CANstress使用教程:快速接入与干扰模拟
需积分: 50 146 浏览量
更新于2024-07-15
3
收藏 647KB PDF 举报
"CANstress快速入门.pdf 是一份关于CANstress的快速入门培训材料,涵盖了CANstress的基本功能、硬件组成和软件使用配置步骤。"
CANstress是一款专业的CAN总线干扰仪,用于测试和评估CAN(Controller Area Network)总线系统的稳定性和抗干扰能力。这款工具支持可编程总线干扰,包括数字干扰和模拟干扰两种方式。数字干扰可以实现从0到1和从1到0的电平转换,模拟干扰则涉及更复杂的信号模拟,如短路和断路情况,以及线长变化等,这些功能能够全面模拟实际环境中可能遇到的各种异常状况。
硬件部分,CANstress具备Trigger In和Trigger Out接口,便于触发和控制干扰动作。PC接口提供了USB和COM串口的选择,适应不同的计算机连接需求。供电接口支持8到40vDC的电压范围,确保了设备在不同环境下的正常工作。此外,CANstress还配备了多个CAN接口,方便连接到不同的CAN节点,如ECU(Electronic Control Unit)。
软件配置是使用CANstress的重要环节。首先,物理连接需要将CANstress与ECU、CAN卡和PC连接起来。对于高速CAN节点,直接使用15-Pin连接器;对于低速CAN节点,需要添加转接器。接着,通过USB或串口将CANstress与PC相连,CAN卡则通过USB或PCMCIA接口与电脑建立连接。
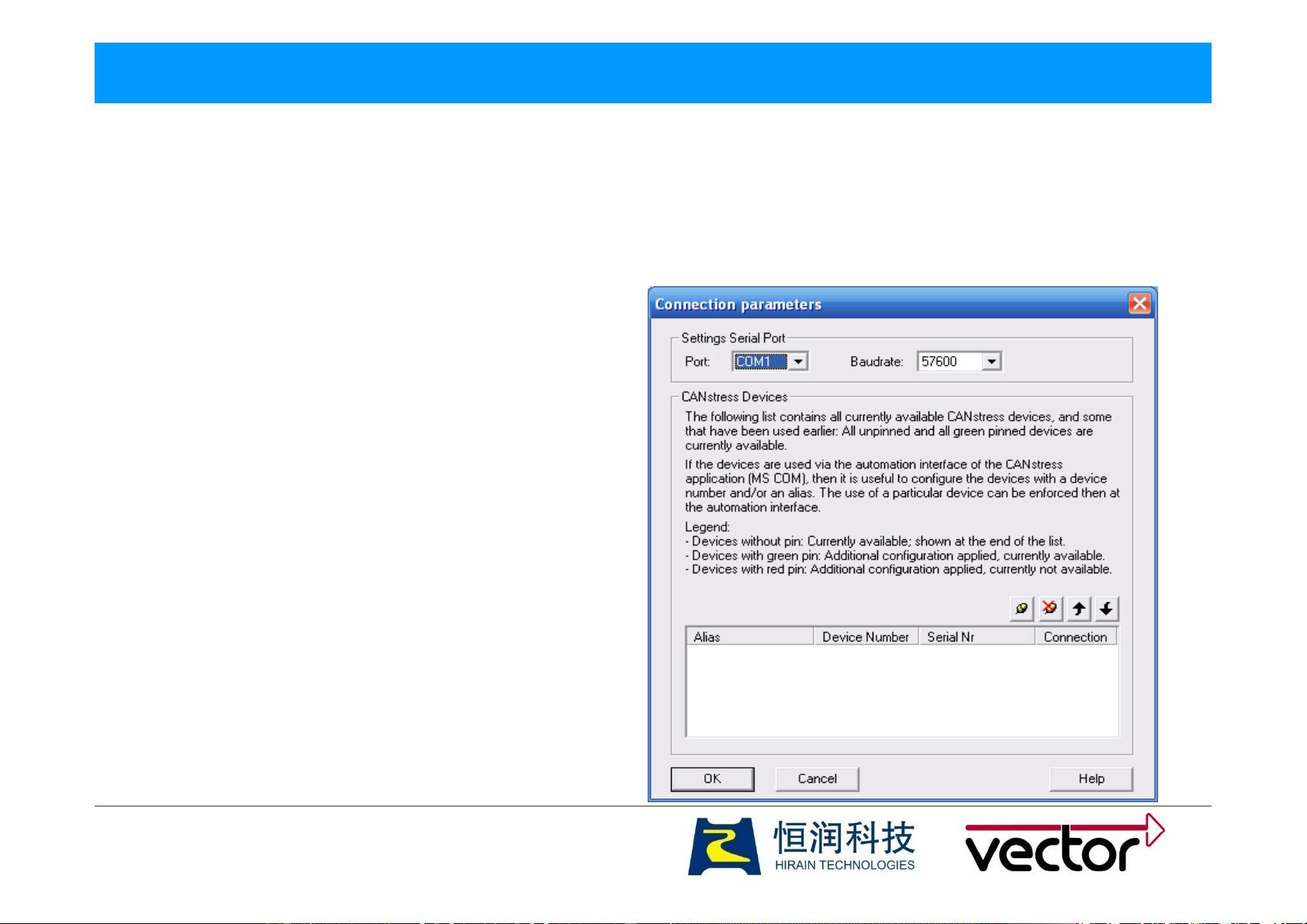
在软件设置方面,用户需要在Options菜单中进行连接设置。对于USB连接,系统自动识别,无需额外配置。如果选择串口连接,则需手动设定为COM1到COM4之间的任意一个端口。另外,还需要设置CAN接口连接,这可以通过Options菜单下的CANIn选项进行。
CANstress是一款强大的CAN总线测试工具,通过其硬件和软件的配合,用户可以有效地模拟和分析CAN总线系统在各种干扰条件下的行为,从而提高系统的可靠性和稳定性。这份快速入门培训材料为用户提供了清晰的操作指南,帮助他们快速掌握CANstress的使用方法。
2023-07-18 上传
2024-02-03 上传
2023-05-26 上传
2023-10-17 上传
2023-08-18 上传
2023-06-08 上传
Chenchen_6656
- 粉丝: 31
- 资源: 49