40 ArcUser October–December 2002 www.esri.com
By Jennifer Cadkin, ESRI Technical Industry Marketing Specialist
Understanding Dynamic Segmentation
Working With Events in ArcGIS 8.2
Dynamic segmentation is the process of trans-
forming linearly referenced data (also known
as events) that have been stored in a table into
features that can be displayed and analyzed on
a map. For example, a utility company may
segment transmission pipes dynamically ac-
cording to the quality of the pipe. Attribute
information describing quality characteristics
specic to each pipeline segment can then
be maintained without splitting the pipeline
network. The dynamic segmentation process
imposes two requirements on the data. Each
event in an event table must include a unique
identier and position along a linear feature.
Each linear feature must have a unique identi-
er and measurement system.
What Is an Event?
There are two types of route locations—point
and linear events—that can be modeled in
ArcGIS 8.2. Point route locations describe
discrete locations on a linear feature (such
as the location of a pipeline leak) and require
only one measure value. Linear route locations
describe portions of a linear feature (such as
pipeline cracking) and require two measure
values, typically referred to as the From and
To measures. Route locations and associated
attributes stored in a thematic table are known
as route events or simply events. A route loca-
tion description requires a unique identier for
the linear feature and the measure value(s) ap-
propriate to the event type. ArcMap uses this
information to spatially render the event.
Dynamic segmentation in ArcGIS supports
event tables in a number of formats including
INFO, Microsoft Access, dBASE, Oracle, Mi-
crosoft SQL Server, delimited text les, and
databases accessed via OLE DB providers.
Some database formats provide advantages
over others. By migrating tables to a geoda-
tabase table, a user can leverage geodatabase
functionality such as domains, eld name
aliases, and relationship classes. For more
information on migrating tables to a geoda-
tabase and geodatabase functionality refer to
Building a Geodatabase, one of the manuals
that comes with ArcGIS.
Adding Route Events
Events are transformed into features that can
be displayed and analyzed on a map using a
process called dynamic segmentation. The
Add Route Events dialog box is used to trans-
form an event table in ArcMap. There are two
ways to access this dialog box. After adding
the event table to the map document and click-
ing on the source tab in the Table of Contents,
right-click on the event table and choose
Create Route Events from the context menu.
Alternatively, choose Tools > Add Route
Events from the main menu and specify the
input table (which does not need to be within
the map document).
Once the event table has been specied,
the type of event, the appropriate measure
elds, the route identier eld, and the route
feature class will also need to be specied.
Any polylines with M feature classes present
in the map document will appear in the route
layer dropdown. Choose the desired route
layer and specify the route identier eld. The
referenced route layer does not have to be in
the map document.
When spatial data is added to an ArcMap
Transmission Pipe 10 = A1
Event ID
Pipe ID
From_M
To_M
Rating
0
1
3
75
3
75
10
fair
good
poor
M=0
M=5
M=10
fair
good
poor
2
3 A
1
A1
A1
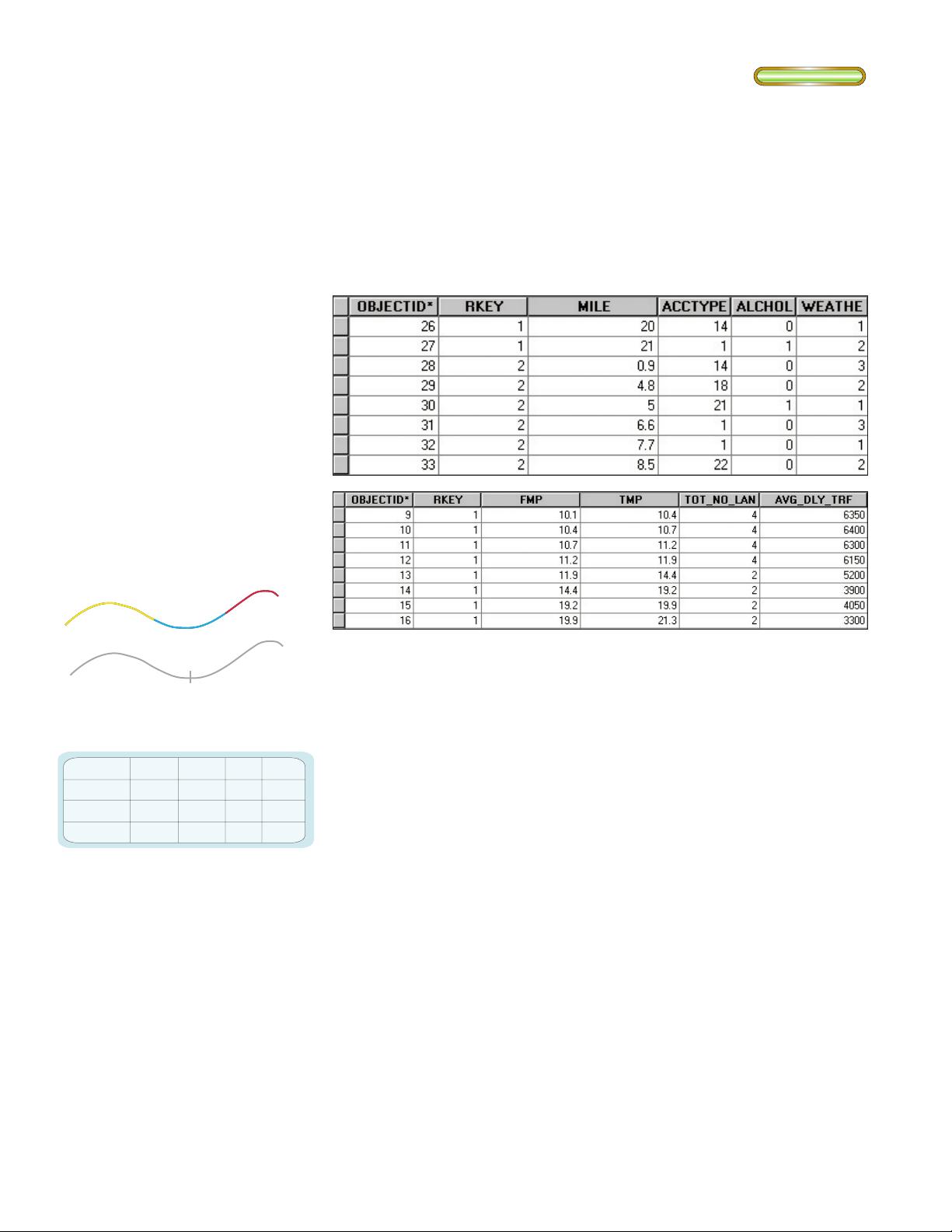
Event tables are thematic collections of events. The upper table describes point events. The
lower table shows linear events.
The dynamic segmentation process for a
pipeline
With the release of ArcGIS 8.1, ArcView,
ArcEditor, and ArcInfo users have a common
environment for the dynamic segmentation
process. This is the second in a two-part ar-
ticle series covering dynamic segmentation
concepts. The rst installment, “Dynamic
Segmentation in ArcGIS,” appeared in the
July–September issue of ArcUser magazine. It
discussed the linear features used to perform
dynamic segmentation including dening
a route, migrating route data between data
formats, and working with routes in ArcMap.
This article discusses event data, including
how to perform the dynamic segmentation
process and work with events as features in
ArcMap.
New/Casual Advanced
User Level


















