"甘氨酸功能化石墨烯量子点荧光传感技术构建及应用"。
版权申诉
144 浏览量
更新于2024-03-17
收藏 4.82MB PDF 举报
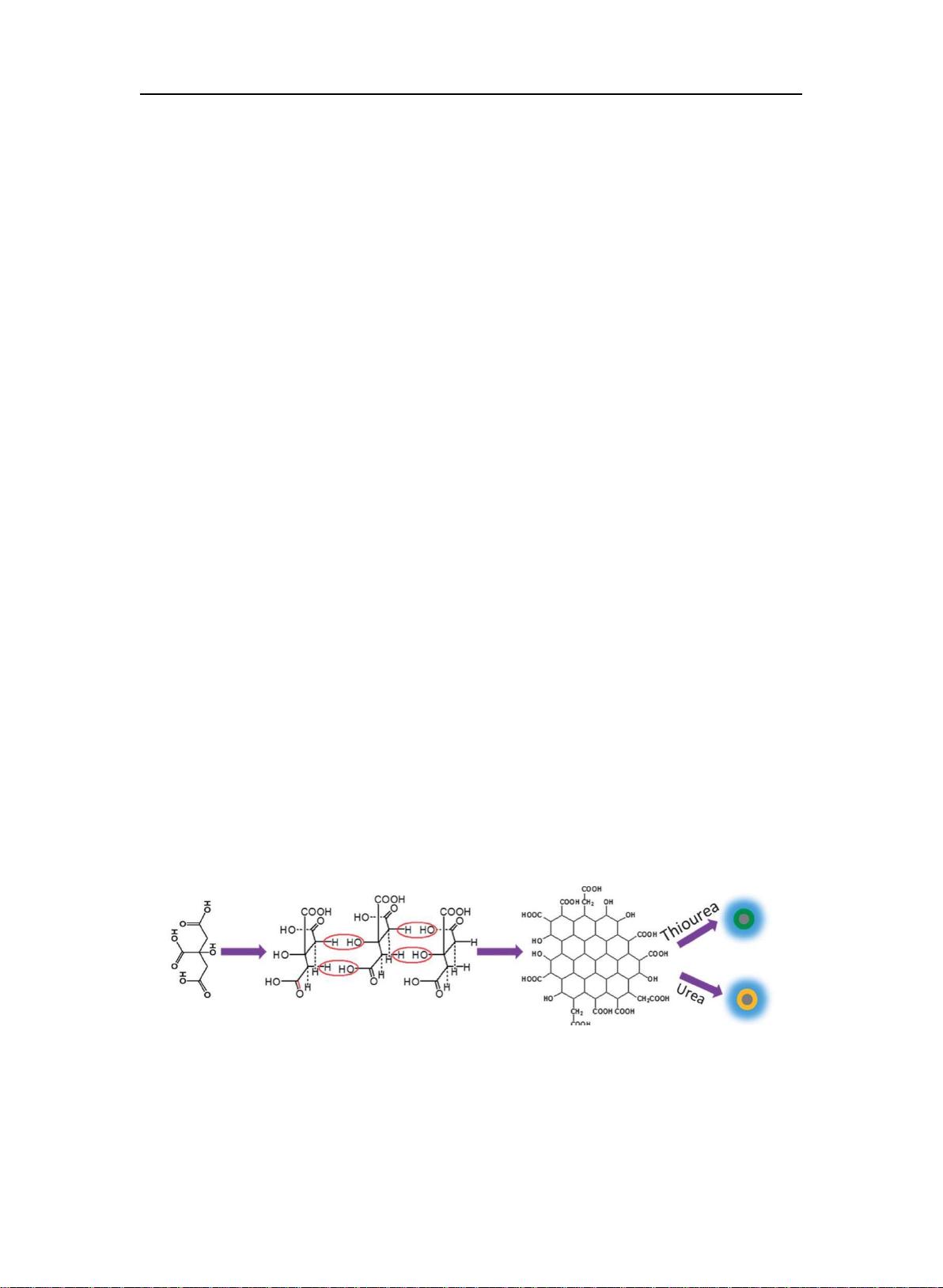
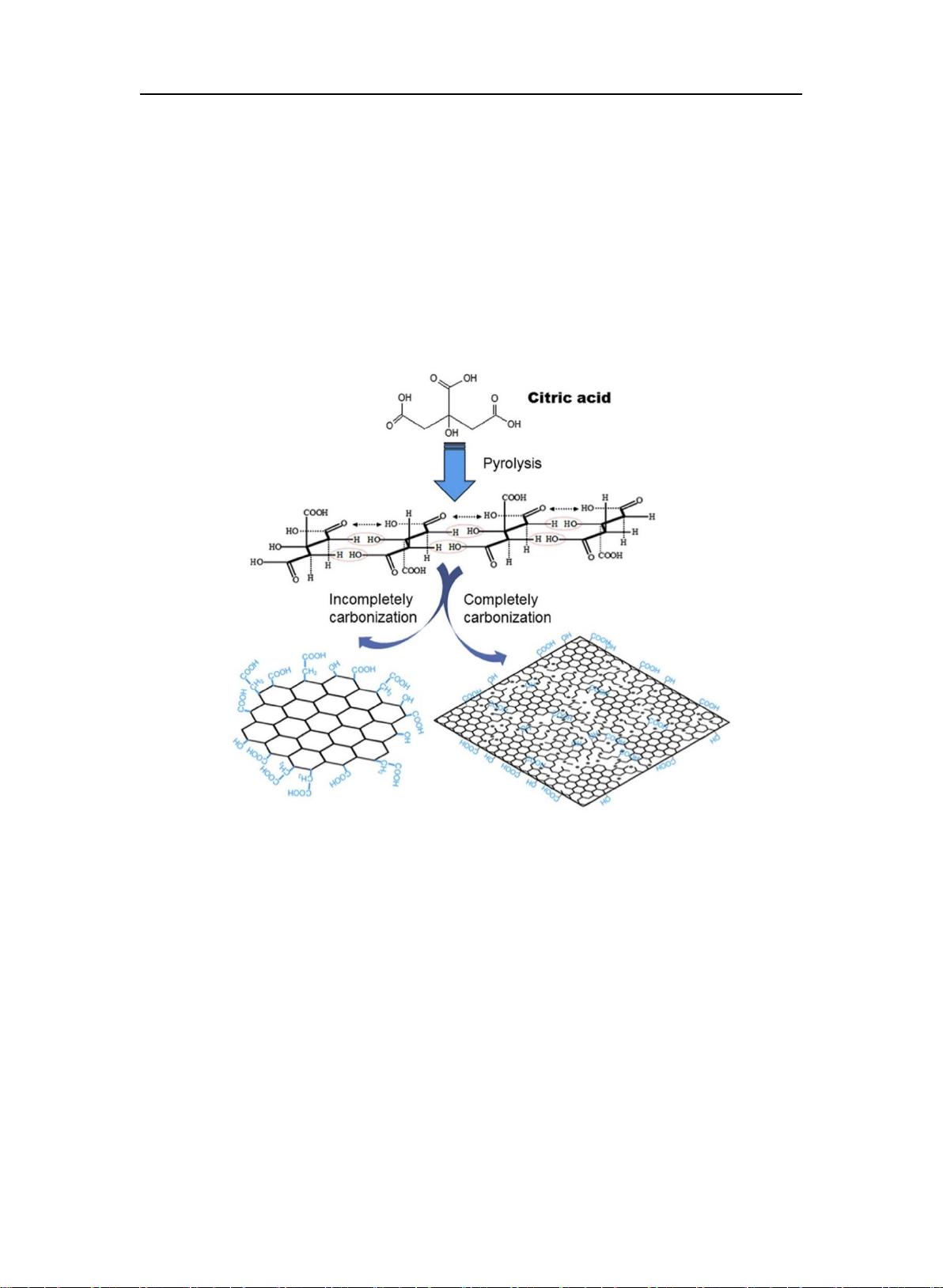
The synthesis of glycine-functionalized graphene quantum dots (GLY-GQDs) and their application in fluorescence sensing of phosphoric acid metabolites are discussed in the research paper "物联网-智慧传输-甘氨酸功能化石墨烯量子点的合成及荧光传感的构建.pdf". Using citric acid as a carbon source and glycine as a functionalizing molecule, GLY-GQDs were synthesized through a method of thermal decomposition. The quantum dots exhibited good water solubility and a high fluorescence quantum yield of 33.34%. Characterization of the synthesized GLY-GQDs was performed using techniques such as TEM, XPS, and AFM. The fluorescence of GLY-GQDs was quenched by Fe(III) due to coordination effects, while fluorescence was restored in the presence of phosphate ions which have a stronger coordination with Fe(III). Based on this principle, a fluorescence sensing system for detecting phosphoric acid metabolites was constructed. The linear range for ATP detection was found to be 0.03-2.0 μmol/L with a detection limit of 15.0 nmol/L. The method was also applied to measure phosphoric acid metabolite concentrations in biological samples such as cells and blood, with results matching previous literature reports. This study provides a simple and efficient method for highly sensitive and selective detection in clinical settings, utilizing GLY-GQDs as a promising platform for fluorescence sensing. Keywords: GLY-GQDs; citric acid; ascorbic acid; phosphoric acid metabolites.
2022-07-12 上传