COL 12(5), 050601(2014) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS May 10, 2014
Suspended twin-core fiber for optical switching
Xiaogang Jiang (
ñññ
fff
)
1,2
, Daru Chen (
XXX
)
1,2∗
, Gaofeng Feng (
¾¾¾
ppp
¸¸¸
)
3
,
and Junyong Yang (
℄℄℄
)
3
1
Institute of Information Optics, Zhejiang Normal University, Jinhua 321004, China
2
Joint Research Laboratory of Optics of Zhejiang Normal University and
Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310058, China
3
Futong Group Co., Ltd, Fuyang 311004, China
∗
Corresponding author: daru@zjnu.cn
Received November 15, 2013; accepted March 27, 2014; posted online April 30, 2014
A kind of novel fiber, comprising two fiber cores which are suspended in air inside the outer cladding via a
central thin membrane, is proposed for optical switching application. When a hydrostatic pressure applied
on t he optical fib er, the pressure-induced refractive index change of the two fiber cores will contribute to
the periodical change of the intensity of guided light in the fiber core. The mode coupling of two cores
under different hydrostatic pressure and influences of each structure parameter of the proposed fiber on
the switching pressure have been numerically investigated.
OCIS codes: 060.2310, 060.4005, 130.4815.
doi: 10.3788/COL201412.050601.
Since the invention of the first low-loss single mode
fib e r in 1970, incredible pro gress in optical fiber fabri-
cation techniques and processes has been seen in the last
decades, espe c ially after the emergence of the microstruc-
tured optical fiber. A lot of theoretical and experimen-
tal research works which aimed at meeting the need of
particular function (e.g. as high birefringence
[1−3]
, flat-
tened dispersion
[4]
, large negative dispersion
[5−7]
, high
nonlinearity
[8]
, endless single mode
[9]
and so on) have
been carried out, resulting in the realization of an in-
creasing number of novel fiber s. Recently, a nanome-
chanical twin-nanoweb fiber in which each fiber core is
held suspended in air from the outer glass cladding by two
glass membranes has been fabr icated
[10]
. Based on such
a twin-nanoweb fiber, different from the early reported
dual-core photonic crystal fiber fo r hydrostatic pressure
sensing
[11]
, another important application, the optical
switching
[12]
can be achieved. As an important support-
ing technology o f optical communication systems, optical
switching is taken account for the key-enabling function
for the deployment of the developing all-optical networks.
The incorporation of switching function into the optical
fib e r offer great promise fo r all-optical communication.
However, in order to achieve the optical switching func-
tion, the twin-nanoweb fiber mentioned above has to be
processed with chemical etching, which makes the fiber
not convenient to use.
In this letter, we proposed a kind of suspended twin-
core fib e r (STCF) based on a single nanoweb structure
for optical switching. T he fiber has two cores which lo-
cate sy mmetrically in the center of the nanoweb, resulting
to the mode coupling for the guiding light in the STCF.
When a hydrostatic pressure applied on the optical fiber,
the pressure-induced refractive index change will con-
tribute to the intensity of c ore-guided mode change pe-
riodically with pre ssure. Compared to the twin-nanoweb
fib e r, the fiber we proposed only incorporates a single
membrane which makes it ea sier to be fabricated. Be-
sides, the STCF can be directly used fo r switching ap-
plication without post proc e ssing. The influences of each
structure parameter on the switching pressure are pre-
sented.
