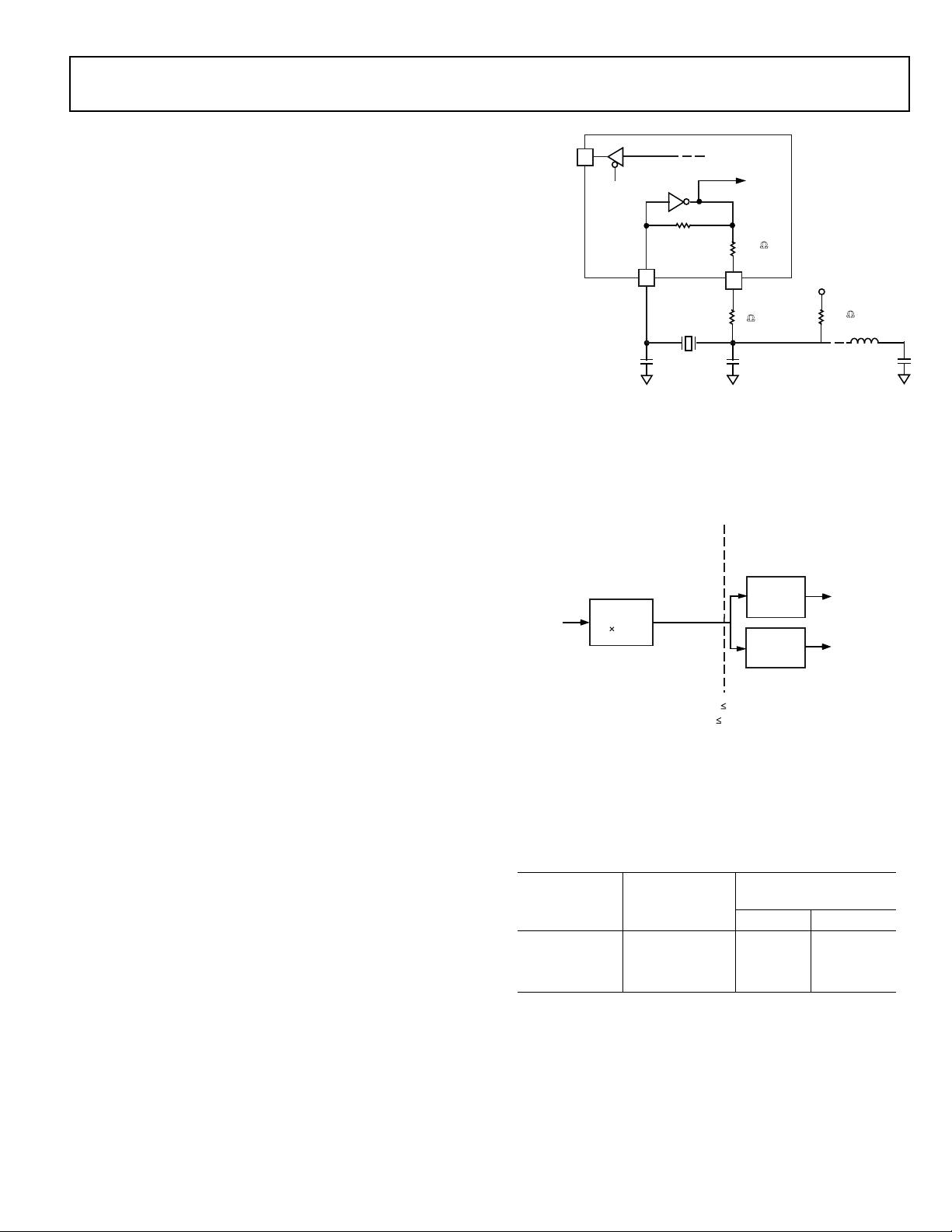
ADSP-BF561
Frame Capture Mode
Frame capture mode allows the video source(s) to act as a slave
(e.g., for frame capture). The ADSP-BF561 processors control
when to read from the video source(s). PPI_FS1 is an HSYNC
output and PPI_FS2 is a VSYNC output.
