AD9854
Rev. E | Page 10 of 52
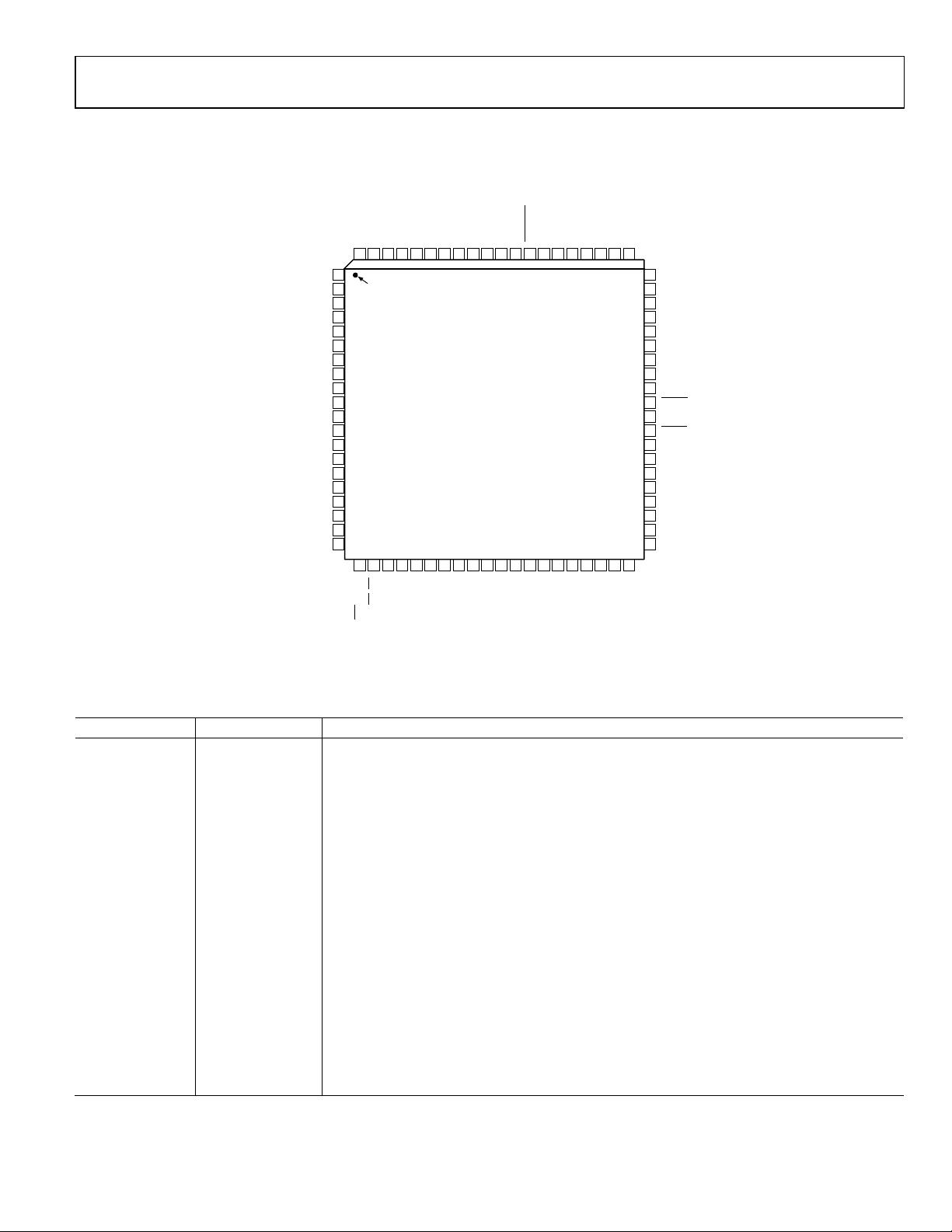
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
20 I/O UD CLK
Bidirectional I/O Update Clock. Direction is selected in control register. If this pin is selected as an
input, a rising edge transfers the contents of the I/O port buffers to the programming registers. If I/O
UD CLK is selected as an output (default), an output pulse (low to high) with a duration of eight
system clock cycles indicates that an internal frequency update has occurred.