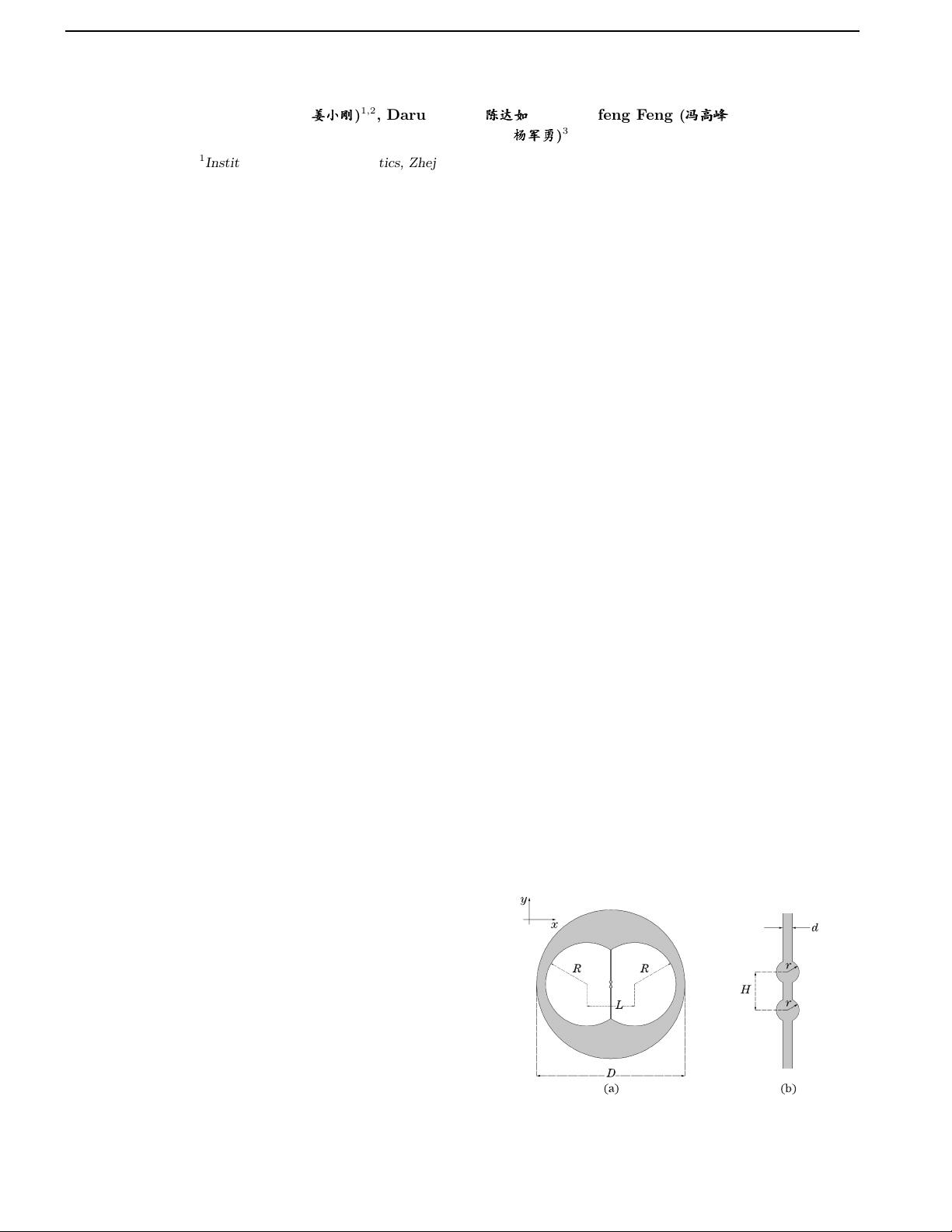
Figure 1 shows the cross- section of the proposed fiber.
The external diameter of the fiber is D, which is kept
being a constant of 125 µm in this letter. A pair of
large air holes with a radius R is employed in the cross-
section. The distance betwe en the center of two air holes
is L, which is smaller than 2R. A thin membrane (so-
called single nanoweb) with thickness d locates in the
intersection area of the two air holes. Two fiber c ores
with diameter of r loca te symmetrically in the center of
the nanoweb. The distance of the two cores is H. A
full-vector finite-element method (FEM) is used to inves-
tigate the mechanical properties and guided modes of the
proposed STCF.
When a hydrostatic pressure is applied on the optical
fib e r, the pressure-induced refractive index change and
the pr e ssure-induced structure deformation will affect
the light guiding in the optical fiber
[13,14]
.
n
x
= n
0
− C
1
σ
x
− C
2
(σ
y
+ σ
z
) , (1)
n
y
= n
0
− C
1
σ
y
− C
2
(σ
x
+ σ
z
) , (2)
n
z
= n
0
− C
1
σ
z
− C
2
(σ
x
+ σ
y
) . (3)
Fig. 1. (a) Cross-section of the proposed STCF. (b) Enlarged
view of the twin-core region of the proposed STCF.
1671-7694/2014/050601(4) 050601-1
c
2014 Chinese Optics Letters









