Angular2 自定义验证指令:实现确认密码功能
161 浏览量
更新于2024-09-02
收藏 92KB PDF 举报
"在Angular2中实现自定义校验指令(确认密码)的方法,包括如何创建自定义验证器以满足特定的业务需求,如确认密码与原始密码一致。"
在Angular 2中,为了提供更灵活的表单验证功能,开发者可以创建自定义的校验指令。这使得我们可以根据业务逻辑定制验证规则,例如在注册表单中,确保用户输入的确认密码与原始密码一致。以下是如何在Angular 2中实现这个功能的详细步骤:
首先,我们需要理解Angular 2的内置验证器。Angular提供了如`required`、`minlength`、`maxlength`和`pattern`等基本验证器,用于处理常见的验证场景。例如,`required`验证器确保字段非空,`minlength`和`maxlength`分别验证字段的最小和最大长度,而`pattern`则用于检查输入值是否符合特定正则表达式。
现在,让我们聚焦于创建一个自定义的`EqualValidator`指令,用于验证确认密码与密码是否匹配。我们先定义一个接口`User`,它包含了用户名、邮箱、密码和确认密码字段,其中密码和确认密码需要通过自定义验证器进行比较:
```typescript
// user.interface.ts
export interface User {
username: string; // required, must be 5-8 characters
email: string; // required, must be valid email format
password: string; // required, value must be equal to confirmPassword.
confirmPassword: string; // required, value must be equal to password.
}
```
接下来,我们创建`equal-validator.directive.ts`文件,定义自定义指令`EqualValidator`。这个指令将监听两个关联的输入字段,并在它们的值不匹配时返回一个错误对象:
```typescript
// equal-validator.directive.ts
import { Directive, forwardRef } from '@angular/core';
import { NG_VALIDATORS, Validator, AbstractControl } from '@angular/forms';
@Directive({
selector: '[appEqualValidator]',
providers: [
{ provide: NG_VALIDATORS, useExisting: forwardRef(() => EqualValidator), multi: true }
]
})
export class EqualValidator implements Validator {
validate(control: AbstractControl): { [key: string]: any } | null {
const password = control.get('password');
const confirmPassword = control.get('confirmPassword');
if (password && confirmPassword) {
if (password.value !== confirmPassword.value) {
return { 'passwordNotMatch': true };
}
}
return null;
}
}
```
在上面的代码中,我们使用了`@Directive`装饰器来定义指令,并通过`NG_VALIDATORS`提供者将其注册为一个验证器。`validate`方法是核心,它比较`password`和`confirmPassword`控件的值,如果它们不相等,则返回一个包含错误信息的对象。
然后,在`app.module.ts`中,我们需要导入`FormsModule`,因为它包含了表单模块的必要组件和指令:
