4 S.P.P. da Silva et al.
There are two main types of methods to localization and mapping of mobile
robots, geometric and topological. In geometric method, the entire navigation
environment is depicted in a coordinate system, as in [3]. On the other hand,
in topological method the total space is configured in a graph, not restricted
to inflexible geometric information, as presented in [4]. There is also the hybrid
approach, where both techniques described before are employed simultaneously,
as in [5].
Localization of a mobile robot in the environment is paramount for its nav-
igation. To achieve this, several technologies can be employed, according to the
environment considered. In outdoor environments, the Global Positioning Sys-
tem (GPS) is a precise form of navigation and can be used for place recogni-
tion [6]. However, in indoors environments, this system is not suitable for the
application [7] and, because of that difficulty, other alternatives were conceived.
Some of the most commonly used processes for locating indoor mobile robots are
ultrasonic, Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Wireless Local Area Network
(WLAN), inertial navigation and image recognition [8]. Image recognition has
been increasingly exploited because they do not suffer sound interference, such as
ultrasound, or coverage limit, similar to Bluetooth [9]. In addition, image-based
systems do not require changes in the environment.
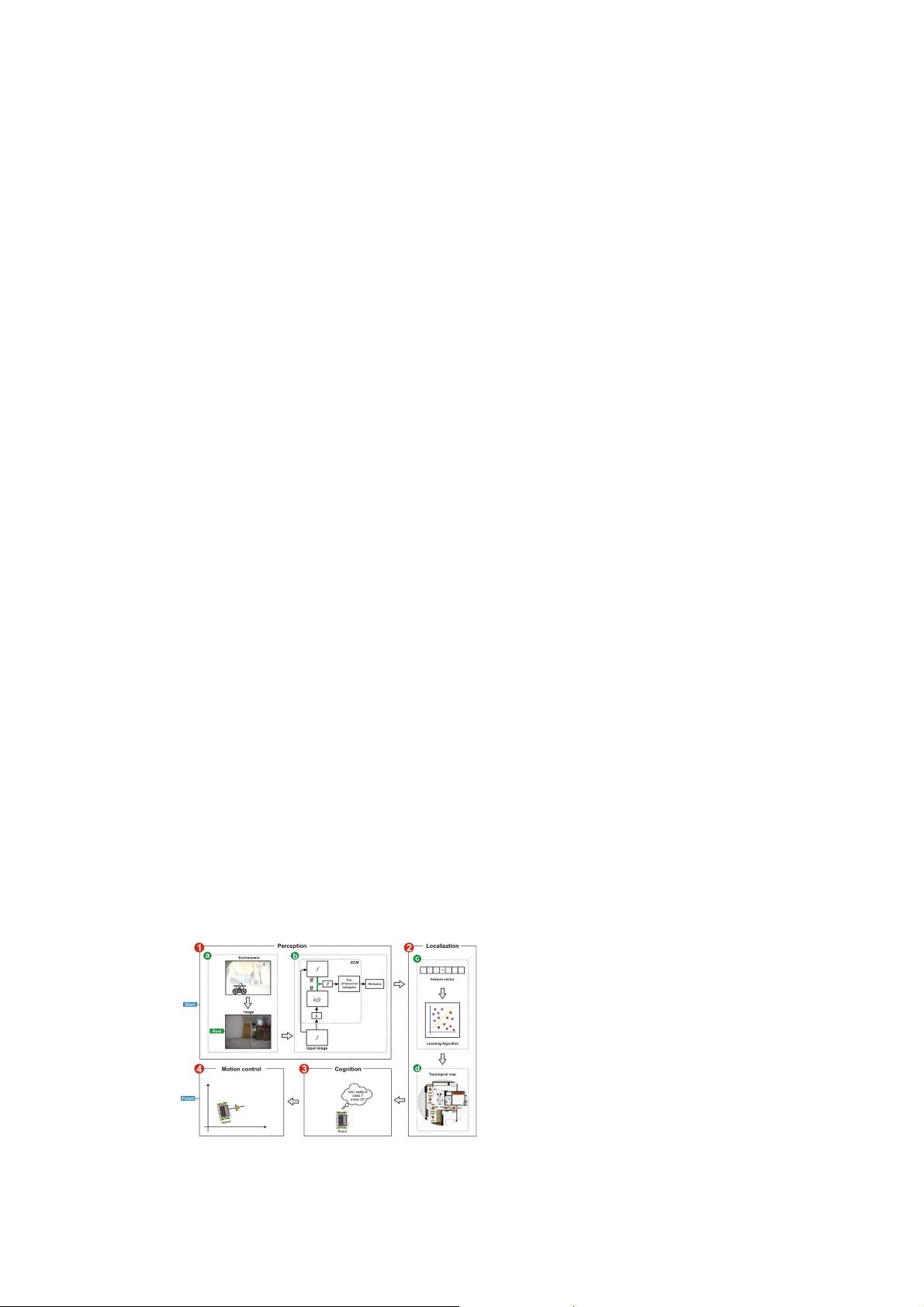
In this paper, a new approach for navigation and localization about the
images analyzed of mobile robots on topological maps using classification with
reject option in attributes obtained from a structural co-occurrence matrix
(SCM) is proposed. SCM is a rotation-invariant feature extraction technique
reasoned on a structural concept using co-occurrence statistics, presented as
advantage to introduce a previous knowledge about the images analyzed, enhanc-
ing the details detection [10]. Furthermore, we perform a study among several
feature extractors and classifiers consolidated in the literature, emphasizing the
robustness and efficiency according to accuracy and processing time because
these properties are fundamental in recognition systems aimed at applications
in the real world. An high-resolution camera, GoPro
R
, was employed for robot
navigation in an indoor environment. The results show that SCM obtained an
average accuracy of 100% during navigation and extraction time of 0.117 s.
2 Review Feature Extraction Techniques
In this work, a region of interest (ROI) is composed of the entire image. Based on
ROI, the attributes are extracted to be subsequently applied in the classification
through machine learning techniques. Next, a brief presentation of the feature
extraction techniques used is presented.
The Gray-Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM) is based on a method created
by Haralick [11], where his main focus is on texture analysis. The method consists
of a second order statistical process, once the co-occurrences between pairs of
pixels is analyzed, [11]. GLCM is a square matrix that stores references of the
relative intensities of the pixels belonging to an image [11].
Local Binary Patterns (LBP) are intelligible and powerful texture descriptors.
The elementary LBP operator, created by [12], binds a label to each of the