Output Mode
Output mode is used for transmitting video or other data with
up to three output frame syncs. Typically, a single frame sync is
appropriate for data converter applications, whereas two or
three frame syncs could be used for sending video with hard-
ware signaling.
ITU-R 656 Mode Descriptions
The ITU-R 656 modes of the PPI are intended to suit a wide
variety of video capture, processing, and transmission applica-
tions. Three distinct submodes are supported:
• Active video only mode
• Vertical blanking only mode
• Entire field mode
Active Video Only Mode
Active video only mode is used when only the active video por-
tion of a field is of interest and not any of the blanking intervals.
The PPI does not read in any data between the end of active
video (EAV) and start of active video (SAV) preamble symbols,
or any data present during the vertical blanking intervals. In this
mode, the control byte sequences are not stored to memory;
they are filtered by the PPI. After synchronizing to the start of
Field 1, the PPI ignores incoming samples until it sees an SAV
code. The user specifies the number of active video lines per
frame (in the PPI_COUNT register).
Vertical Blanking Interval Mode
In this mode, the PPI only transfers vertical blanking interval
(VBI) data.
Entire Field Mode
In this mode, the entire incoming bit stream is read in through
the PPI. This includes active video, control preamble sequences,
and ancillary data that may be embedded in horizontal and ver-
tical blanking intervals. Data transfer starts immediately after
synchronization to Field 1.
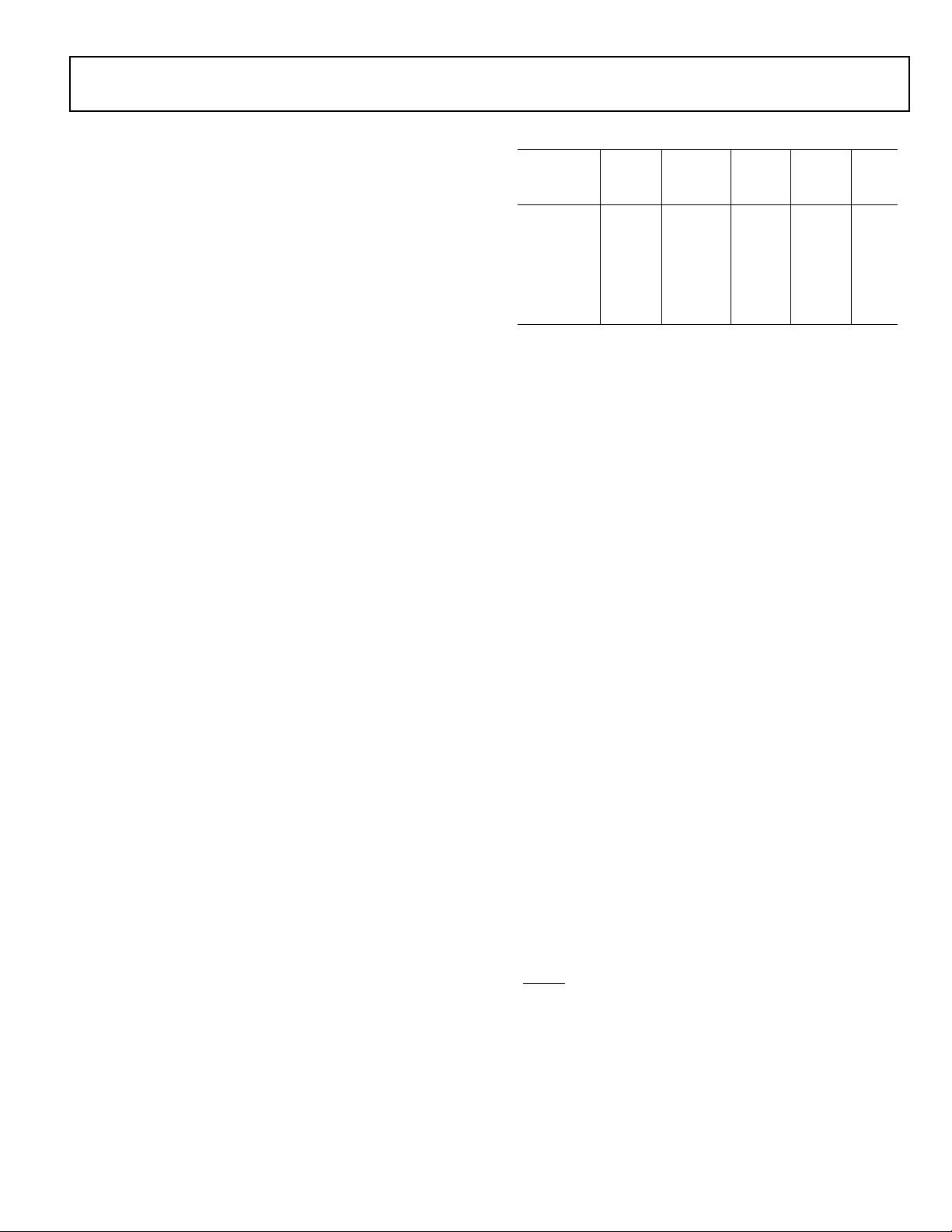
DYNAMIC POWER MANAGEMENT
The ADSP-BF561 provides four power management modes and
one power management state, each with a different perfor-
mance/power profile. In addition, dynamic power management
provides the control functions to dynamically alter the proces-
sor core supply voltage, further reducing power dissipation.
Control of clocking to each of the ADSP-BF561 peripherals also
reduces power consumption. See Table 3 for a summary of the
power settings for each mode.
Table 3. Power Settings
Mode/State PLL
PLL
Bypassed
Core
Clock
(CCLK)
System
Clock
(SCLK)
Core
Power
Full-On
Active
Sleep
Deep Sleep
Hibernate
Enabled
Enabled/
Disabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
No
Yes
–
