Philips Semiconductors Preliminary data
P89C51X2/52X2/54X2/58X2
80C51 8-bit Flash microcontroller family
4K/8K/16K/32K Flash
2002 Jun 06
9
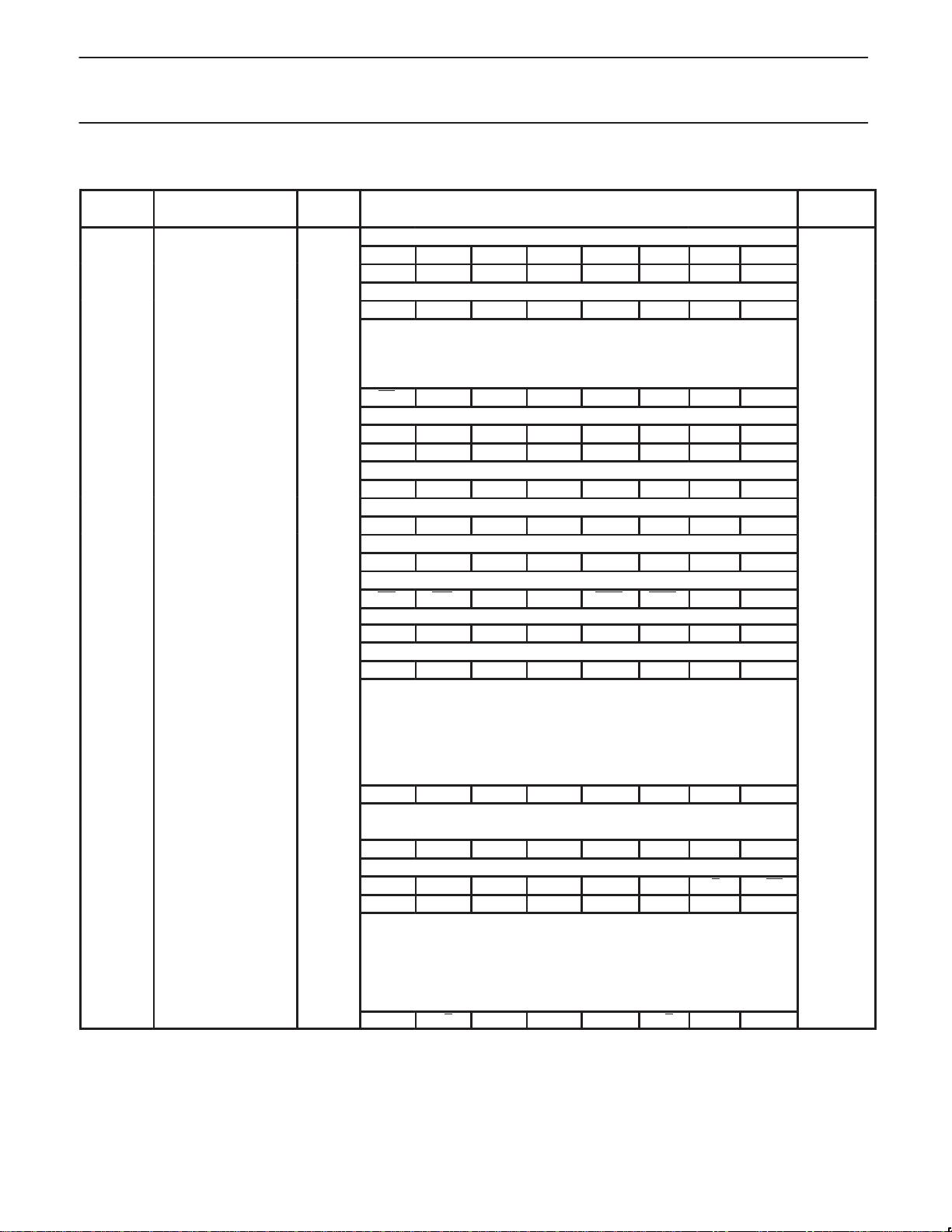
PIN DESCRIPTIONS
PIN NUMBER
MNEMONIC DIP PLCC LQFP TYPE NAME AND FUNCTION
V
SS
20 22 16 I Ground: 0 V reference.
