1784 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON IMAGE PROCESSING, VOL. 21, NO. 4, A PRIL 201 2
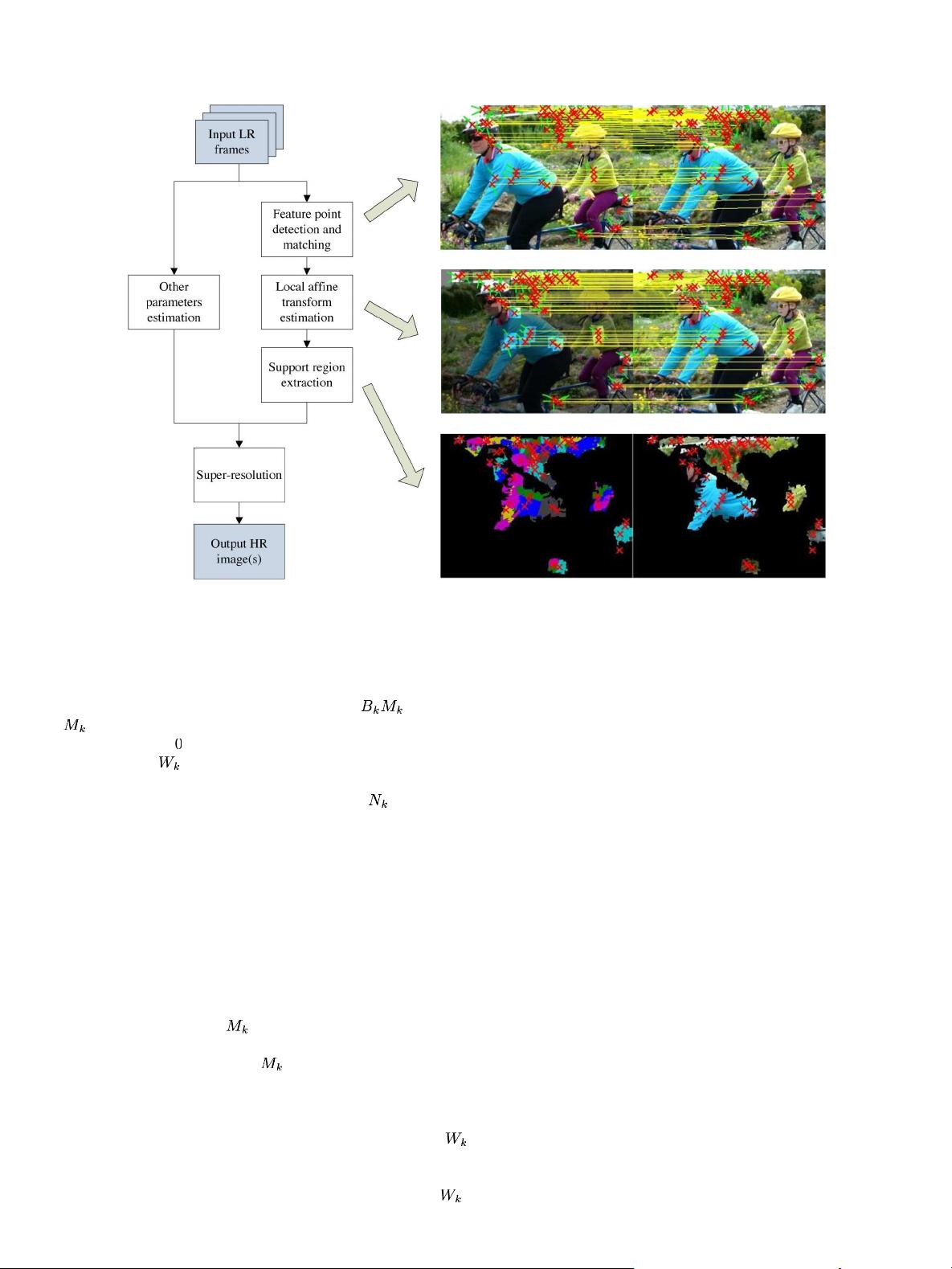
Fig. 2. Super-resolution without dense flow. Images in the first r ow: SIF T featu re poin t ma tch ing resu lt. Second row : local affine transformatio n estimatio n result.
The l ighter p arts of the left image indicate th e loca l transformed patches. Third row: support region s eg mentation result and compen sated image re sult. The black
regions indicate motion outlier. The red crosses represent the locations of feature points, the short green lines are the orientations of the SIFT feature points, and
the long yellow lines show feature point correspondences.
In other words, the rows in product matrix in (6) [or
in ( 7) ] correspo ndi ng to mot ion o utl ier regio ns are elim i-
nated and set as
sintheconfiden ce map method. The diag-
onal entries of
, which is also known as the confidence map,
is usually generated by thresholding the m otion compensation
error. However, because of the imaging noise
and the ab-
sence of HR original images, the confidence map itself is not
accurate, which affects the result quality, particularly within the
motion boundary regions. On the contrary, the proposed algo-
rithm is based o n the sparse significant feature point correspon-
dences, which are both accurate and robust. The details of the
proposed algorithm are shown in t he succeeding sections.
III. A
LGORITH
M
OVERVIEW
Essentially, the goal of m ot ion estimation in super-resolution
is to determ ine matr ices
in (1). As previously men tio ned,
motion estimation is signi fi cant to the performance of super-
resolution because inaccurate
matrices affects the result’s
quality greatly. However, it is very difficult to find an accurate
dense flow field for real-world videos with complicated motion
fields. On the other hand, optical flow estimation does not have
to be dense over the im age in su per-reso lution , as matrix
basedontheconfidence map can be incorporated to eliminate
the region without optical flow in the utility function [see (6)].
Thus,weproposetofind a more rob ust confidence map (
)
rather than an accurate dense flow field ov e r the whole image,
and within the confidence map, a reliable local optical flow field
is guaranteed.
The flowchart of the proposed algorithm is shown in Fig. 2.
First, feature points are detected in the input images, and then,
correspondences of the points b etween input frames are deter-
mined. Note that the correspondences are only a sparse flow
field between images, w hich is different from dense flow es-
timation required by conventional super-resolution algorithms
in Fig. 1. Motion vectors with subpixel accuracy at the feature
points can be ob tained by sim ply adopting state-of-the-art image
feature detection and matching approaches, such as the SIFT
method [27]. Even when large-scale local motion and image
noise are presented, the correspondences are still reli able, be-
cause motion estimation on a sparse set of well-selected feature
points is m uch more robust.
Second, we estimate a local affine transforma tion within an
adaptive-sized neighborhood of each pair of corresponding fea-
ture points. Th e n, the proposed algorithm expands a support
region from the corresponding feature pair, within which the
affine transformation provides accurate motion est im ation. All
the su pport regions within the input image are com bined, and
the local fl ow is generated. Finally, super-resolution alg orith ms
are applied based on the local flow fields.
One of the advantag es of the proposed algorithm is that only
local regions with accurate enough flow contribute in super-res-
olution reconstruction. The area without accurate motion field
is never processed and will not affect the result quality. More-
over, the local regions are based on very reliable feature point









