逆向C++:解析二进制中的类与对象
需积分: 49 7 浏览量
更新于2024-08-01
收藏 1MB PDF 举报
"这篇文档是关于逆向C++的详细指南,由Paul Vincent Sabanal和Mark Vincent Yason撰写,Hannibal509@gmail.com翻译。文档介绍了如何手动和自动化地分析C++编译后的二进制代码,以识别类、构造函数、析构函数、多态性、类关系以及成员变量。它强调了随着C++在应用程序和恶意软件开发中的广泛使用,逆向工程的重要性日益增加。"
逆向C++是逆向工程领域的一个关键技能,因为许多现代软件,尤其是恶意软件,使用C++进行编写。在反汇编过程中,理解和解析C++的面向对象特性,如类、构造函数、析构函数、运行时类型信息(RTTI)和多态性,变得至关重要。
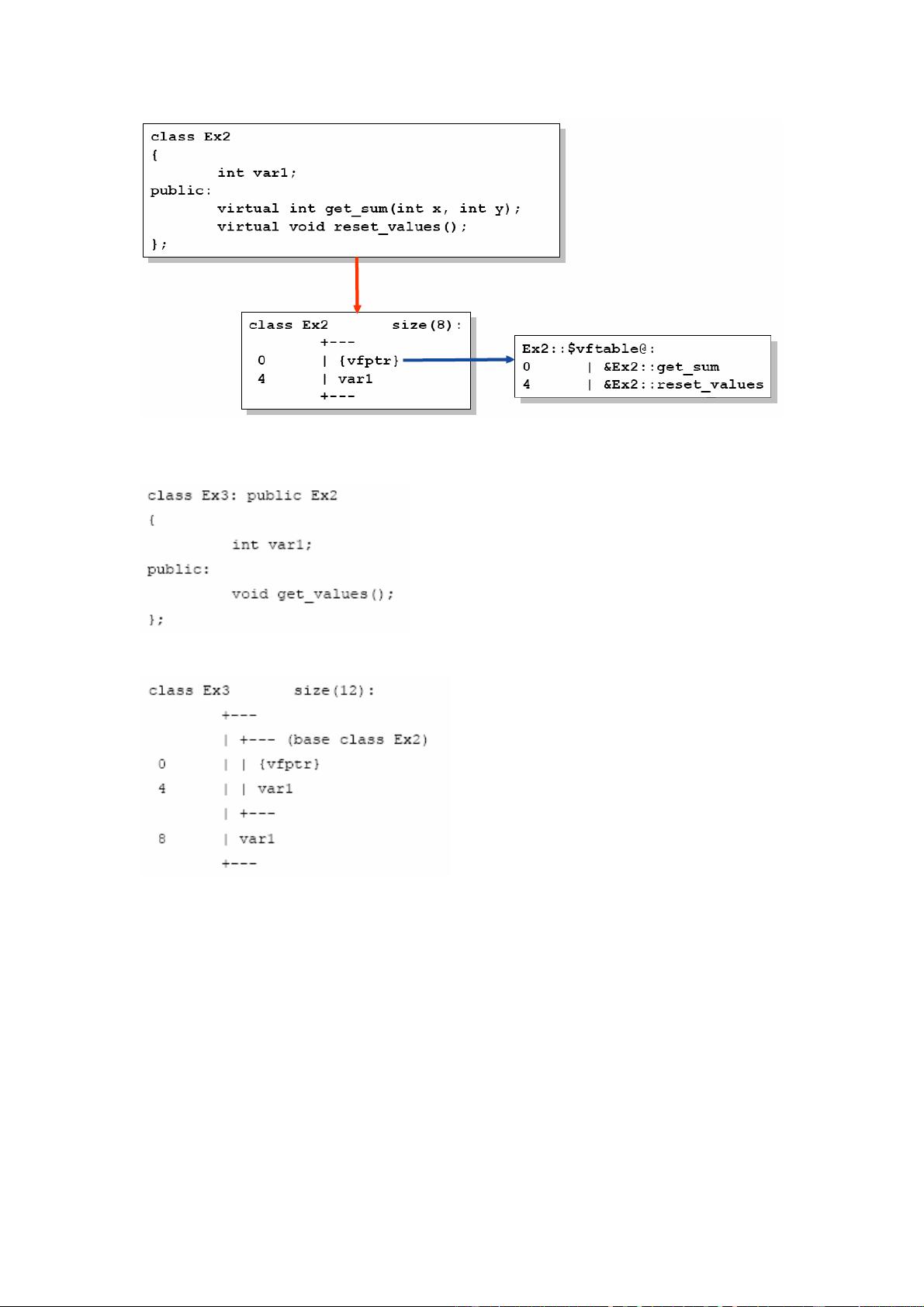
I. 引言和必要性部分指出,逆向工程师需要识别二进制文件中的C++结构,包括类、继承关系和成员,以便理解程序的工作原理。这需要识别类、类关系和成员变量的能力。
II. 手工方法详细阐述了识别C++特性的步骤。这部分包括:
- A. 识别类及其构造函数,这是理解对象创建和初始化的关键。
- B. 进一步探讨了如何识别构造函数和析构函数,以及利用RTTI识别多态类。
- C. 通过分析构造函数和RTTI来判断类与类之间的关系。
- D. 辨别类的成员,这是理解对象行为的基础。
III. 自动化部分介绍了名为OOP_RE的自动化工具,讨论了为什么选择静态分析,以及采用的不同策略和算法,如利用RTTI和虚函数表识别多态类,通过搜索构造/析构函数识别类,以及识别继承关系和成员变量。这部分还提到了结果的可视化,如生成UML图,以帮助理解程序结构。
IV. 小结部分总结了整个过程,强调了学习逆向C++的重要性和应用价值,特别是在应对越来越多的C++恶意软件分析时。
这篇文档提供了从基础到高级的逆向C++技术,旨在帮助读者提升逆向工程能力,以应对日益复杂的软件逆向挑战。通过手动分析和自动化工具的结合,逆向工程师可以更有效地理解并解构C++程序,这对于安全分析、漏洞挖掘和软件调试等领域都具有重要意义。
2012-09-03 上传
2024-10-14 上传
2023-05-26 上传
2024-10-05 上传
2023-05-05 上传
2023-04-23 上传
2023-08-04 上传
LalaIDK
- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 3
最新资源
- Aspose资源包:转PDF无水印学习工具
- Go语言控制台输入输出操作教程
- 红外遥控报警器原理及应用详解下载
- 控制卷筒纸侧面位置的先进装置技术解析
- 易语言加解密例程源码详解与实践
- SpringMVC客户管理系统:Hibernate与Bootstrap集成实践
- 深入理解JavaScript Set与WeakSet的使用
- 深入解析接收存储及发送装置的广播技术方法
- zyString模块1.0源码公开-易语言编程利器
- Android记分板UI设计:SimpleScoreboard的简洁与高效
- 量子网格列设置存储组件:开源解决方案
- 全面技术源码合集:CcVita Php Check v1.1
- 中军创易语言抢购软件:付款功能解析
- Python手动实现图像滤波教程
- MATLAB源代码实现基于DFT的量子传输分析
- 开源程序Hukoch.exe:简化食谱管理与导入功能