Day2磁盘分区详解:硬盘结构、MBR与GPT分区、分区工具fdisk使用总结
需积分: 5 104 浏览量
更新于2024-03-20
收藏 905KB DOC 举报
Day 2 focused on disk partitioning and detailed notes were documented on the process. The structure of a disk consists of tracks, sectors, heads, and cylinders. Each sector contains 512 bytes, with 63 sectors per track and 255 logical heads per cylinder. A cylinder's size is calculated as 8MB. The capacity of a hard drive or partition is determined by the size of the cylinder multiplied by the number of cylinders.
There are two main disk partitioning schemes discussed in Day 2: MBR (Master Boot Record) partition and GPT (GUID Partition Table) partition. MBR partition uses the first sector as the MBR sector, which stores the boot program and partition table. It allows for 4 primary partitions (3 primary and 1 extended), with a maximum disk capacity of 2.2TB. On the other hand, GPT partition supports a maximum of 18EB disk capacity, making it more suitable for larger storage requirements.
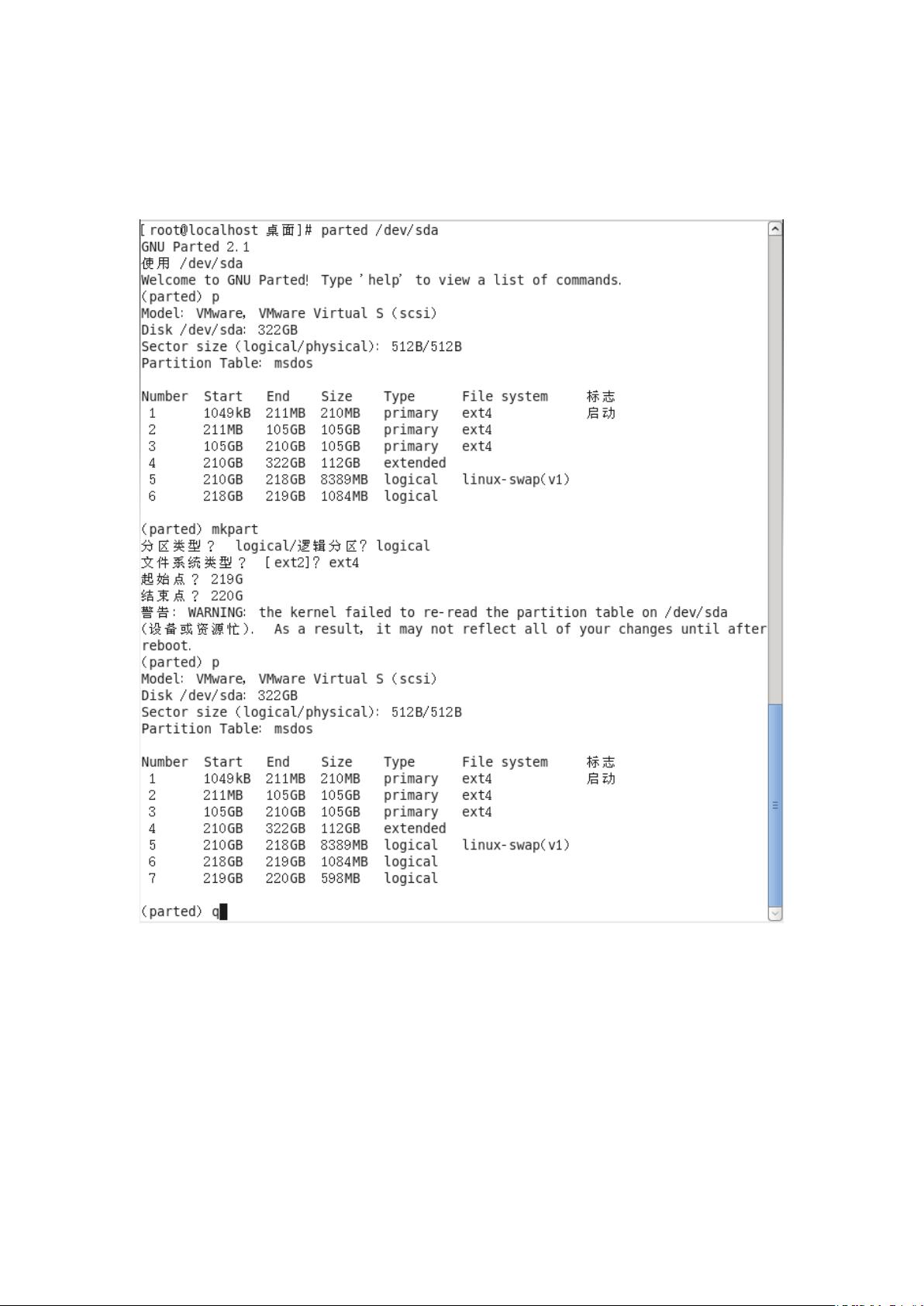
The partitioning tools covered in the session included fdisk, which supports only MSDOS partition layout and interactive partitioning. It is important to understand the differences between MBR and GPT partitions, as well as the limitations and capabilities of each partitioning scheme.
Overall, Day 2 provided a comprehensive overview of disk partitioning concepts and practices. Participants learned about the different components of a disk, the structure of sectors and cylinders, and the partitioning schemes available for organizing disk storage. By using partitioning tools like fdisk, users can effectively manage their disk partitions based on their needs and system requirements.
2023-07-17 上传
2023-07-17 上传
点击了解资源详情
点击了解资源详情
2023-06-30 上传
2023-07-17 上传
运维实战课程
- 粉丝: 1581
- 资源: 410
最新资源
- 温特线性matlab代码-matlab_NS_solvers:旧的研究代码。主要是涡量公式中的2DNS求解器
- 行业文档-设计装置-一种切纸机的双位刀头.zip
- Lora-32-Connect-by-Wifi
- 视图:场景模块的界面,为发送到渲染器的显示对象提供用户交互输入输出和剔除管理
- omniauth-rails_csrf_protection:在Rails应用程序的OmniAuth请求端点上提供CSRF保护
- ryanatkn
- 基于神经网络的人脸识别.zip
- derrobott.github.io:没事了
- matlab导弹落点代码-missile_simulation_matlab:导弹仿真Matlab代码
- iains:TestAccount
- xlog:xlog是netcontext感知HTTP应用程序的记录器
- 自动驾驶汽车案例研究
- 「基于图像识别的收银台」客户端软件,基于OpenCV + Qt,需要搭配「基于图像识别的收银台」后端服务使用。.zip
- darwish-rainmeter
- CSCI3800_Sp15_Team8:CSCI3800 Spring 2015 Team 8项目
- blog