21
WR/SCLK Write Parallel Data to I/O Port Buffers. Shared function with SCLK. Serial clock signal associated
with the serial programming bus. Data is registered on the rising edge. This pin is shared with
WR
when the parallel mode is selected. The mode is dependent on Pin 70 (S/P SELECT).
22
RD/CS Read Parallel Data from Programming Registers. Shared function with CS. Chip-select signal
associated with the serial programming bus. Active low. This pin is shared with
RD when the
parallel mode is selected.
29 FSK/BPSK/HOLD
Multifunction pin according to the mode of operation selected in the programming control
register. In FSK mode, logic low selects F1 and logic high selects F2. In BPSK mode, logic low
selects Phase 1 and logic high selects Phase 2. In chirp mode, logic high engages the hold
function, causing the frequency accumulator to halt at its current location. To resume or
commence chirp mode, logic low is asserted.
30 OSK
Output Shaped Keying. Must first be selected in the programming control register to function. A
logic high causes the I and Q DAC outputs to ramp up from zero-scale to full-scale amplitude at a
preprogrammed rate. Logic low causes the full-scale output to ramp down to zero scale at the
preprogrammed rate.
31, 32, 37, 38, 44,
50, 54, 60, 65
AVDD
Connections for the Analog Circuitry Supply Voltage. Nominally 3.3 V more positive than AGND
and DGND.
33, 34, 39, 40, 41,
45, 46, 47, 53, 59,
62, 66, 67
AGND Connections for Analog Circuitry Ground Return. Same potential as DGND.
36 VOUT
Noninverted Output of the Internal High Speed Comparator. Designed to drive 10 dBm to 50 Ω
load as well as standard CMOS logic levels.
42 VINP Voltage Input Positive. The noninverting input of the internal high speed comparator.
43 VINN Voltage Input Negative. The inverting input of the internal high speed comparator.
48 IOUT1 Unipolar Current Output of I, or the Cosine DAC. (Refer to Figure 3.)
49
IOUT1
Complementary Unipolar Current Output of I, or the Cosine DAC.
51
IOUT2
Complementary Unipolar Current Output of Q, or the Sine DAC.
52 IOUT2
Unipolar Current Output of Q, or the Sine DAC. This DAC can be programmed to accept external
12-bit data in lieu of internal sine data, allowing the AD9854 to emulate the AD9852 control DAC
function.
55 DACBP
Common Bypass Capacitor Connection for Both I and Q DACs. A 0.01 μF chip capacitor from this
pin to AVDD improves harmonic distortion and SFDR slightly. No connect is permissible, but
results in a slight degradation in SFDR.
56 DAC R
SET
Common Connection for Both I and Q DACs. Used to set the full-scale output current. R
SET
= 39.9/I
OUT
.
Normal R
SET
range is from 8 kΩ (5 mA) to 2 kΩ (20 mA).
61 PLL FILTER
Connection for the External Zero-Compensation Network of the REFCLK Multiplier’s PLL Loop
Filter. The zero-compensation network consists of a 1.3 kΩ resistor in series with a 0.01 μF
capacitor. The other side of the network should be connected to AVDD as close as possible to
Pin 60. For optimum phase noise performance, the REFCLK multiplier can be bypassed by setting
the bypass PLL bit in Control Register 1E hex.
64 DIFF CLK ENABLE
Differential REFCLK Enable. A high level of this pin enables the differential clock inputs, REFCLK
and
REFCLK (Pin 69 and Pin 68, respectively).
68
REFCLK Complementary (180° Out of Phase) Differential Clock Signal. User should tie this pin high or low
when single-ended clock mode is selected. Same signal levels as REFCLK.
69 REFCLK
Single-Ended Reference Clock Input (CMOS Logic Levels Required) or One of Two Differential
Clock Signals. In differential reference clock mode, both inputs can be CMOS logic levels or have
greater than 400 mV p-p square or sine waves centered about 1.6 V dc.
70 S/P SELECT Selects serial programming mode (logic low) or parallel programming mode (logic high).
71 MASTER RESET
Initializes the serial/parallel programming bus to prepare for user programming; sets
programming registers to a do-nothing state defined by the default values listed in
Table 8.
Active on logic high. Asserting this pin is essential for proper operation upon power-up.