Analog Circuit and Device Interaction in High-Speed SerDes Design in 16nm
FinFET CMOS Technology
Freeman Zhong, Ashutosh Sinha
Avago Technologies Inc, San Jose, CA 95131
Abstract
SerDes deals with data serialization, deserialization and
channel equalization up to data rate of 28+Gb/s. Process
technology and device characteristic greatly impacts
architecture, circuit topology, and design merit of a SerDes.
Several architecture choices, analog circuits, and techniques
to mitigate undesired device characteristic in 16nm FinFET
are discussed in this paper. With advanced CMOS technology
and mitigation techniques, a prototype 28Gb/s SerDes was
developed and demonstrated desired performance, power and
die area.
Introduction
SerDes is one of the most critical components in
communication systems. As data traffic increases
exponentially and CMOS technology advances to 16nm in
past 15 years, data rate of SerDes has increased from
1.25Gb/s to 28+Gb/s. As shown in Fig. 1, 2, 3, a serial link
consists of a transmitter, channel, and receiver. It not only
functions as data serialization from N to 1 bit, and
deserialization from 1 to N bit, but also deals with signal
integrity challenges, such as inter-symbol-interference, cross-
talk, reflection and system jitter as data rate increases. Due to
low-pass nature of a channel, the received eye is totally
closed at a receiver. With channel equalization from both
transmitter and receiver, the equalized eye is open enough for
clock and data recovery as shown in Fig. 4. Many SerDes
were designed and fabricated in 250nm to 28nm CMOS
technology (1), (2), (3).
Fig. 1– Block diagram of a serial link
Fig. 2 – Block diagram of a transmitter
Figure 3 – Block diagram of a receiver
Fig. 4 – Received and equalized eyes at a receiver with 28Gb/s PRBS31 data
traffic over a channel of 34dB loss
SerDes architecture and process technology interaction
Process technology greatly impacts the architecture,
implementation, performance and power consumption of a
SerDes. The critical process parameters, such as unity gain
frequency, threshold voltage, leakage, and maximum supply
voltage of devices, are dominant considerations for SerDes
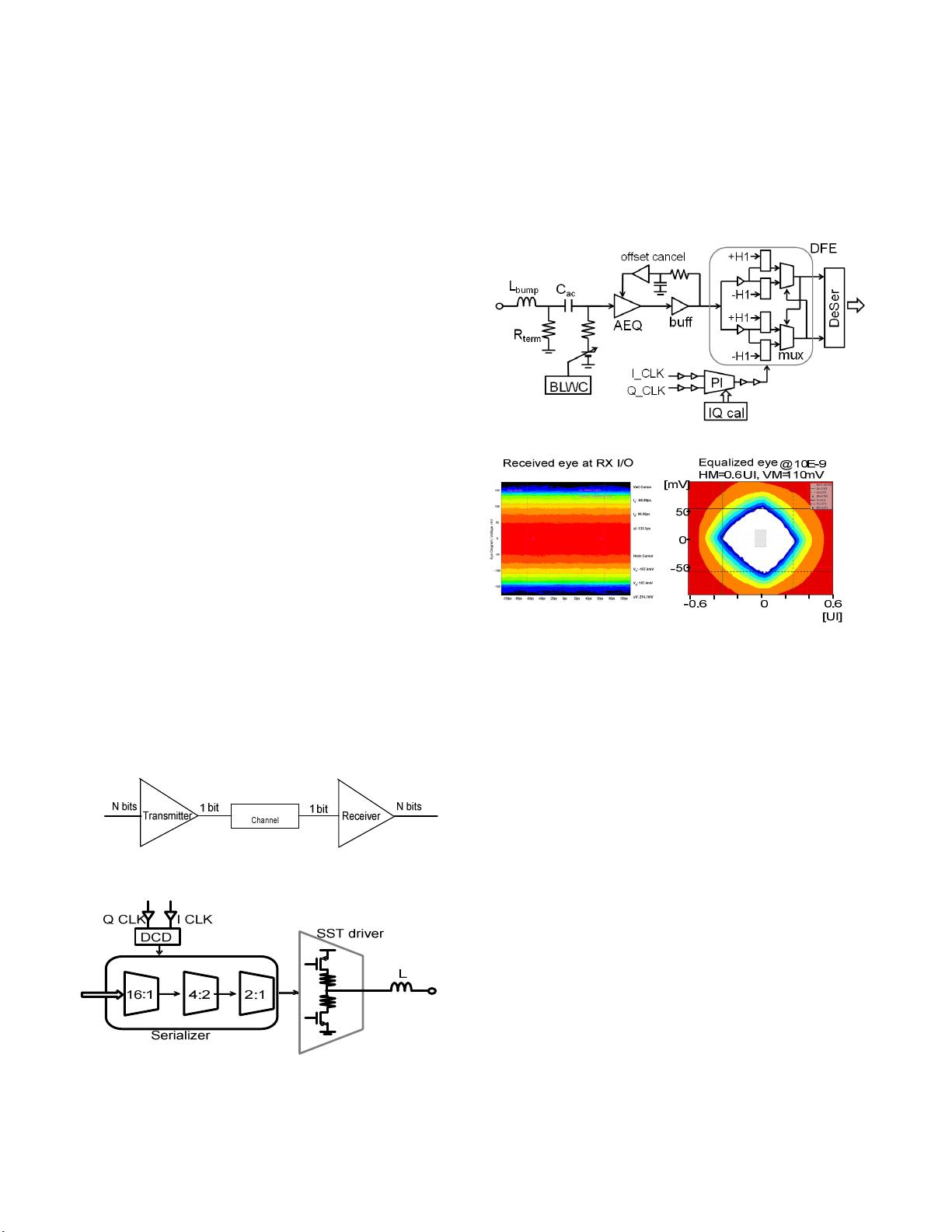
architecture choice. For example, a decision feedback
equalizer (DFE) is a timing critical circuit that generates a
feedback signal and adds it to the received signal within one
unit interval (UI). For data rate below 16Gb/s, direct
feedback DFE, as shown in Fig. 5, is an optimal
implementation where the timing constraint of Tck-q + Tdac
+ Tsum + Tsetup < 1UI can be met in in 28nm/16nm process.
However, when data rate increases to 28Gb/s where 1UI is
only 35.7ps, the timing constraint of direct DFE is no longer
met. A h1 loop unrolled DFE, shown in Fig. 6, was
developed where the +/-h1 feedback signals are pre-
calculated and added to received signal, and 2 speculative
outputs are selected based on previous data decision, thus,
new timing constraint of Tck-q + Tmux + Tsetup < 1UI can
be met in 28nm/16nm CMOS.
As CMOS technology scales down to16nm, thin-oxide device
operates at lower supply voltage that presents challenges of
headroom and linearity to analog circuits. To tackle these
3.2.1 IEDM14-52978-1-4799-8001-7/14/$31.00 ©2014 IEEE









