"深入理解数据结构教学:树与二叉树,堆与线索化二叉树"
版权申诉
112 浏览量
更新于2024-04-18
收藏 1.87MB PPT 举报
Chapter Six of the data structure teaching course focuses on the concept of trees and forests. A tree is a hierarchical data structure consisting of nodes connected by edges, where each node has a parent node and zero or more child nodes. A forest is a collection of disjoint trees.
The key topics covered in this chapter include the definition of trees and forests, binary trees, binary tree representation, binary tree traversal techniques, threaded binary trees, heaps, and the relationship between trees and forests.
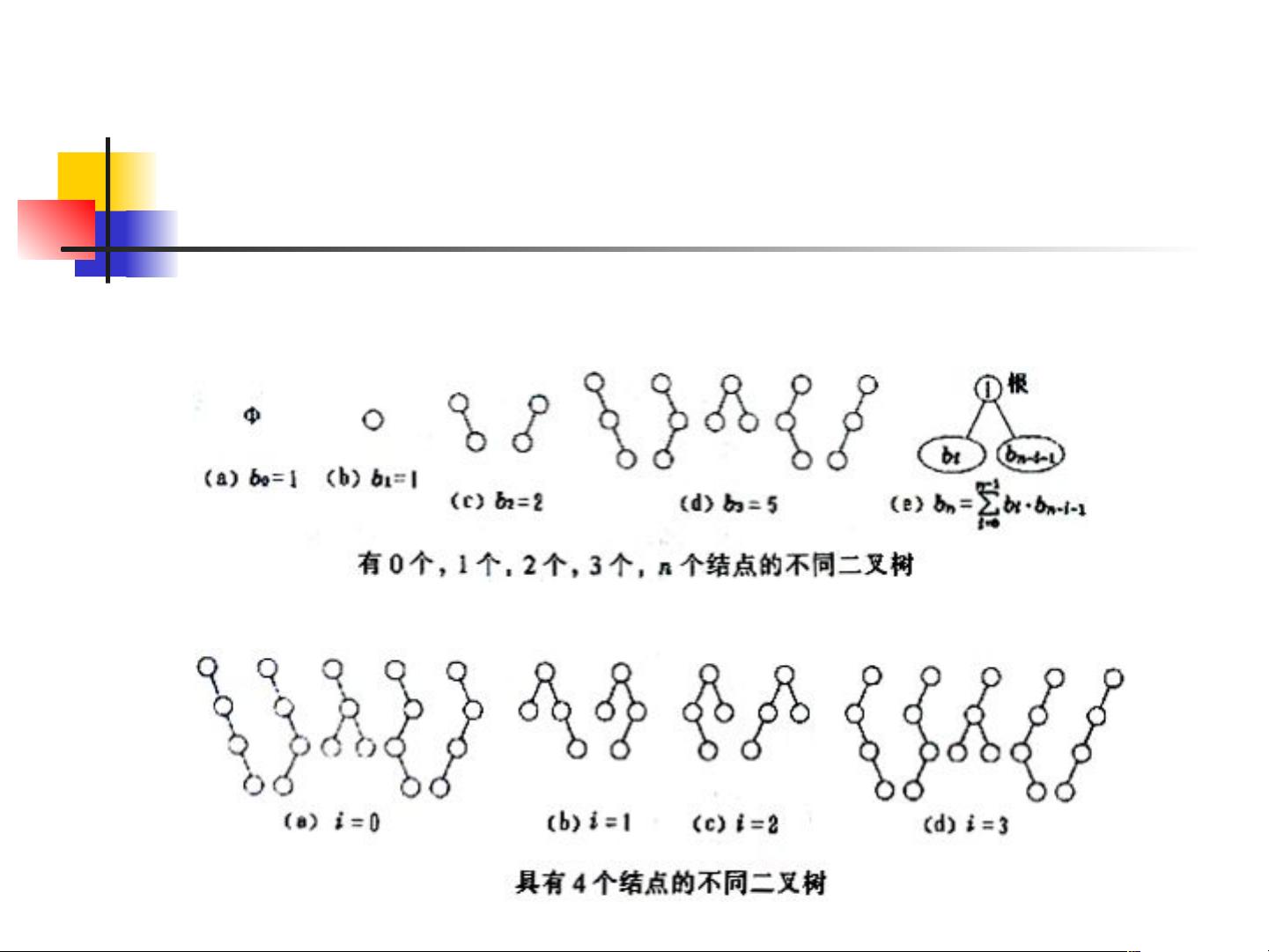
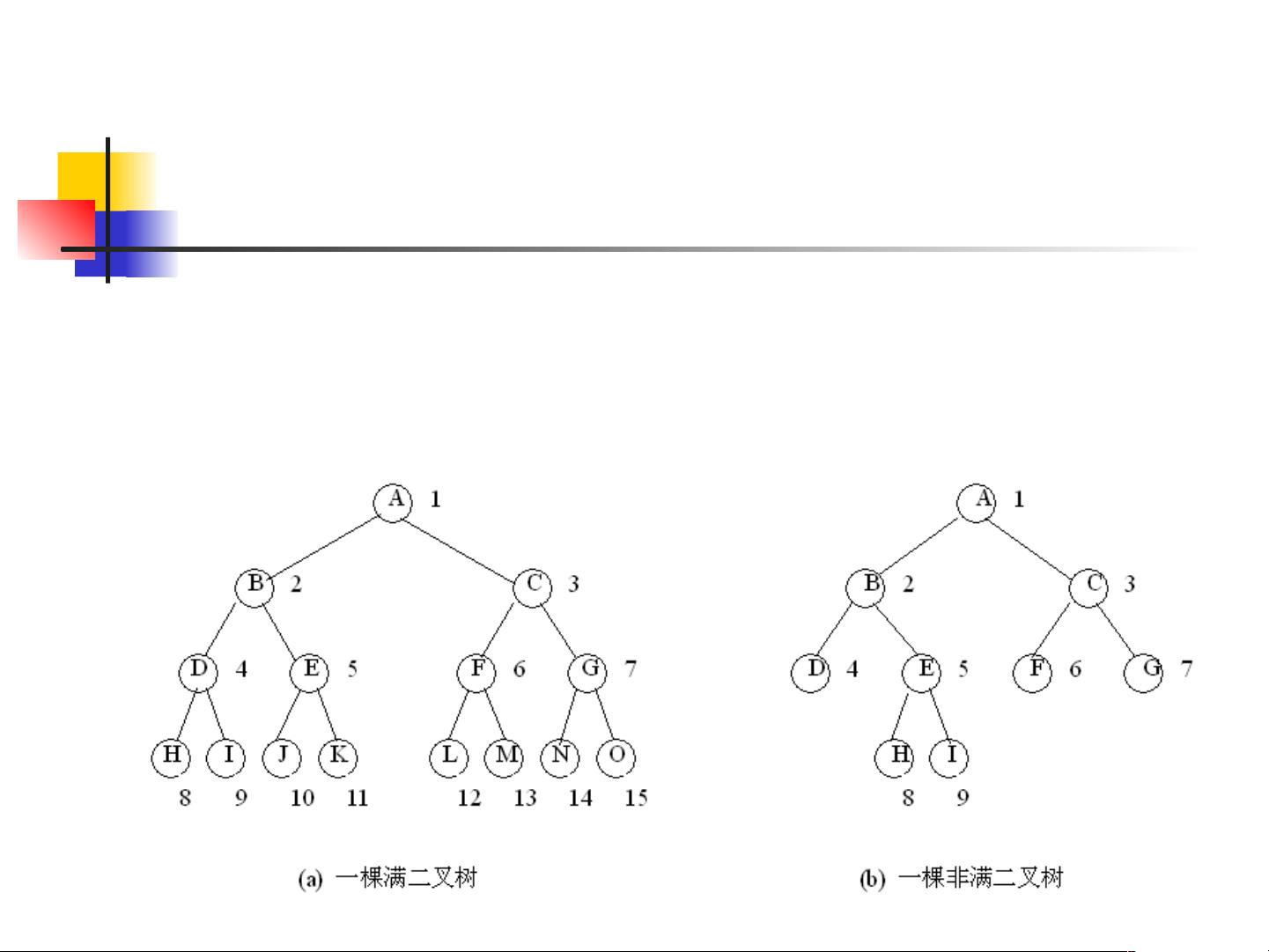
A binary tree is a tree data structure in which each node has at most two children, referred to as the left child and the right child. It is represented using linked data structures or arrays. The traversal of a binary tree involves visiting nodes in a specific order, such as pre-order, in-order, post-order, or level order traversal.
Threaded binary trees are binary trees in which nodes are threaded with pointers to their in-order successors or predecessors. This allows for efficient traversal without the need for stack data structures. Heaps are specialized binary trees used in priority queues, where the root node stores the minimum or maximum value in the tree.
