"深入理解RDS技术:从基础知识到物理层解析"
需积分: 14 53 浏览量
更新于2024-04-17
收藏 362KB PPT 举报
Radio Data System (RDS) is a system that allows the transmission of data over FM radio frequencies, ranging from 87.5MHz to 108MHz. It was developed to make radio broadcasting more user-friendly and useful, and has been widely adopted in Europe since its inception. The specifications for RDS were first published in 1984, with upgrades made in 1998 to further enhance its capabilities.
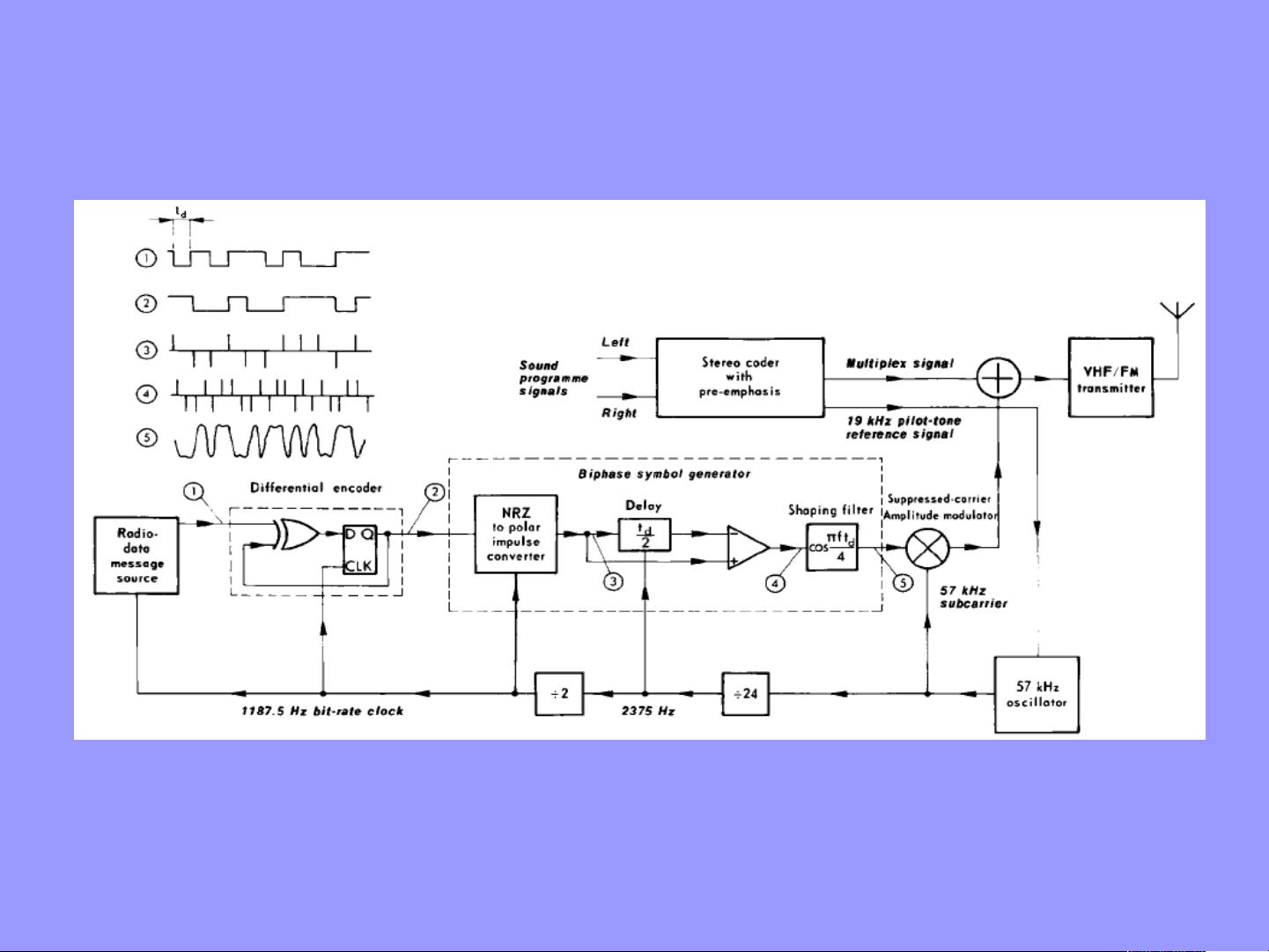
One of the key components of RDS is its physical layer, which includes the use of a subcarrier frequency that is the 3rd harmonic of the pilot tone, calculated as 19 kHz multiplied by 3 to equal 57 kHz. This subcarrier frequency can be either in-phase or in quadrature with the pilot tone's 3rd harmonic, allowing for the transmission of data alongside the audio signal.
In addition to the physical layer, RDS also includes a variety of other features that contribute to its functionality. These features include program service name (PS) which displays the station name, traffic program (TP) which alerts listeners to traffic updates, and program type (PTY) which categorizes broadcasts into different genres.
Furthermore, RDS incorporates functions such as traffic announcement (TA) which automatically switches to stations providing traffic information, alternative frequencies (AF) which allows for seamless switching between frequencies for the same station, and clock time (CT) which synchronizes the radio's clock with the broadcasted time.
Overall, RDS is a sophisticated system that enhances the radio listening experience by providing additional information and services to the listener. Its widespread adoption in Europe and continual advancements in technology highlight the importance and effectiveness of RDS in the realm of FM radio broadcasting. As technology continues to evolve, RDS will likely continue to be a crucial component in radio broadcasting, providing listeners with a more interactive and engaging experience.
2018-12-23 上传
2008-07-28 上传
2015-07-04 上传
2012-05-11 上传
2013-09-24 上传
2021-09-21 上传
weixin_38680506
- 粉丝: 4
- 资源: 927
最新资源
- PureMVC AS3在Flash中的实践与演示:HelloFlash案例分析
- 掌握Makefile多目标编译与清理操作
- STM32-407芯片定时器控制与系统时钟管理
- 用Appwrite和React开发待办事项应用教程
- 利用深度强化学习开发股票交易代理策略
- 7小时快速入门HTML/CSS及JavaScript基础教程
- CentOS 7上通过Yum安装Percona Server 8.0.21教程
- C语言编程:锻炼计划设计与实现
- Python框架基准线创建与性能测试工具
- 6小时掌握JavaScript基础:深入解析与实例教程
- 专业技能工厂,培养数据科学家的摇篮
- 如何使用pg-dump创建PostgreSQL数据库备份
- 基于信任的移动人群感知招聘机制研究
- 掌握Hadoop:Linux下分布式数据平台的应用教程
- Vue购物中心开发与部署全流程指南
- 在Ubuntu环境下使用NDK-14编译libpng-1.6.40-android静态及动态库