"中红外LED光声检测二氧化碳的研究与实验"
版权申诉
88 浏览量
更新于2024-03-07
收藏 2.11MB DOCX 举报
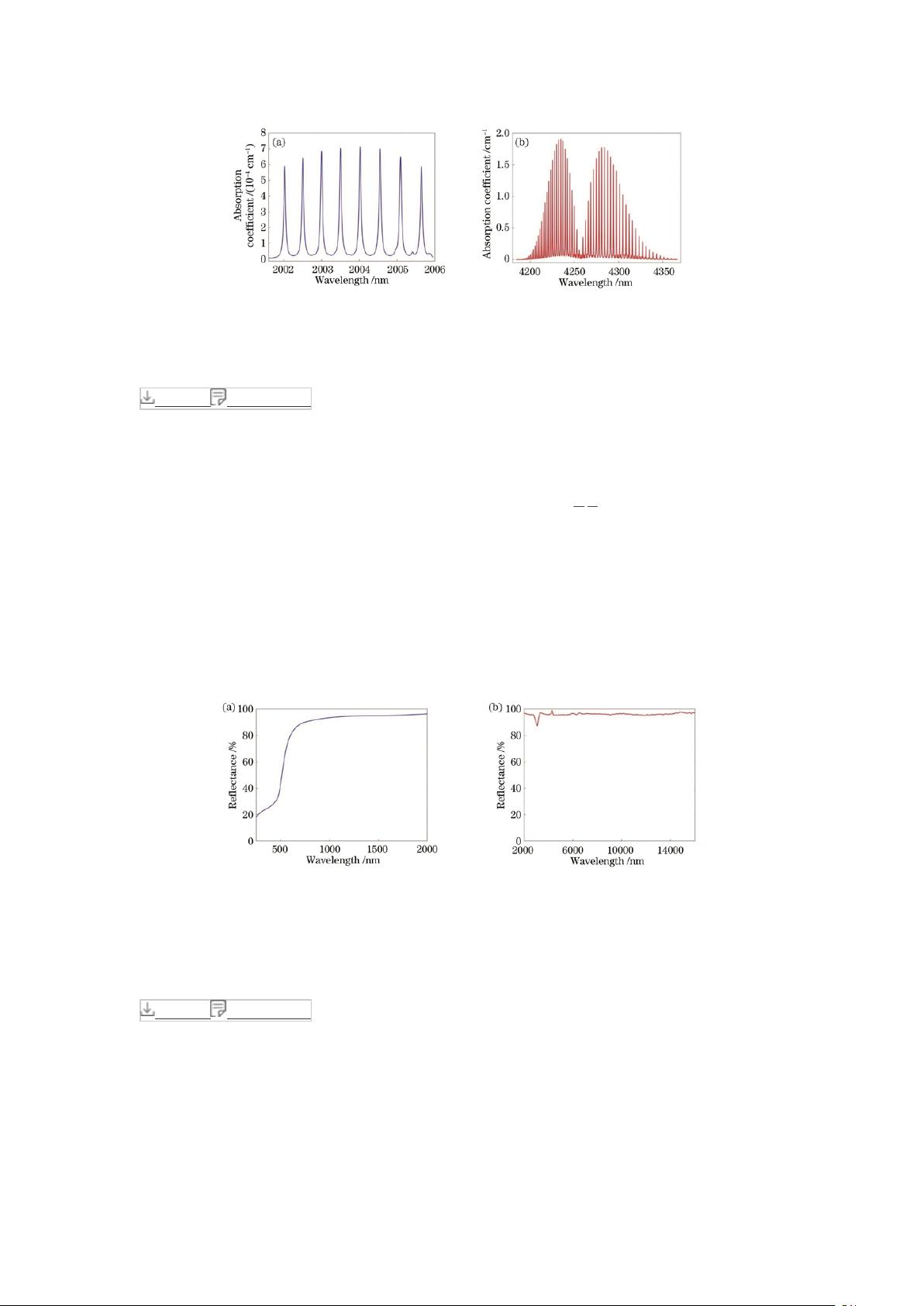
Gas detection is crucial in various industries, and photoacoustic spectroscopy technology has gained increasing attention due to its high sensitivity and rapid response. In light of this, a new approach using a mid-infrared LED with a center wavelength of 4300 nm as the excitation source for the detection of carbon dioxide gas has been developed.
The research team combined long optical path and acoustic resonance technologies to create a T-type photoacoustic cell, with the inner wall of the absorption cell plated with gold and a sound resonance tube coupled to the cell body. Finite element simulation was utilized to determine the first-order longitudinal resonance mode and resonance frequency of the photoacoustic cell. Additionally, a hardware driver circuit was designed to modulate the output of the LED light source.
Building upon these advancements, an automated process for carbon dioxide gas photoacoustic detection was established. Experimental results demonstrated a strong linear relationship between the photoacoustic signal and the sample concentration, with a noise equivalent concentration (volume fraction) of 1.24×10-4. The stability of the device was evaluated using Allan deviation, and a detection sensitivity of 1.8×10-5 was achieved with an average time of 200 seconds.
Overall, the utilization of a mid-infrared LED as the excitation source for carbon dioxide gas detection in photoacoustic spectroscopy has shown promise in providing a highly sensitive and efficient method for gas detection applications. This innovative approach holds great potential for further advancements in gas sensing technology.
2021-11-11 上传
2022-06-29 上传
2022-11-10 上传
2021-09-26 上传
2022-06-24 上传
2022-06-24 上传
2022-06-23 上传
罗伯特之技术屋
- 粉丝: 4501
- 资源: 1万+
最新资源
- ballista:现代网络的互操作性系统
- gsheet-planner:聪明的,可自动排序的Google表格计划器
- 翻译翻译什么叫HTML5(一)配套代码资源包
- Towering Yoga Masters Free Game-crx插件
- 我的
- Toolint-tests-Empty-TC-Add-Tools-2021-03-11T20-17-21.121Z:为工具链创建
- List:用CodeSandbox创建
- timecat-mmo::smiling_cat_with_heart-eyes: 时间猫,但是一个 MMO
- 视觉暂留测试工具-crx插件
- 变色龙:BAOBAB服务器的“第二层”模型交互层
- Perifa_Acessa:Com recursos de voz(acessibilidade)podendo ser a Alexa(Firefox)ou o Watson(Microsoft),Recursos de Hand Talk eImplementaçõesde melhorias a fazer,esteéum eta(protótipo)
- posterus:具有取消功能,可调度控制和协程的可组合异步原语(期货)
- OS-Places:演示和代码示例的OS Places存储库
- Commando Girl Free Games-crx插件
- PSTools GUI:PSTools 的图形前端-开源
- 彼得里斯