5G Services Innovation – 5G Americas White Paper 14
same scenarios is needed in homes and businesses as well as traditional medical settings such as clinics
and hospitals.
2.2.3 MOBILITY SCENARIO
Given the wide range of healthcare applications and devices, the mobility needs are diverse. In a hospital
or clinical setting, the devices may be completely stationary. Video and vital sign monitors may be
permanently affixed in an operating or examining room. Other devices in such a setting may be nomadic.
For example, vital sign monitors may be moveable from one room or one patient to another, with activity
enabled only when connected to a given patient in a given bed. In other scenarios, devices may need to be
connected for full mobility at speeds ranging from pedestrian for a wristband monitor to high speeds for
devices in an ambulance or medivac helicopter.
2.3 REQUIREMENTS AND KPIS ON 5G
3GPP has identified KPIs for healthcare applications in three categories: static local, static remote and
moving conditions. Within each category, characteristic parameters are identified for communication
service availability, communication service reliability (Mean Time Between Failure), maximum end-to-end
latency, bitrate, and direction. Influence quantities are also identified for message size, survival time, User
Equipment (UE) speed in kilometer/hour (km/h), number of UEs, and service area.
A wireless operating room is an example of a static local condition. Using wireless communication in this
environment provides comprehensive connectivity and communication between all devices, from vital sign
monitors and medicine drips, to lighting and imaging machines. This type of comprehensive communication
is typically not available today as manufacturers of different components use different technologies and
even proprietary communications mechanisms for their products. Full communication and synchronization
of all devices in an operating room gives the medical personnel the best and most accurate information of
the patient’s condition and allows them to make real-time decisions to improve patient outcomes. An
additional benefit of a fully wireless operating room is the removal of cables, wires and cords which may
impede movement around the patient and potentially be a source of increased infection risk.
Treatment in an ambulance is an example of a moving condition. Wireless communications, even at high
speed, allows the Emergency Medical Techs (EMT) to communicate with the hospital while the patient is
enroute. For medical conditions such as a stroke, where specific interventions are needed within a narrow
time window for best patient outcomes, having this communication path established as soon as possible
allows the tending physician to have information at the earliest possible moment and to provide the most
accurate treatment guidance to the EMTs before the patient reaches the hospital.
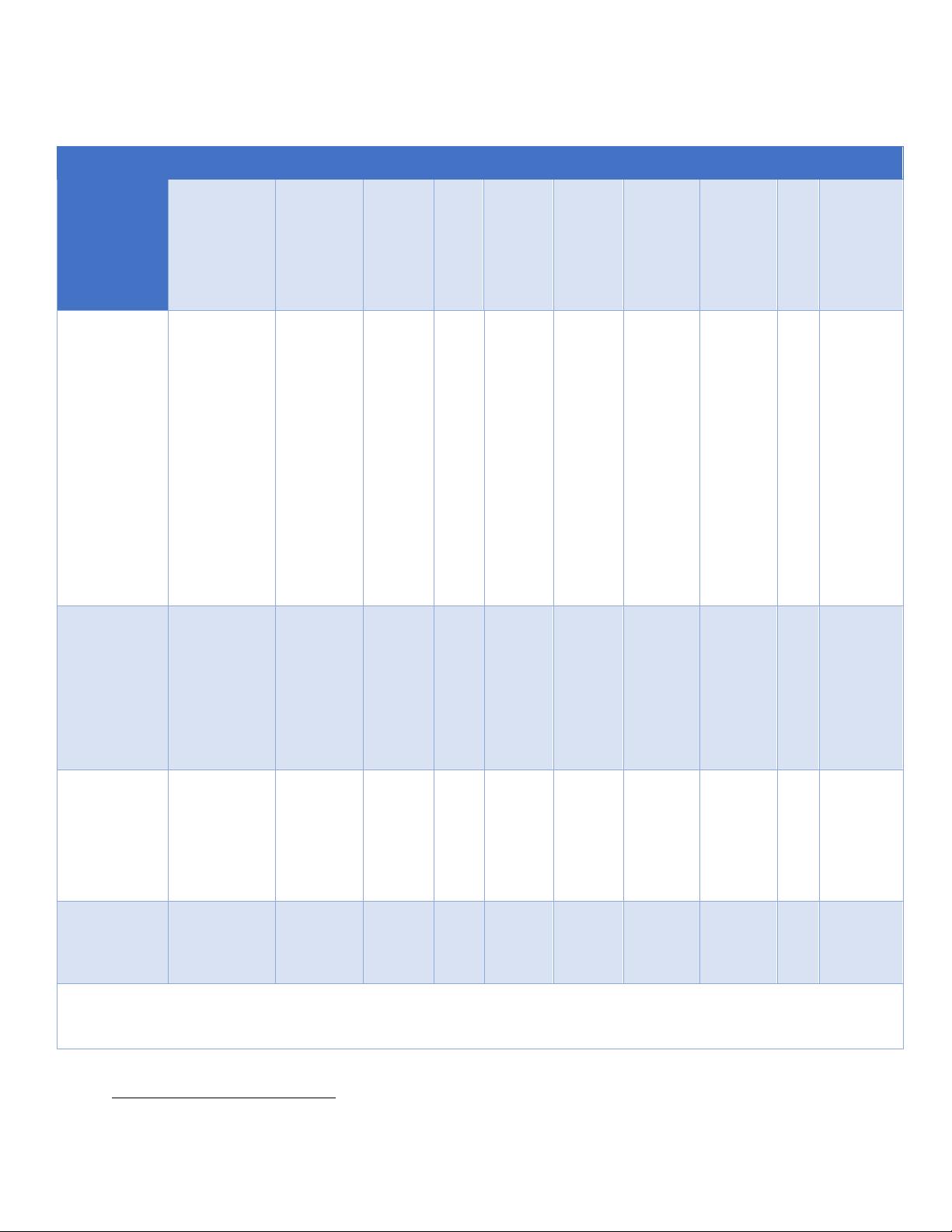
The full set of KPIs can be found in 3GPP TR 22.826 however the KPIs for static local conditions is
shown in Table 2.2.