The chapter also explores the relationship between trees and forests, where a forest is a collection of disjoint trees with no cycles. Trees and forests are fundamental data structures used in various applications, such as file systems, database indexing, and network routing algorithms.
In conclusion, Chapter Six of the data structure teaching course provides a comprehensive overview of trees and forests, including their definitions, representations, traversal techniques, and specialized variants like threaded binary trees and heaps. Understanding these concepts is essential for designing efficient algorithms and data structures in computer science and software development.
2022-06-16 上传
2022-06-16 上传
智慧安全方案
- 粉丝: 3817
- 资源: 59万+
最新资源
- MATLAB新功能:Multi-frame ViewRGB制作彩色图阴影
- XKCD Substitutions 3-crx插件:创新的网页文字替换工具
- Python实现8位等离子效果开源项目plasma.py解读
- 维护商店移动应用:基于PhoneGap的移动API应用
- Laravel-Admin的Redis Manager扩展使用教程
- Jekyll代理主题使用指南及文件结构解析
- cPanel中PHP多版本插件的安装与配置指南
- 深入探讨React和Typescript在Alias kopio游戏中的应用
- node.js OSC服务器实现:Gibber消息转换技术解析
- 体验最新升级版的mdbootstrap pro 6.1.0组件库
- 超市盘点过机系统实现与delphi应用
- Boogle: 探索 Python 编程的 Boggle 仿制品
- C++实现的Physics2D简易2D物理模拟
- 傅里叶级数在分数阶微分积分计算中的应用与实现
- Windows Phone与PhoneGap应用隔离存储文件访问方法
- iso8601-interval-recurrence:掌握ISO8601日期范围与重复间隔检查