V
CC
40 44 38 I Power Supply: This is the power supply voltage for normal, idle, and power-down operation.
P0.0-0.7 39–32 43–36 37–30 I/O Port 0: Port 0 is an open-drain, bidirectional I/O port. Port 0 pins that have 1s written to
them float and can be used as high-impedance inputs. Port 0 is also the multiplexed
low-order address and data bus during accesses to external program and data memory. In
this application, it uses strong internal pull-ups when emitting 1s. Port 0 also outputs the
code bytes during program verification and received code bytes during Flash programming.
External pull-ups are required during program verification.
P1.0–P1.7 1–8 2–9 40–44,
1–3
I/O Port 1: Port 1 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 1 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 1 pins that are externally pulled low will source current because of the internal pull-ups.
(See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 1 also receives the low-order address byte
during program memory verification. Alternate functions for Port 1 include:
1 2 40 I/O T2 (P1.0): Timer/Counter 2 external count input/clockout (see Programmable Clock-Out)
2 3 41 I T2EX (P1.1): Timer/Counter 2 Reload/Capture/Direction control
P2.0–P2.7 21–28 24–31 18–25 I/O Port 2: Port 2 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 2 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 2 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the internal
pull-ups. (See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 2 emits the high-order address byte
during fetches from external program memory and during accesses to external data memory
that use 16-bit addresses (MOVX @DPTR). In this application, it uses strong internal
pull-ups when emitting 1s. During accesses to external data memory that use 8-bit addresses
(MOV @Ri), port 2 emits the contents of the P2 special function register. Some Port 2 pins
receive the high order address bits during Flash programming and verification.
P3.0–P3.7 10–17 11,
13–19
5,
7–13
I/O Port 3: Port 3 is an 8-bit bidirectional I/O port with internal pull-ups. Port 3 pins that have 1s
written to them are pulled high by the internal pull-ups and can be used as inputs. As inputs,
port 3 pins that are externally being pulled low will source current because of the pull-ups.
(See DC Electrical Characteristics: I
IL
). Port 3 also serves the special features of the 80C51
family, as listed below:
