CIA-SSD: Confident IoU-Aware Single-Stage Object Detector From Point Cloud
Wu Zheng, Weiliang Tang, Sijin Chen, Li Jiang, Chi-Wing Fu
The Chinese University of Hong Kong, China
{wuzheng, lijiang, cwfu}@cse.cuhk.edu.hk, {tangwl123, chensjvin}@foxmail.com
Abstract
Existing single-stage detectors for locating objects in point
clouds often treat object localization and category classifica-
tion as separate tasks, so the localization accuracy and clas-
sification confidence may not well align. To address this is-
sue, we present a new single-stage detector named the Con-
fident IoU-Aware Single-Stage object Detector (CIA-SSD).
First, we design the lightweight Spatial-Semantic Feature Ag-
gregation module to adaptively fuse high-level abstract se-
mantic features and low-level spatial features for accurate
predictions of bounding boxes and classification confidence.
Also, the predicted confidence is further rectified with our
designed IoU-aware confidence rectification module to make
the confidence more consistent with the localization accu-
racy. Based on the rectified confidence, we further formulate
the Distance-variant IoU-weighted NMS to obtain smoother
regressions and avoid redundant predictions. We experiment
CIA-SSD on 3D car detection in the KITTI test set and show
that it attains top performance in terms of the official ranking
metric (moderate AP 80.28%) and above 32 FPS inference
speed, outperforming all prior single-stage detectors. The
code is available at https://github.com/Vegeta2020/CIA-SSD.
1 Introduction
To detect objects in autonomous driving, point clouds are
often adopted to offer robust information. In general, there
are two classes of methods to detect objects in point clouds:
single-stage and two-stage. Though two-stage detectors usu-
ally attain higher average precisions benefited from an extra
refinement stage, single-stage detectors are typically more
efficient due to their simpler network structures. Also, the
detection precisions of recent single-stage detectors (He
et al. 2020; Yang et al. 2020; Shi and Rajkumar 2020) gradu-
ally approach that of the state-of-the-art two-stage detectors.
The advantages of time efficiency and competitive precision
motivate us to focus this work on single-stage detectors.
Existing 3D object detectors often treat object localization
and category classification as separate tasks, so the local-
ization accuracy and classification confidence may not align
well (Jiang et al. 2018). Hence, two-stage detectors (Yang
et al. 2019; Shi et al. 2020a) extract features from the region
Copyright © 2021, Association for the Advancement of Artificial
Intelligence (www.aaai.org). All rights reserved.
1
[CVPR 2020]
[CVPR 2020]
[CVPR 2020]
[AAAI 2020]
[CVPR 2019]
[Sensor 2018]
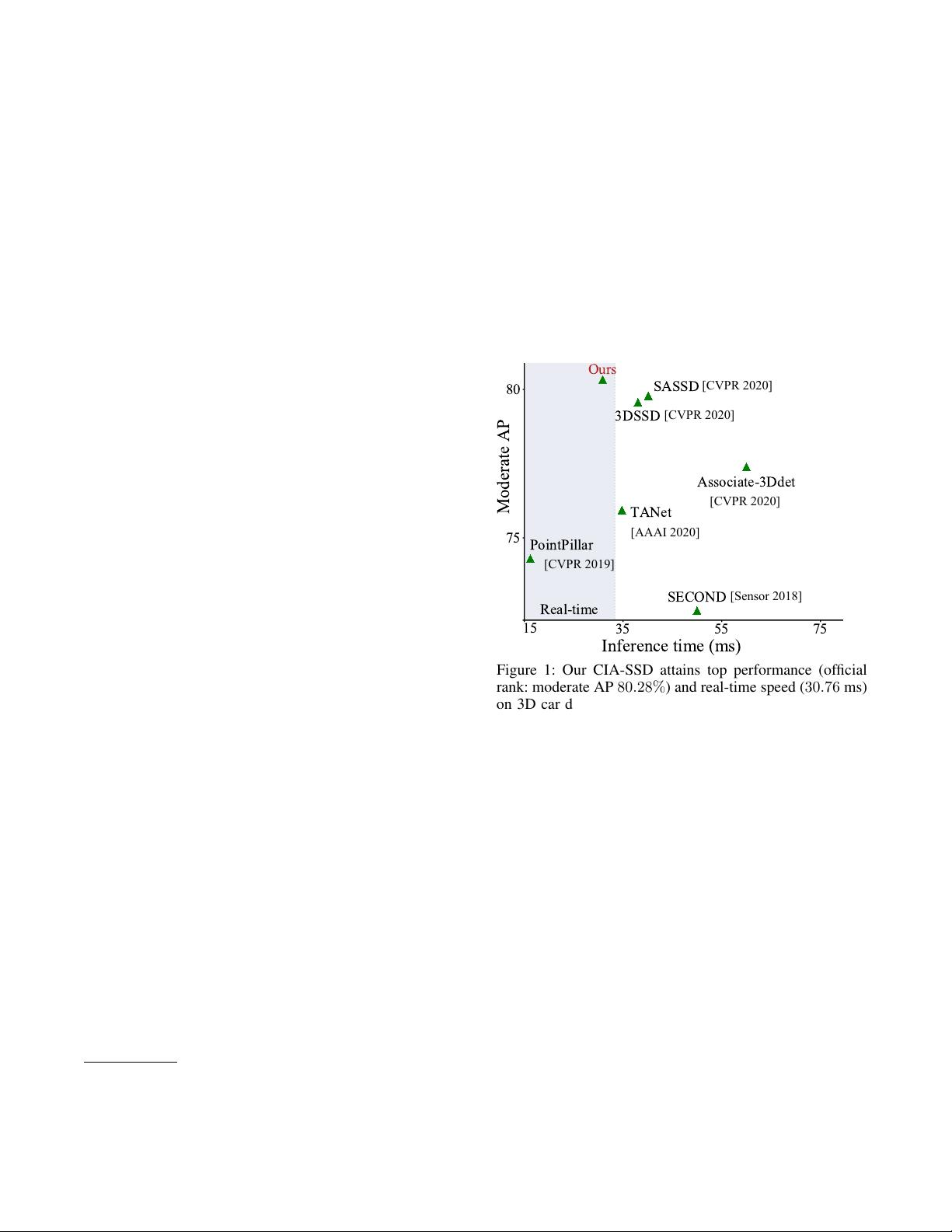
Figure 1: Our CIA-SSD attains top performance (official
rank: moderate AP 80.28%) and real-time speed (30.76 ms)
on 3D car detection in KITTI test set (Geiger et al. 2013),
compared with the state-of-the-art single-stage detectors.
proposals generated by the first-stage backbone and predict
the IoUs between the regressed bounding boxes and ground-
truth boxes in the second stage to refine the confidence pre-
dictions. Compared with hard-category labels, the soft IoU
labels are usually more consistent with the localization qual-
ities, thus leading to more accurate confidence predictions.
Compared with two-stage detectors, single-stage detec-
tors cannot train features extracted from their predicted
bounding boxes with a second-stage network. Also, their
features are learned mostly based on the pre-defined anchors
or classified positive points, so the resulting IoU predictions
may not be as accurate as those in the two-stage networks.
Hence, general single-stage detectors cannot effectively rec-
tify confidence predictions like the two-stage ones.
To resolve this issue, SASSD (He et al. 2020), a very re-
cent single-stage detector, exploits an interpolation approach
to obtain the region proposal features for confidence rectifi-
cation. Their approach is, however, very complex with the
interpolation operation. In this work, we design a new confi-
dence rectification module embedded in our Confident IoU-
arXiv:2012.03015v1 [cs.CV] 5 Dec 2020









