3/11
Application Note
PCB Layout Techniques of Buck Converter
© 2012 ROHM Co., Ltd.
No. 60AN066E Rev.003
OCTOBER 2017
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
0.01 0.1 1 10 100 1000
Impedance (Ω)
Frequency (MHz)
1µF
10µF
10µF + 0.1µF
10µF + 0.47µF
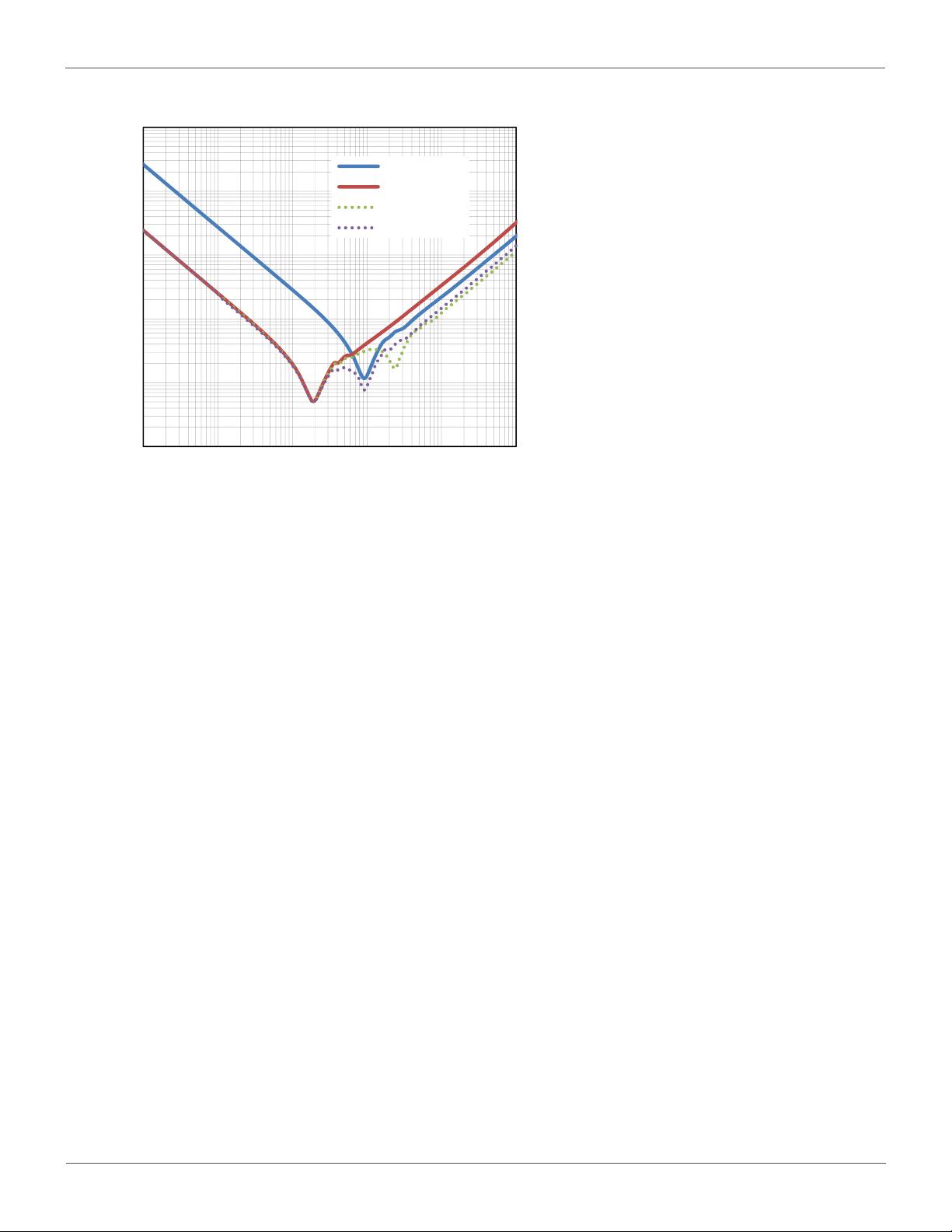
Figure 2. Frequency characteristics of Ceramic capacitor
Figure 3-f shows unsuitable layout. Voltage noise will be
generated by the influence of wiring inductance for C
BYPASS
, V
IN
terminal and GND terminal of IC has some distance. Shortening
the wiring even by 1mm is highly recommended.
In case of buck converter, high frequency of several hundred
MHz will be loaded to the ground of C
IN
even with C
BYPASS
placed
close to IC. Therefore placing ground of C
IN
and C
O
must be
separated from each other by at least 1cm to 2cm.
Free-wheel diode D
1
must be placed closer and on same surface
of IC terminal. Figure 3-e shows suitable layout. With long
distance between IC terminal and diode, the spike noise will be
induced due to wiring inductance, that will be piled up at the
output. Use short and wide wiring for free-wheel diode, and
connect directly to GND terminal and switching terminal of IC.
Do not place it on bottom surface layer through via, as noise will
be worse, which is influenced by via inductance.
Figure 3-f shows unsuitable layout. Wiring inductance increases
due to distance between diode and switching terminal, and GND
terminal of IC and spike noise gets higher. To improve spike
noise caused by unsuitable layout the RC snubber-circuit may
be added as a countermeasure. This snubber-circuit must be
placed closer to switching terminal and GND terminal of IC
(Figure 3-g). Placing it at the both ends of diode will not absorb
spike noise generated by wiring inductance. (Figure 3-h).
Introduce Thermal Via
Copper area of PCB contributes to heat dissipation, but because
it does not have enough thickness, the heat dissipation result
that meets area cannot be achieved from limited PCB size. Heat
is dissipated using base material of board as a radiator. To
deliver heat to opposite layer of the board efficiently and to highly
reduce heat resistance, the thermal via are introduced.
Thermal via dimension of HTSOP-J8, reverse-side thermal pad
package is shown in Figure 4. To increase heat conductivity,
thermal via with small-diameter, inner diameter of 0.3mm which
can fill solder, is recommended. With large diameter, problem of
solder suction may occur at reflow solder process. Spacing
between thermal via is about 1.2mm and placed directly below
the thermal pad which is at the reverse-side of IC.
Place additional thermal via around IC like in Figure 3-a, if via
below the IC’s reverse-side thermal pad are not enough. Heat
sink of HTSOP-J8 reverse-side thermal pad package is at
ground potential, so EMI does not increase with wide copper
pattern.
C
IN
1µF 50V X5R GRM188R61H105KAAL (Murata)
10µF 50V X5R GRM31CR61H106KA12 (Murata)
C
BYPASS
0.1µF 50V X7R GRM188R71H104KA93 (Murata)
0.47µF 50V X7R GRM21BR71H474KA88 (Murata)


