10 11 5 I RxD (P3.0): Serial input port
11 13 7 O TxD (P3.1): Serial output port
12 14 8 I INT0 (P3.2): External interrupt
13 15 9 I INT1 (P3.3): External interrupt
14 16 10 I T0 (P3.4): Timer 0 external input
15 17 11 I T1 (P3.5): Timer 1 external input
16 18 12 O WR (P3.6): External data memory write strobe
17 19 13 O RD (P3.7): External data memory read strobe
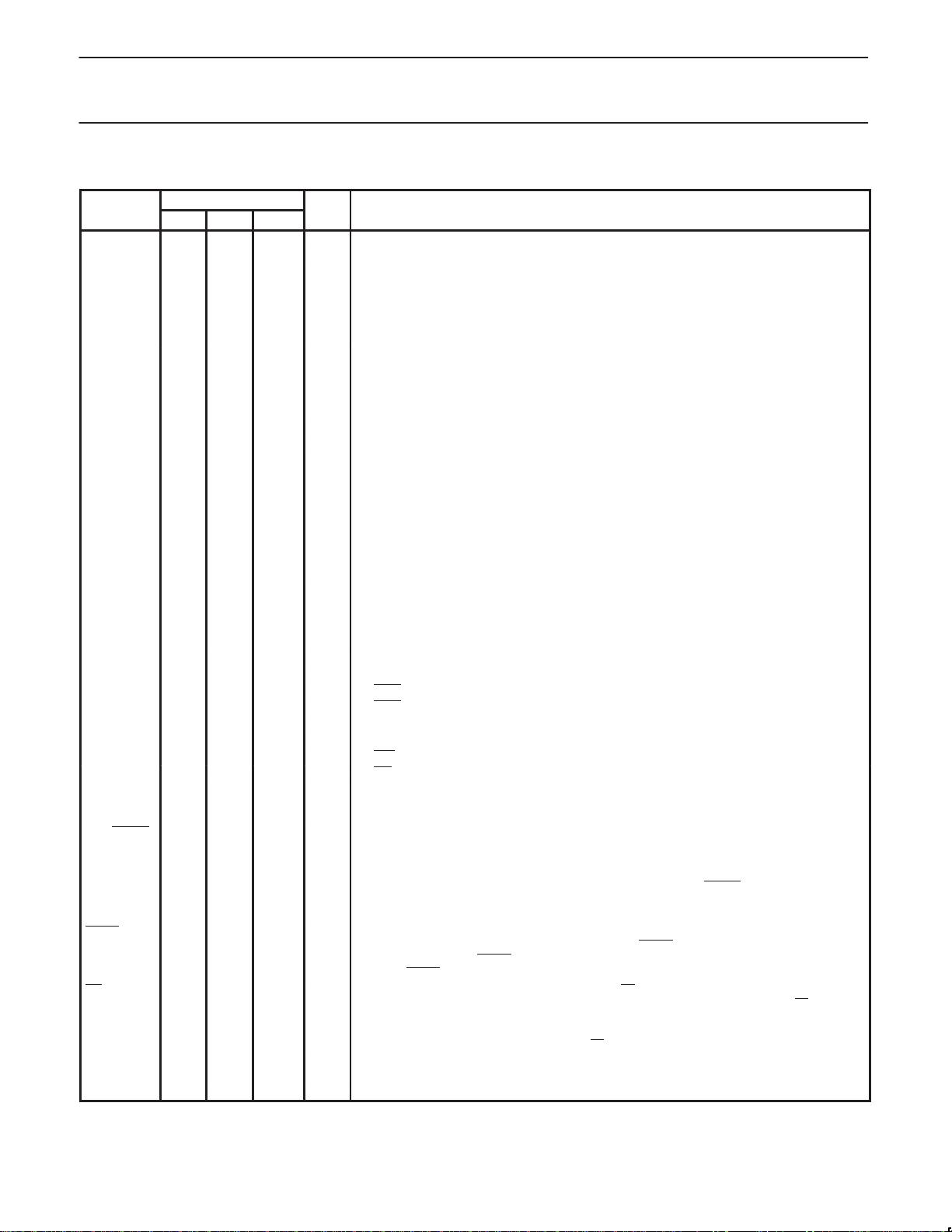
RST 9 10 4 I Reset: A high on this pin for two machine cycles while the oscillator is running, resets the
device. An internal diffused resistor to V
SS
permits a power-on reset using only an external
capacitor to V
CC
.
ALE/PROG 30 33 27 O Address Latch Enable/Program Pulse: Output pulse for latching the low byte of the
address during an access to external memory. In normal operation, ALE is emitted at a
constant rate of 1/6 (12-clk) or 1/3 (6-clk Mode) the oscillator frequency, and can be used for
external timing or clocking. Note that one ALE pulse is skipped during each access to
external data memory. This pin is also the program pulse input (PROG
) during Flash
programming. ALE can be disabled by setting SFR auxiliary.0. With this bit set, ALE will be
active only during a MOVX instruction.
PSEN 29 32 26 O Program Store Enable: The read strobe to external program memory. When the device is
executing code from the external program memory, PSEN is activated twice each machine
cycle, except that two PSEN activations are skipped during each access to external data
memory. PSEN is not activated during fetches from internal program memory.
EA/V
PP
31 35 29 I External Access Enable/Programming Supply Voltage: EA must be externally held low to enable the device
to fetch code from external program memory locations 0000H to 0FFFH/1FFFH/3FFFH/7FFFH. If EA is held
high, the device executes from internal program memory unless the program counter contains an address
greater than the on-chip Flash. This pin also receives the 5 V / 12 V programming supply voltage (V
PP
) during
Flash programming. If security bit 1 is programmed, EA will be internally latched on Reset.
XTAL1 19 21 15 I Crystal 1: Input to the inverting oscillator amplifier and input to the internal clock generator
circuits.
XTAL2 18 20 14 O Crystal 2: Output from the inverting oscillator amplifier.
NOTE:
To avoid “latch-up” effect at power-on, the voltage on any pin at any time must not be higher than V
CC
+ 0.5 V or V
SS
– 0.5 V, respectively.