现MYQQ
- action-notify:涡轮行动通知
- react-reality-holokit:Holokit绑定用于React现实
- riemann-test-prototype:编写和测试 Riemann 配置的另一种方法
- terraform-azure-poc
- haku0x666