```typescript
// app.module.ts
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser';
import { FormsModule } from '@angular/forms'; // Import the FormsModule
@NgModule({
imports: [BrowserModule, FormsModule],
...
})
export class AppModule { }
```
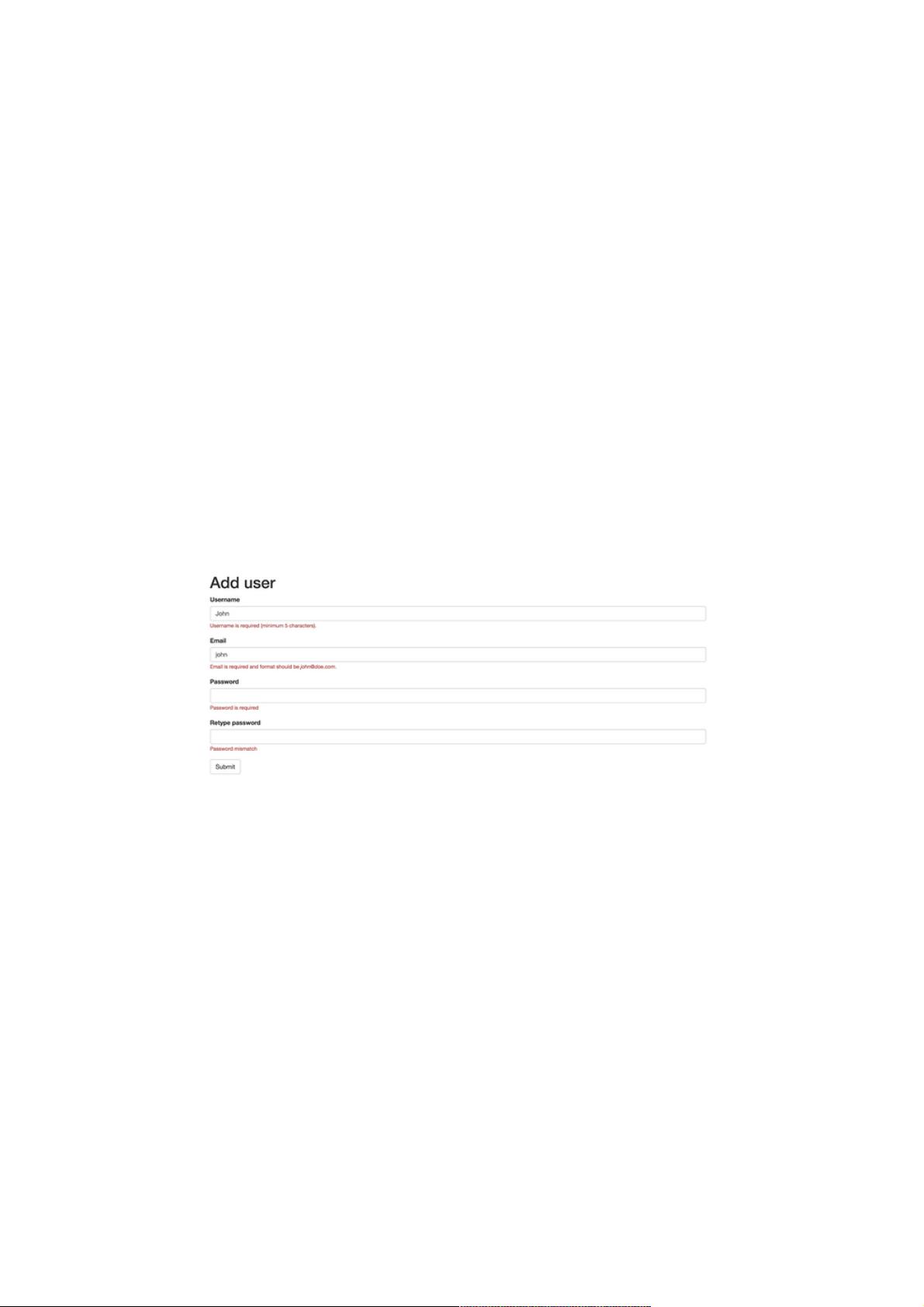
最后,我们在HTML模板中应用这个自定义验证器。假设我们有一个`UserFormComponent`,其模板如下:
```html
<!-- app.component.html -->
<form [formGroup]="userForm" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()">
<input type="text" formControlName="username" placeholder="Username" required>
<input type="email" formControlName="email" placeholder="Email" required>
<input type="password" formControlName="password" placeholder="Password" required>
<input type="password" formControlName="confirmPassword" placeholder="Confirm Password" appEqualValidator required>
<button type="submit">Submit</button>
<div *ngIf="userForm.controls.confirmPassword.errors?.passwordNotMatch">
Passwords do not match!
</div>
</form>
```
在这个模板中,我们在确认密码输入框上添加了`appEqualValidator`指令,并在`*ngIf`指令中检查`confirmPassword`控件的错误对象,以显示相应的错误消息。
总结来说,Angular 2允许我们通过创建自定义验证指令来扩展其验证功能。在这个例子中,我们创建了一个名为`EqualValidator`的指令,用于验证确认密码是否与原始密码一致。这不仅提高了代码的可复用性,还使我们能够更好地控制表单的验证逻辑,以适应不同的业务需求。
2020-08-29 上传
2020-10-17 上传
2020-12-10 上传
点击了解资源详情
2020-12-11 上传
2020-10-17 上传
2016-07-05 上传
2016-07-05 上传
2020-08-29 上传
weixin_38568548
- 粉丝: 4
- 资源: 901
最新资源
- Android圆角进度条控件的设计与应用
- mui框架实现带侧边栏的响应式布局
- Android仿知乎横线直线进度条实现教程
- SSM选课系统实现:Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis源码剖析
- 使用JavaScript开发的流星待办事项应用
- Google Code Jam 2015竞赛回顾与Java编程实践
- Angular 2与NW.js集成:通过Webpack和Gulp构建环境详解
- OneDayTripPlanner:数字化城市旅游活动规划助手
- TinySTM 轻量级原子操作库的详细介绍与安装指南
- 模拟PHP序列化:JavaScript实现序列化与反序列化技术
- ***进销存系统全面功能介绍与开发指南
- 掌握Clojure命名空间的正确重新加载技巧
- 免费获取VMD模态分解Matlab源代码与案例数据
- BuglyEasyToUnity最新更新优化:简化Unity开发者接入流程
- Android学生俱乐部项目任务2解析与实践
- 掌握Elixir语言构建高效分布式网络爬虫