–
–
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
Disabled
On
On
On
On
Off
Full-On Operating Mode—Maximum Performance
In the full-on mode, the PLL is enabled and is not bypassed,
providing capability for maximum operational frequency. This
is the default execution state in which maximum performance
can be achieved. The processor cores and all enabled peripherals
run at full speed.
Active Operating Mode—Moderate Power Savings
In the active mode, the PLL is enabled but bypassed. Because the
PLL is bypassed, the processor’s core clock (CCLK) and system
clock (SCLK) run at the input clock (CLKIN) frequency. In this
mode, the CLKIN to CCLK multiplier ratio can be changed,
although the changes are not realized until the full-on mode is
entered. DMA access is available to appropriately configured L1
and L2 memories.
In the active mode, it is possible to disable the PLL through the
PLL control register (PLL_CTL). If disabled, the PLL must be
re-enabled before transitioning to the full-on or sleep modes.
Sleep Operating Mode—High Dynamic Power Savings
The sleep mode reduces power dissipation by disabling the
clock to the processor core (CCLK). The PLL and system clock
(SCLK), however, continue to operate in this mode. Typically an
external event will wake up the processor. When in the sleep
mode, assertion of wakeup will cause the processor to sense the
value of the BYPASS bit in the PLL control register (PLL_CTL).
When in the sleep mode, system DMA access is only available to
external memory, not to L1 or on-chip L2 memory.
Deep Sleep Operating Mode—Maximum Dynamic Power
Savings
The deep sleep mode maximizes power savings by disabling the
clocks to the processor cores (CCLK) and to all synchronous
peripherals (SCLK). Asynchronous peripherals will not be able
to access internal resources or external memory. This powered-
down mode can only be exited by assertion of the reset pin
(RESET). If BYPASS is disabled, the processor will transition to
the full-on mode. If BYPASS is enabled, the processor will tran-
sition to the active mode.
Hibernate State—Maximum Static Power Savings
The hibernate state maximizes static power savings by disabling
the voltage and clocks to the processor core (CCLK) and to all
the synchronous peripherals (SCLK). The internal voltage
Rev. E | Page 11 of 64 | September 2009