探索4G演进:LTE-Advanced技术概览
需积分: 9 5 浏览量
更新于2024-08-02
收藏 1.04MB PDF 举报
LTE Advanced, also known as Long-Term Evolution Advanced or 4G+, is the next generation of mobile broadband technology built upon and extending the foundation of Long-Term Evolution (LTE) that was initially introduced by the 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP). The term "Advanced" signifies a significant evolution in wireless communication capabilities, aiming to deliver enhanced performance, spectral efficiency, and overall user experience.
The development of LTE-Advanced began in 2007 with the concept outlined in 3GPP's specifications. This technology was designed to address the increasing demand for faster data rates, wider coverage, and improved network capacity. Key features of LTE-Advanced include:
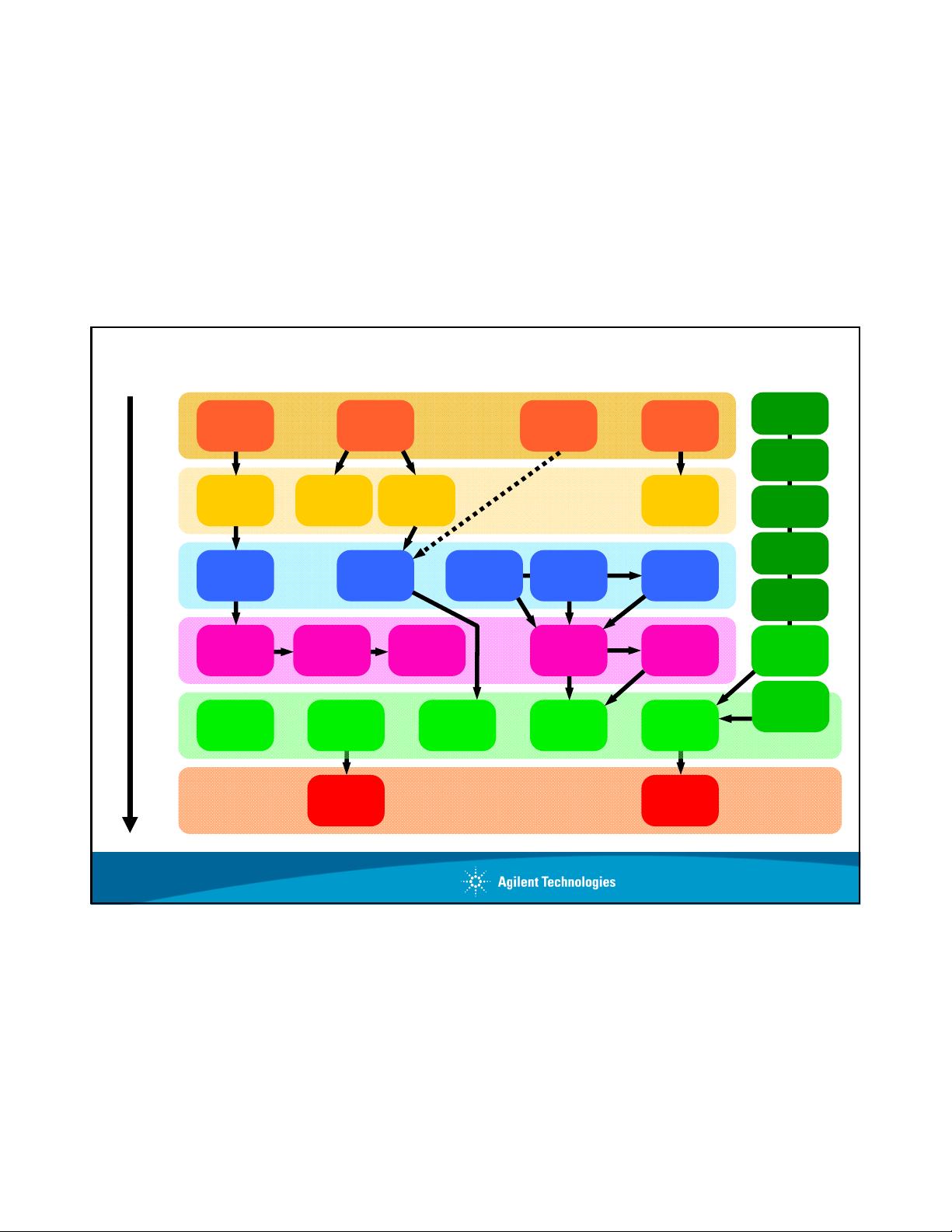
1. Wireless Evolution: LTE-Advanced focused on advancing the wireless ecosystem, incorporating technologies such as MIMO (Multiple-Input Multiple-Output) for increased data throughput, and small cell deployment to provide better coverage and capacity in dense urban areas.
2. High Data Rates: With peak speeds reaching up to 1 Gbps, LTE-Advanced offered a substantial boost compared to its predecessor, LTE's initial 100 Mbps. This was achieved through enhancements like carrier aggregation, which combined multiple frequency bands to create a larger bandwidth.
3. Network Architecture: The system architecture evolved to support more efficient and flexible operation, including the use of eNodeB (evolved NodeB) base stations and the adoption of a flat hierarchical structure, simplifying network management.
4. Key Documents: Important documents for LTE-Advanced included Release 8 and later releases, which specified technical details, requirements, and standards for the advanced features. These documents were instrumental in guiding the development and implementation of the technology.
5. Timeline: The timeline for LTE-Advanced involved multiple milestones, from the initial standardization efforts to the commercial deployment of the technology, which started around 2010 and continued to evolve with subsequent releases.
6. Requirements: IMT-Advanced, an international standard set by 3GPP, defined strict requirements for 4G systems, pushing for not just higher speeds but also lower latency, improved spectral efficiency, and energy efficiency.
7. Solution Proposals: Industry players and researchers proposed innovative solutions for LTE-Advanced, including densification strategies, HetNets (heterogeneous networks), and the integration of new radio access technologies.
8. Book Resources: The availability of dedicated books, such as "The Agilent LTE Book" and "Looking Towards 4G: LTE-Advanced," provided comprehensive guides for designers, engineers, and researchers to understand and work with the new standard. These books covered topics ranging from air interface concepts, physical layer design, upper layer signaling, and the overall system architecture.
In summary, LTE-Advanced represents a major leap forward in cellular communication, driven by 3GPP's efforts to meet the growing demands of users for faster, more reliable, and ubiquitous connectivity. Its introduction marked the transition from 3G to the next generation of mobile broadband, paving the way for technologies like 5G and beyond. By embracing innovations like MIMO, network densification, and stringent performance targets, LTE-Advanced delivered a robust foundation for the future of mobile communications.
2022-09-22 上传
2014-06-13 上传
2023-07-14 上传
2023-07-26 上传
2023-07-12 上传
2024-11-10 上传
2024-10-29 上传
2024-10-29 上传