WELCOME TO ARCGIS 9
You can use ArcGIS in different ways, depending on the
complexity of your needs.
Some people use ArcGIS primarily as a single-user
mapping and analysis tool, usually in the context of a well-
defined, finite project. This common use of ArcGIS is
sometimes called project GIS. Other people use ArcGIS in
a multiuser system designed to serve an organizations
ongoing needs for geographic information. Multiuser GIS
is sometimes divided into departmental and enterprise GIS,
according to a systems level of complexity and integration
with the day-to-day operation of an organization.
This book presents ArcGIS in the context of project GIS
because a project is a good, self-contained way to explore a
variety of basic GIS functions.
Project GIS
In a GIS analysis project, an analyst faces a variety of tasks
that can be grouped into four basic steps.
The first step is to convert a question, such as Where is
the best place for a new building? or How many potential
customers are near this store?, into a GIS database design
and an analysis plan. This involves breaking the question
into logical parts, identifying what layers of data will be
needed to answer each part, and developing a strategy for
combining the answers to each part of the question into a
final answer.
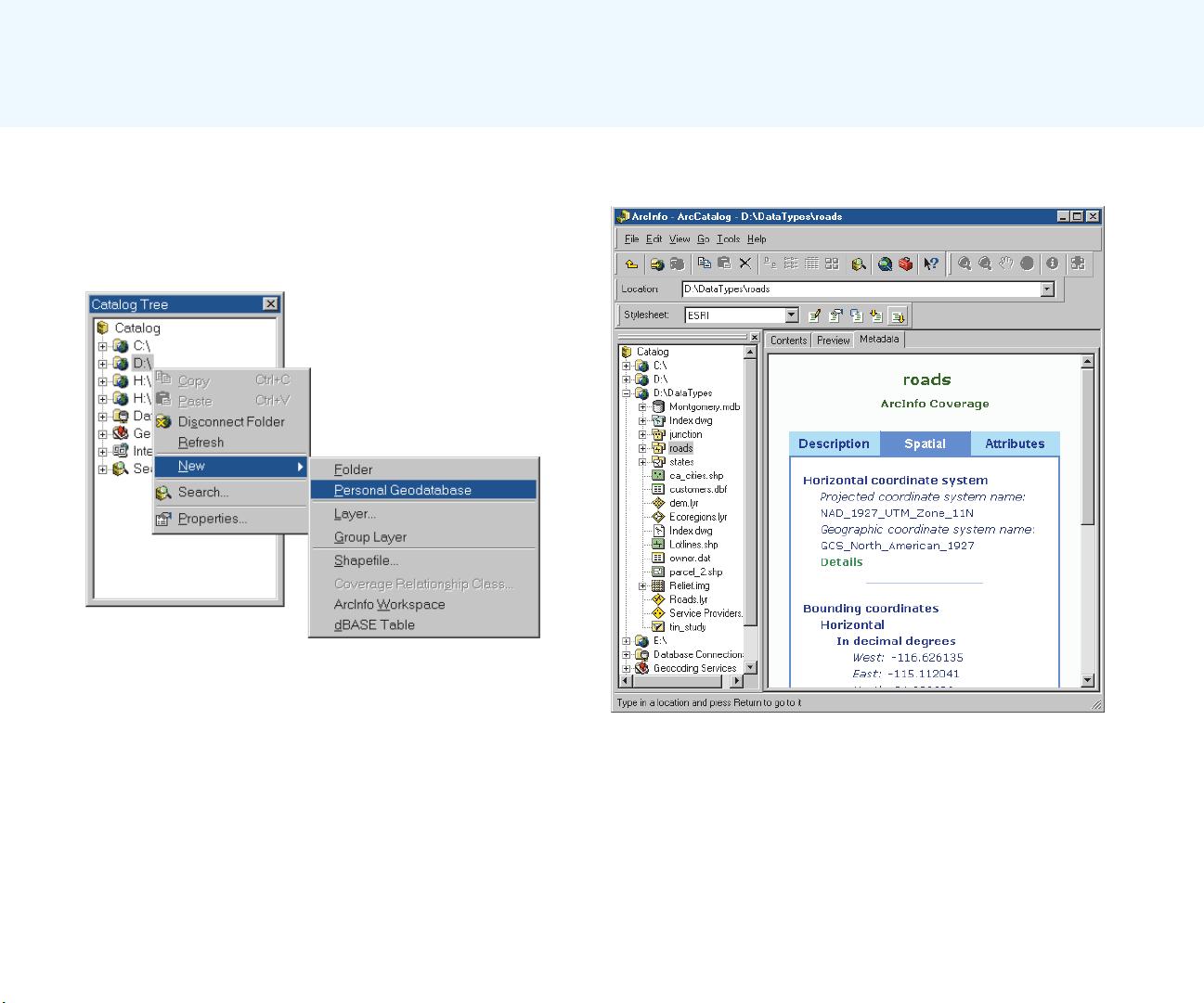
The next step is to create a database that contains the
geographic data required to answer the question. This may
involve digitizing existing maps, obtaining and translating
electronic data from a variety of sources and formats,
making sure the layers are of adequate quality for the task,
making sure the layers are in the same coordinate system
and will overlay correctly, and adding items to the data to
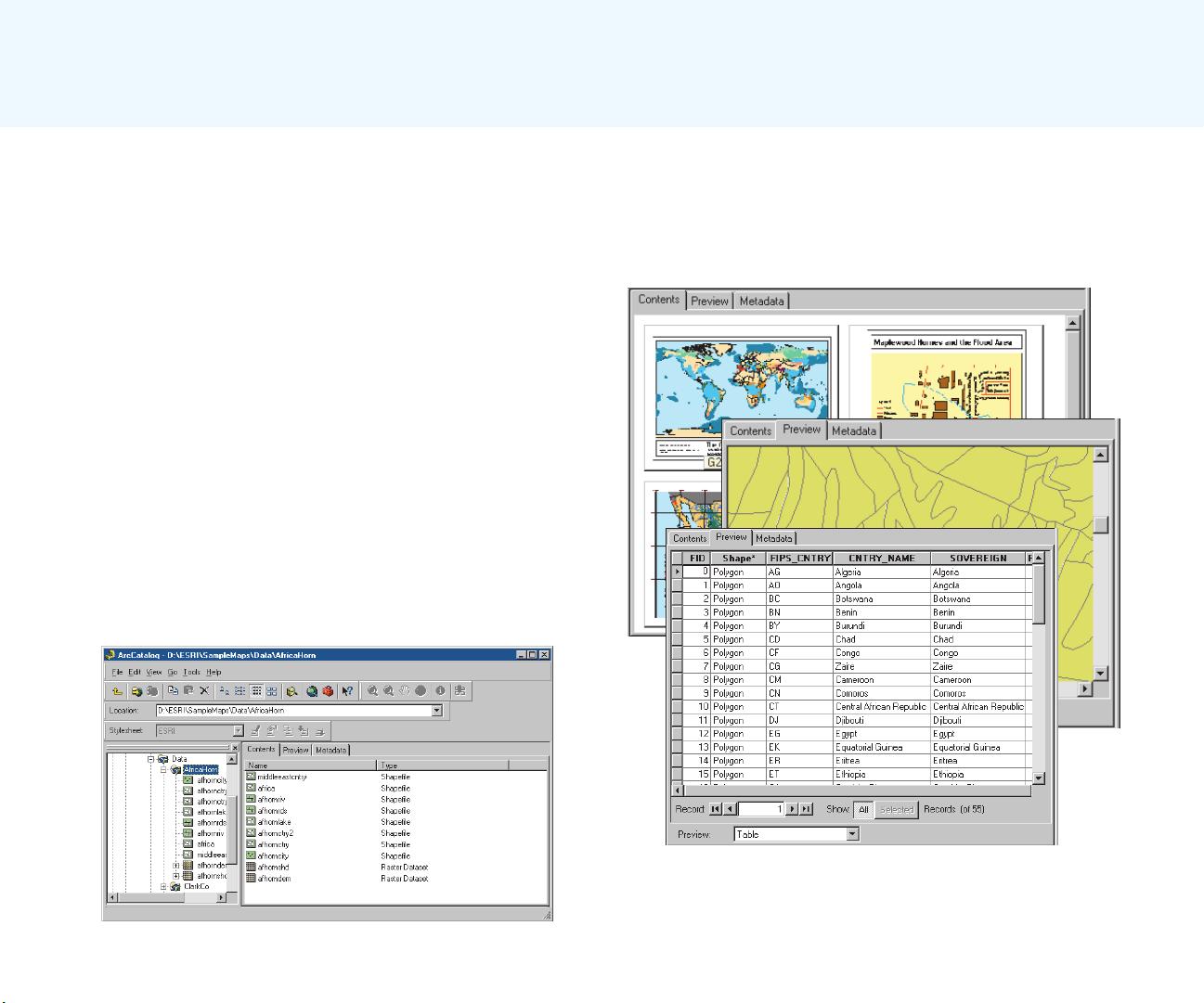
track analysis result values. Personal workspaces of file-
based data and personal geodatabases are used to organize
project GIS geodatabases.
