没有合适的资源?快使用搜索试试~ 我知道了~
首页计算机组成与设计软硬件接口 课后答案
资源详情
资源评论
资源推荐

Solution* for Chapter 1 Exercise*
Solutions for Chapter 1 Exercises
1.1
5,
CPU
1.2 1, abstraction
1.3
3,
bit
1.4 8, computer family
1.5 19, memory
1.6 10, datapath
1.7 9, control
1.8 11, desktop (personal computer)
1.9 15, embedded system
1.10 22, server
1.11
18,
LAN
1.12
27,
WAN
1.13 23, supercomputer
1.14 14, DRAM
1.15 13, defect
1.16 6, chip
1.17 24, transistor
1.18
12,
DVD
1.19 28, yield
1.20 2, assembler
1.21 20, operating system
1.22 7, compiler
1.23 25, VLSI
1.24 16, instruction
1.25 4, cache •
1.26 17, instruction set architecture

Solutions for Chapter 1 Exercises
1.27 21, semiconductor
1.28 26, wafer
1.29 i
1.30 b
1.31 e
1.32 i
1.33 h
1.34 d
1.35 f
1.36 b
1.37 c
1.38 f
1.39
d
1.40 a
1.41 c
1.42 i
1.43 e
1.44 g
1.45 a
1.46 Magnetic disk:
Time for 1/2 revolution =1/2 rev x 1/7200 minutes/rev X 60 seconds/
minutes
3
4.17 ms
Time for 1/2 revolution = 1/2 rev x 1/10,000 minutes/rev X 60 seconds/
minutes = 3 ms
Bytes on center circle = 1.35 MB/seconds X 1/1600 minutes/rev x 60
seconds/minutes = 50.6 KB
Bytes on outside circle = 1.35 MB/seconds X 1/570 minutes/rev X 60
seconds/minutes = 142.1 KB
1.48 Total requests bandwidth = 30 requests/sec X 512 Kbit/request = 15,360
Kbit/sec < 100 Mbit/sec. Therefore, a 100 Mbit Ethernet link will be sufficient.

