优化气道喷射方式的液压自由活塞发动机燃油效率研究
版权申诉
82 浏览量
更新于2024-02-25
收藏 6.54MB DOCX 举报
The study "Analysis and Optimization of Injection Methods for Two-Stroke Hydraulic Free Piston Engine with Airway Injection" aims to reduce fuel consumption when using airway injection in a two-stroke hydraulic free piston engine (HFPE). By placing the injector at the airway intake, a three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics simulation model was established using CONVERGE software to analyze the fuel injection process and the generation of the fuel-air mixture. The study focused on the effects of fuel injection phase, injection angle, and injector flow rate on the mixture formation process.
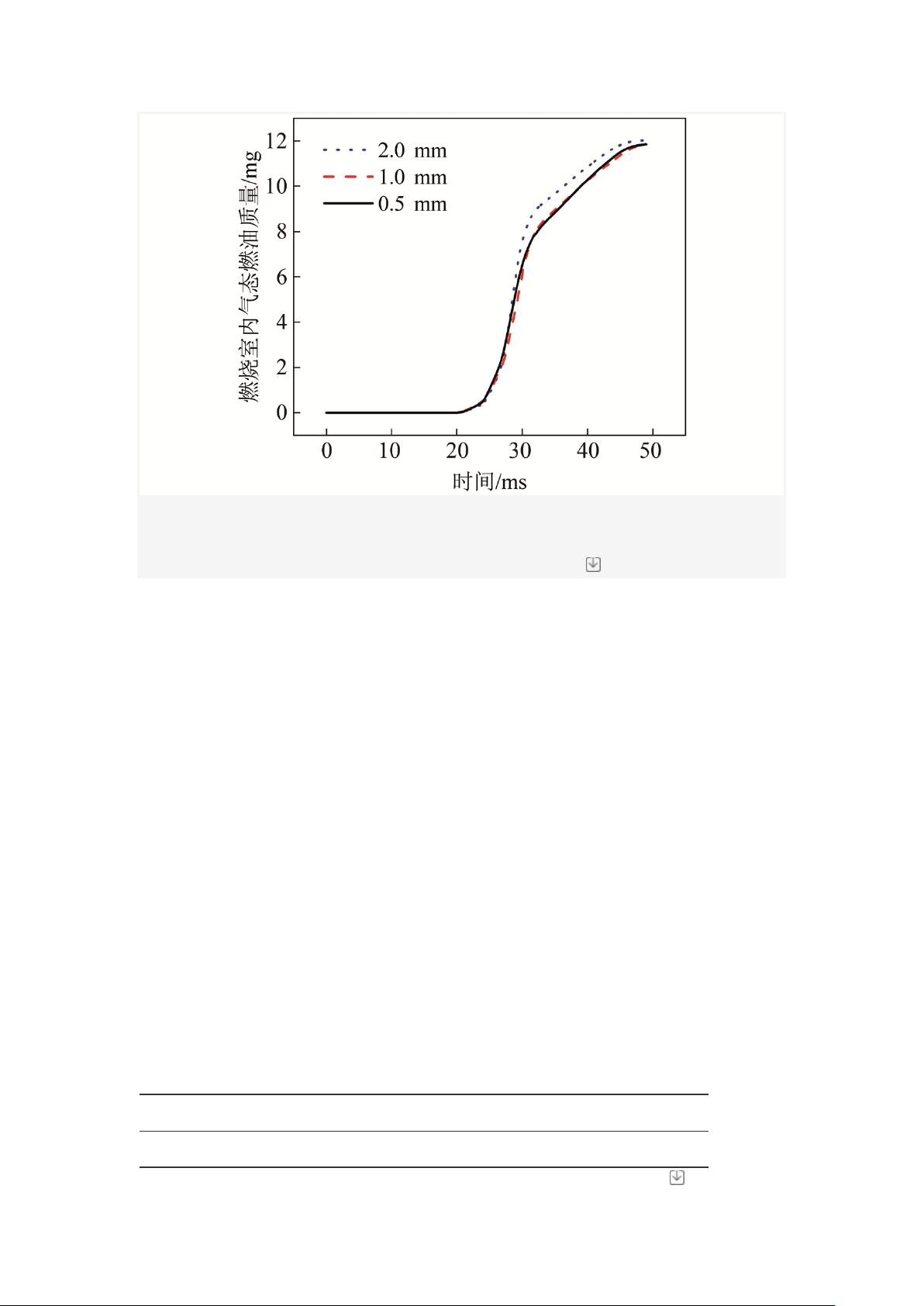
The results showed that a smaller fuel injection angle and a later injection phase led to a higher fuel capture rate, reaching up to 99%, which was 39% higher than the fresh air capture rate. This resulted in a significant reduction in fuel consumption. However, excessively large or small fuel injection angles would deteriorate the atomization effectiveness of the fuel. The optimal fuel injection angle (43°-48° from the cylinder head normal direction) achieved the highest fuel atomization rate. Yet, an earlier injection phase would alter the actual flow direction of the fuel spray in the cylinder, leading to an increase in the formation of oil film on the cylinder wall and a decrease in the fuel atomization rate.
Furthermore, a high-flow injector exhibited better fuel capture and atomization effects at the optimal injection angle. It also provided a wider range of effective injection phase intervals compared to a low-flow injector, offering greater injection flexibility.
In conclusion, optimizing the fuel injection angle, phase, and injector flow rate is crucial in improving the fuel efficiency of a two-stroke HFPE with airway injection. This research provides valuable insights into the design and operation of such engines, contributing to the advancement of sustainable and energy-efficient transportation technology.
2023-06-10 上传
2023-02-24 上传
2023-05-30 上传
2023-05-31 上传
2023-05-27 上传
2023-09-04 上传
2023-05-31 上传
2023-12-01 上传
罗伯特之技术屋
- 粉丝: 4409
- 资源: 1万+
最新资源
- 磁性吸附笔筒设计创新,行业文档精选
- Java Swing实现的俄罗斯方块游戏代码分享
- 骨折生长的二维与三维模型比较分析
- 水彩花卉与羽毛无缝背景矢量素材
- 设计一种高效的袋料分离装置
- 探索4.20图包.zip的奥秘
- RabbitMQ 3.7.x延时消息交换插件安装与操作指南
- 解决NLTK下载停用词失败的问题
- 多系统平台的并行处理技术研究
- Jekyll项目实战:网页设计作业的入门练习
- discord.js v13按钮分页包实现教程与应用
- SpringBoot与Uniapp结合开发短视频APP实战教程
- Tensorflow学习笔记深度解析:人工智能实践指南
- 无服务器部署管理器:防止错误部署AWS帐户
- 医疗图标矢量素材合集:扁平风格16图标(PNG/EPS/PSD)
- 人工智能基础课程汇报PPT模板下载