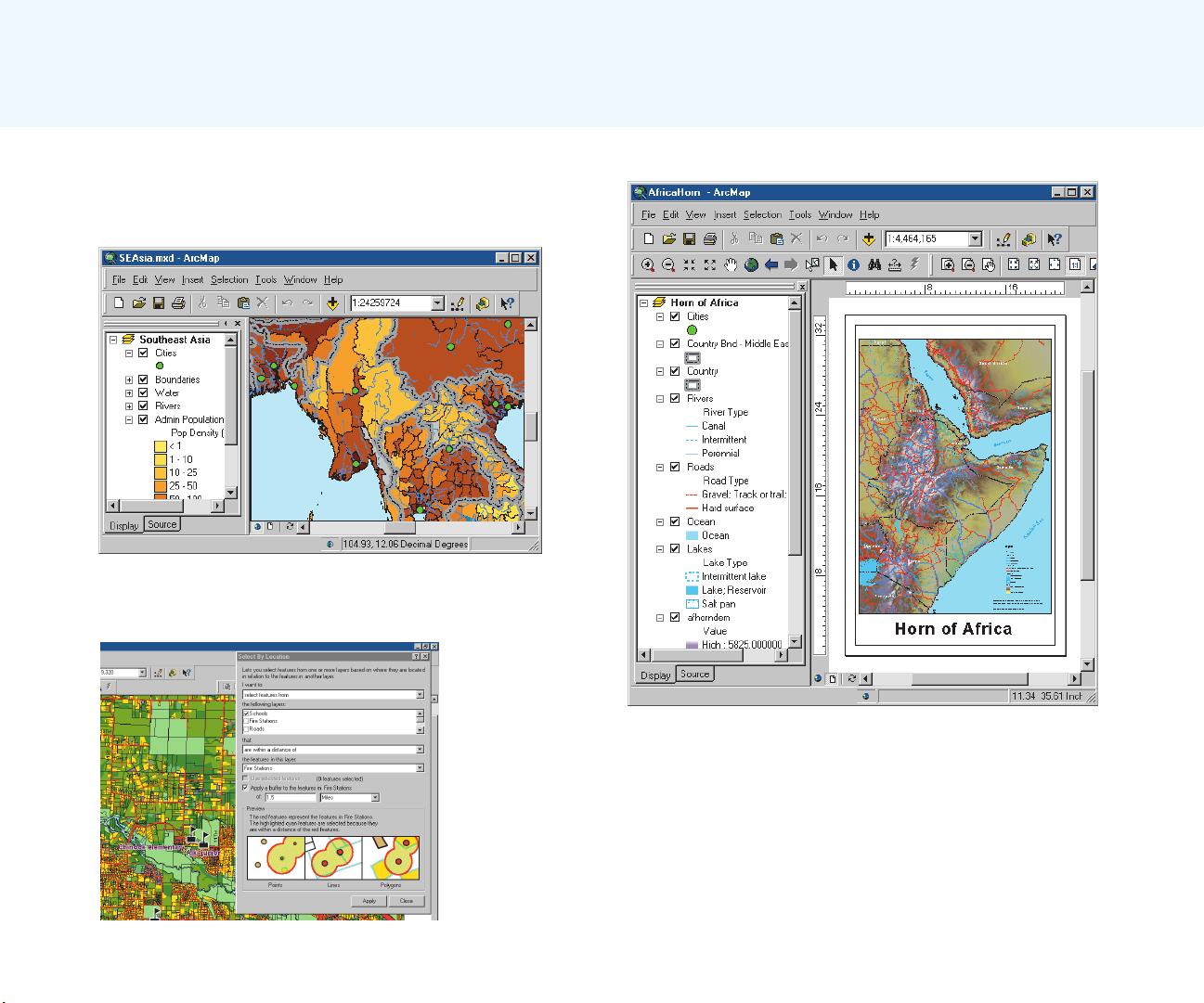
The next step is to analyze the data. This usually involves
overlaying different layers, querying attributes and feature
locations to answer each logical part of the question,
storing the answers to the logical parts of the question, and
retrieving and combining those answers to provide a
complete answer to the question.
The final step in a project-based analysis is to
communicate the results of the analysis, usually to people
who do not use GIS and who have different levels of
experience in dealing with maps. Maps, reports, and graphs
are all used, often together, to communicate the answer to
the question.
Multiuser GIS
In a multiuser GIS, people in an organizationfrom a few
in a single office to hundreds in different branchesuse
the GIS in different ways to support their daily tasks.
Departmental GIS refers to systems developed within a
single department to support a key function of the
department. For example, a planning department might
routinely use GIS to notify property owners of proposed
zoning changes near their property.
A departmental GIS is usually managed within the
department and often has specialists devoted to different
Unique projects to daily business
ch01.p65 02/15/2001, 9:17 AM9