Solution* for Chapter X Exarclsm
1.49 Possible solutions:
Ethernet, IEEE 802.3, twisted pair cable, 10/100 Mbit
Wireless Ethernet, IEEE 802.1 lb, no medium, 11 Mbit
Dialup, phone lines, 56 Kbps
ADSL, phone lines, 1.5 Mbps
Cable modem, cable, 2 Mbps
1.50
a. Propagation delay = mis sec
Transmission time = LIR sec
End-to-end delay =m/s+L/R
b. End-to-end delay =mls+ LJR+t
c. End-to-end delay = mis + 2I/R + f/2
1.51 Cost per die = Cost per wafer/(Dies per wafer x Yield) = 6000/( 1500 x 50%)
= 8
Cost per chip = (Cost per die + Cost_packaging + Cost_testing)/Test yield =
(8 + 10)/90% = 20
Price = Cost per chip x (1 + 40%) - 28
If we need to sell n chips, then 500,000 + 20« = 28», n = 62,500.
1.52 CISCtime = Px8r=8Prns
RISC time = 2Px 2T= 4 PTns
RISC time = CISC time/2, so the RISC architecture has better performance.
1.53 Using a Hub:
Bandwidth that the other four computers consume = 2 Mbps x 4 = 8 Mbps
Bandwidth left for you = 10 - 8 = 2 Mbps
Time needed = (10 MB x 8 bits/byte) / 2 Mbps = 40 seconds
Using a Switch:
Bandwidth that the other four computers consume = 2 Mbps x 4 = 8 Mbps
Bandwidth left for you = 10 Mbps. The communication between the other
computers will not disturb you!
Time needed = (10 MB x 8 bits/byte)/10 Mbps = 8 seconds
Solutions for Chapter 1
EXWCIMS
1.54 To calculate d = axfc-axc, the CPU will perform 2 multiplications and 1
subtraction.
Time needed =10x2+1x1=21 nanoseconds.
We can simply rewrite the equation &sd = axb-axc= ax (b-c). Then 1 multi-
plication and 1 subtraction will be performed.
Time needed =10x1 + 1x1 = 11 nanoseconds.
1.55 No solution provided.
1.56 No solution provided.
1.57 No solution provided.
1.68 Performance characteristics:
Network address
Bandwidth (how fast can data be transferred?)
Latency (time between a request/response pair)
Max transmission unit (the maximum number of data that can be transmit-
ted in one shot)
Functions the interface provides:
Send data
Receive data
Status report (whether the cable is connected, etc?)
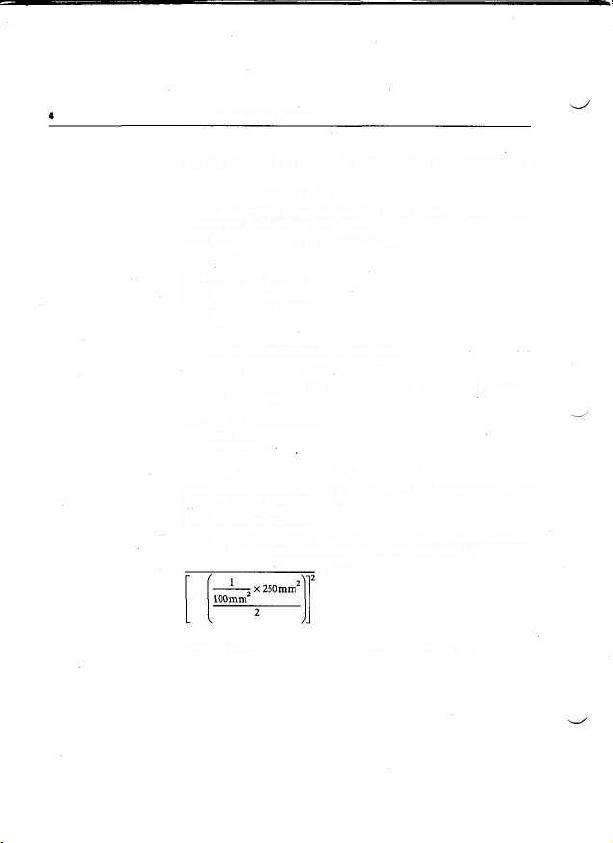
1.69 We can write Dies per wafer = /((Die area)"
1
) and Yield = /((Die area)"
2
)
and thus Cost per die = /((Die area)
3
).
1.60 No solution provided.
1.61 From the caption in Figure 1.15, we have 165 dies at 100% yield. If the defect
density is 1 per square centimeter, then the yield is approximated by
1
1 +
=
.198.
Thus, 165 x .198 = 32 dies with a cost of $1000/32 = $31.25 per die.
Solution* for Chapter 1 Exercises
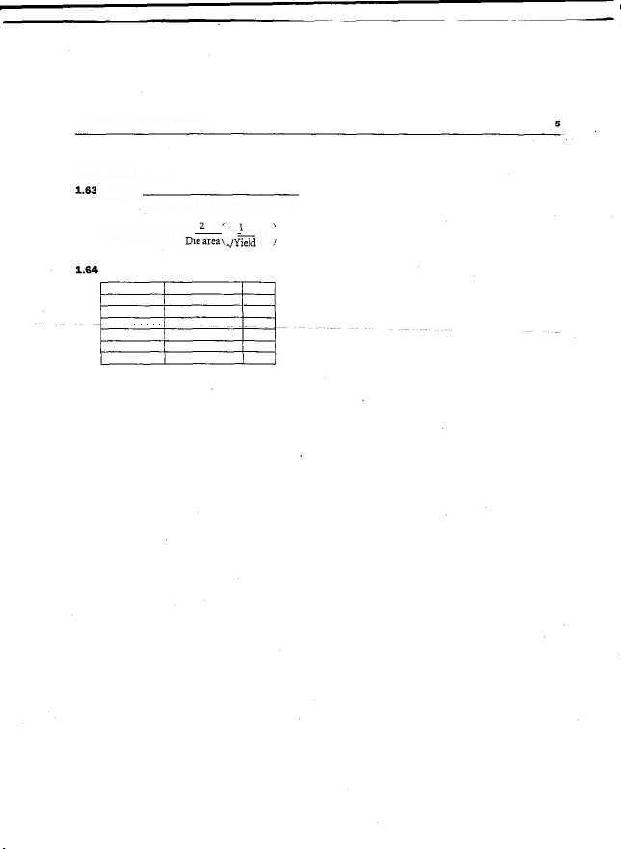
1.62 Defects per area.
1
Yield =
1
(1 + Defects per area x Die area/2)
2
Defects per area = —
:
j —
L
••— - 1 |
1980
1992
1992 + 19S0
Die ares
Yield
Defect density
Die area
Yield
Defect density
improvement
0.16
0.48
5.54
0.97
0.48
0.91
6.09
剩余122页未读,继续阅读
McWings
- 粉丝: 0
- 资源: 3
上传资源 快速赚钱
 我的内容管理
收起
我的内容管理
收起
 我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
我的资源
快来上传第一个资源
 我的收益 登录查看自己的收益
我的收益 登录查看自己的收益 我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
我的积分
登录查看自己的积分
 我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
我的C币
登录后查看C币余额
 我的收藏
我的收藏  我的下载
我的下载  下载帮助
下载帮助

会员权益专享
最新资源
- RTL8188FU-Linux-v5.7.4.2-36687.20200602.tar(20765).gz
- c++校园超市商品信息管理系统课程设计说明书(含源代码) (2).pdf
- 建筑供配电系统相关课件.pptx
- 企业管理规章制度及管理模式.doc
- vb打开摄像头.doc
- 云计算-可信计算中认证协议改进方案.pdf
- [详细完整版]单片机编程4.ppt
- c语言常用算法.pdf
- c++经典程序代码大全.pdf
- 单片机数字时钟资料.doc
- 11项目管理前沿1.0.pptx
- 基于ssm的“魅力”繁峙宣传网站的设计与实现论文.doc
- 智慧交通综合解决方案.pptx
- 建筑防潮设计-PowerPointPresentati.pptx
- SPC统计过程控制程序.pptx
- SPC统计方法基础知识.pptx
资源上传下载、课程学习等过程中有任何疑问或建议,欢迎提出宝贵意见哦~我们会及时处理!
点击此处反馈



安全验证
文档复制为VIP权益,开通VIP直接复制
 信息提交成功
信息提交成功
评论6