MDIN-165
Datasheet Version 0.1
Macro Image Technology, Inc. Confidential
11
2.4 Auto Detection and Compensation of Input Video Sync
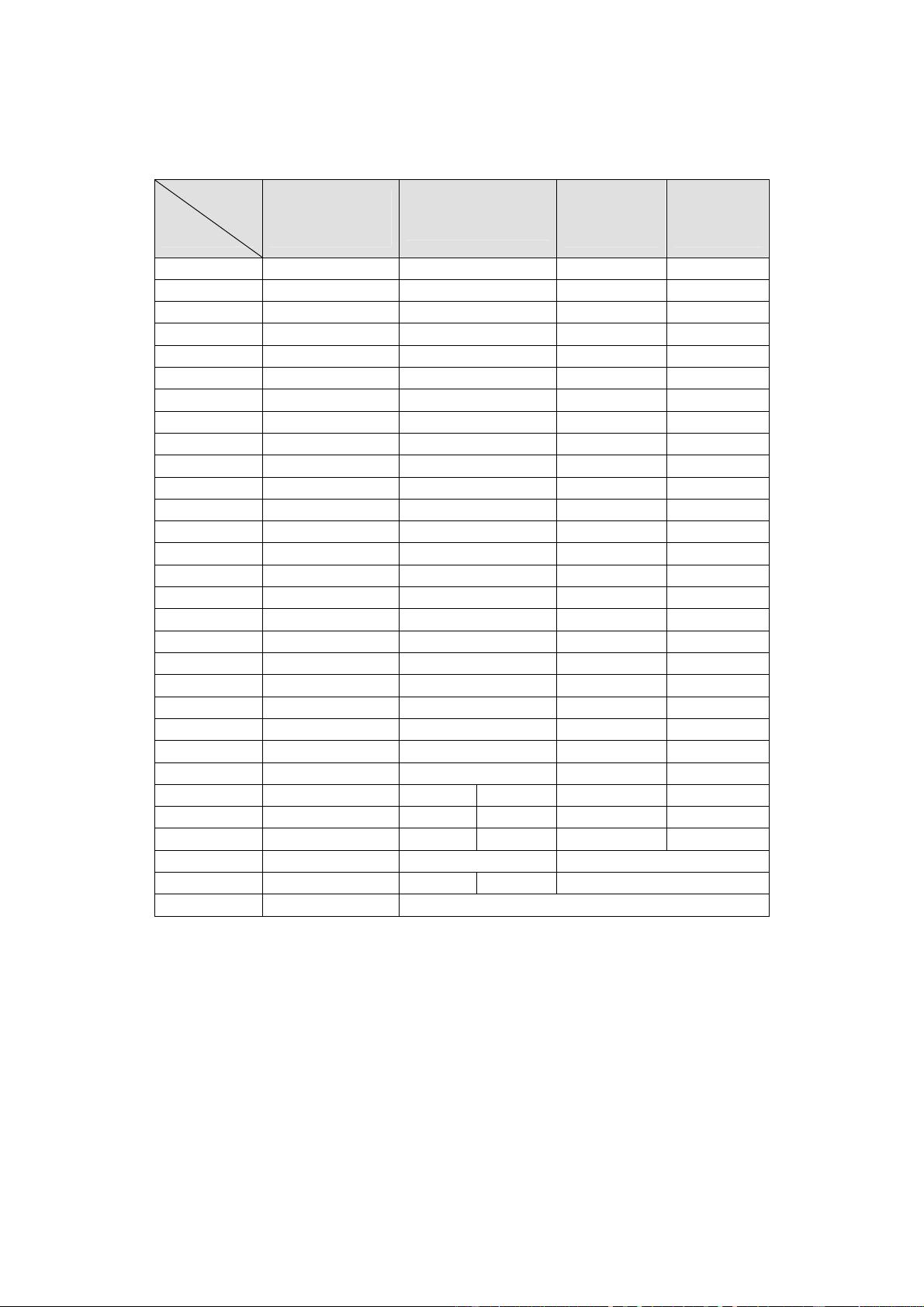
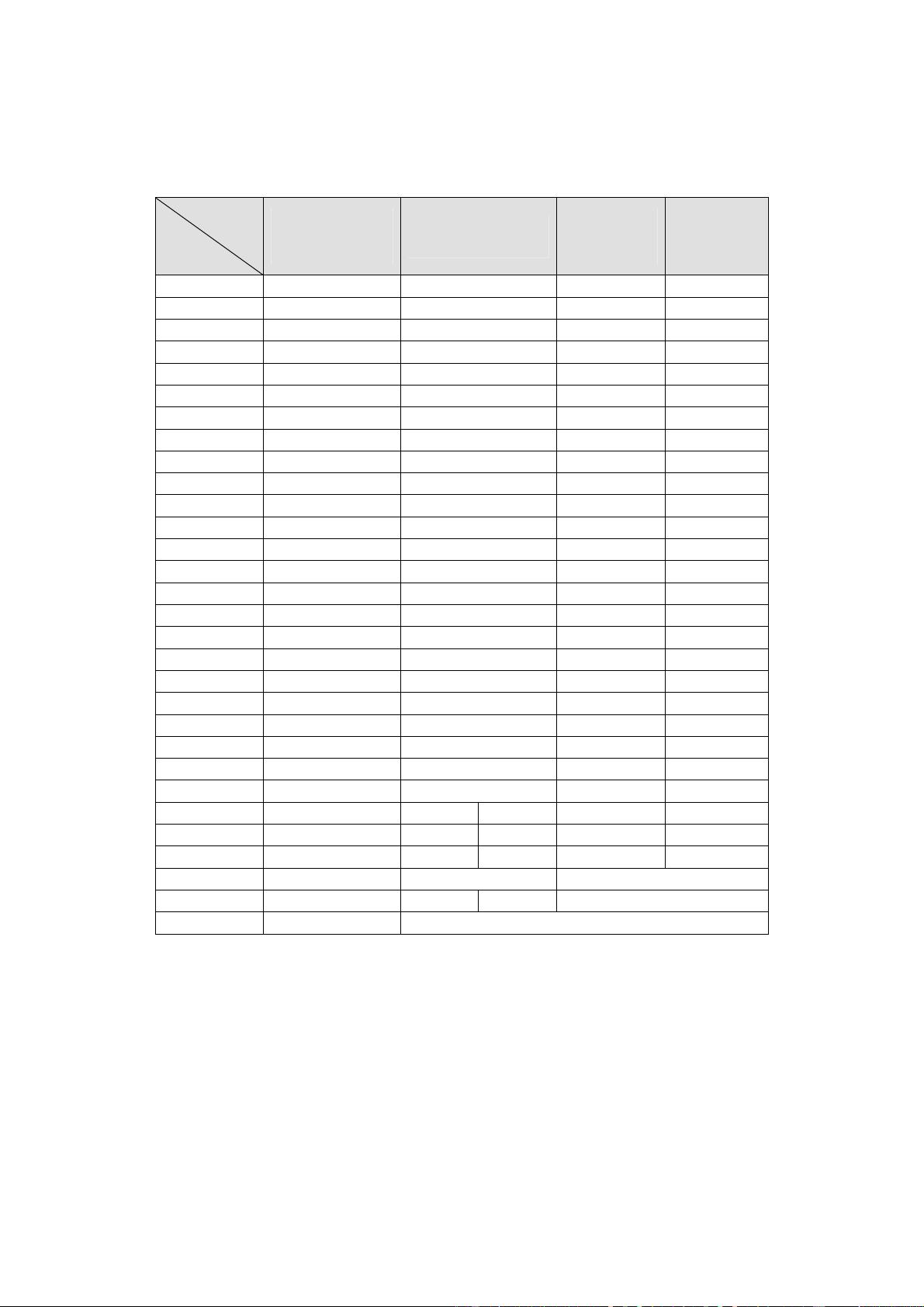
MDIN-165 provides input auto detection capability. Auto detection of the follwing parameters is supported - horizontal
sync period, horizontal size or the number of horizontal pixels for both the high and low period of horizontal sync, vertical
size or the number of vertical lines for both high and low period of vertical sync, and scan type. Auto detection on the
input port B is not necessary since it always receives video data with embedded timing references.
MDIN-165 also detects the existence of video sync signal and the change in the horizontal and vertical sync period. Auto
detection of sync existence or sync change is always performed and the other auto detection features are performed by
setting in_detect_en register. The results of auto detection are stored in input status registers (in_sync_lost, in_hsync,
in_scan_i, in_hsync_high, in_hsync_low, in_vsync_high, in_vsync_low) and they can be read and used by an
external host processor for the detection of exact input video format.
MDIN-165 supports composite sync input. It can extract the hsync and vsync from the composite sync signal which can
be obtained by slicing the bi-level or tri-level sync tips of the input video signal. MDIN-165 can receive a composite sync
signal through HACTIVE_A pin by setting in_sync_ctrl register.
And MDIN-165 can extract the sync information even though the input sync signals are in non-standard format. When the
timing of vsync-transition to hsync is different from the standard timing it can be compensated by setting
vsync_forced_rising_a register. In this case, the horizontal total size of input signal needs to be specified in
in_fieldid_ctrl register. And as prevention against unstable vsync-rising, the internal vsync signal can be forced to rise at
any position by setting vsync_forced_rising_a register. in_sync_sel register determines which input sync will be
selected between the original and compensated input sync signals.
2.5 Front Noise Reduction Filter
MDIN-165 has two blocks to perform noise reduction function. The first block is the front noise reduction filter and the
second block is the 3D noise reduction.
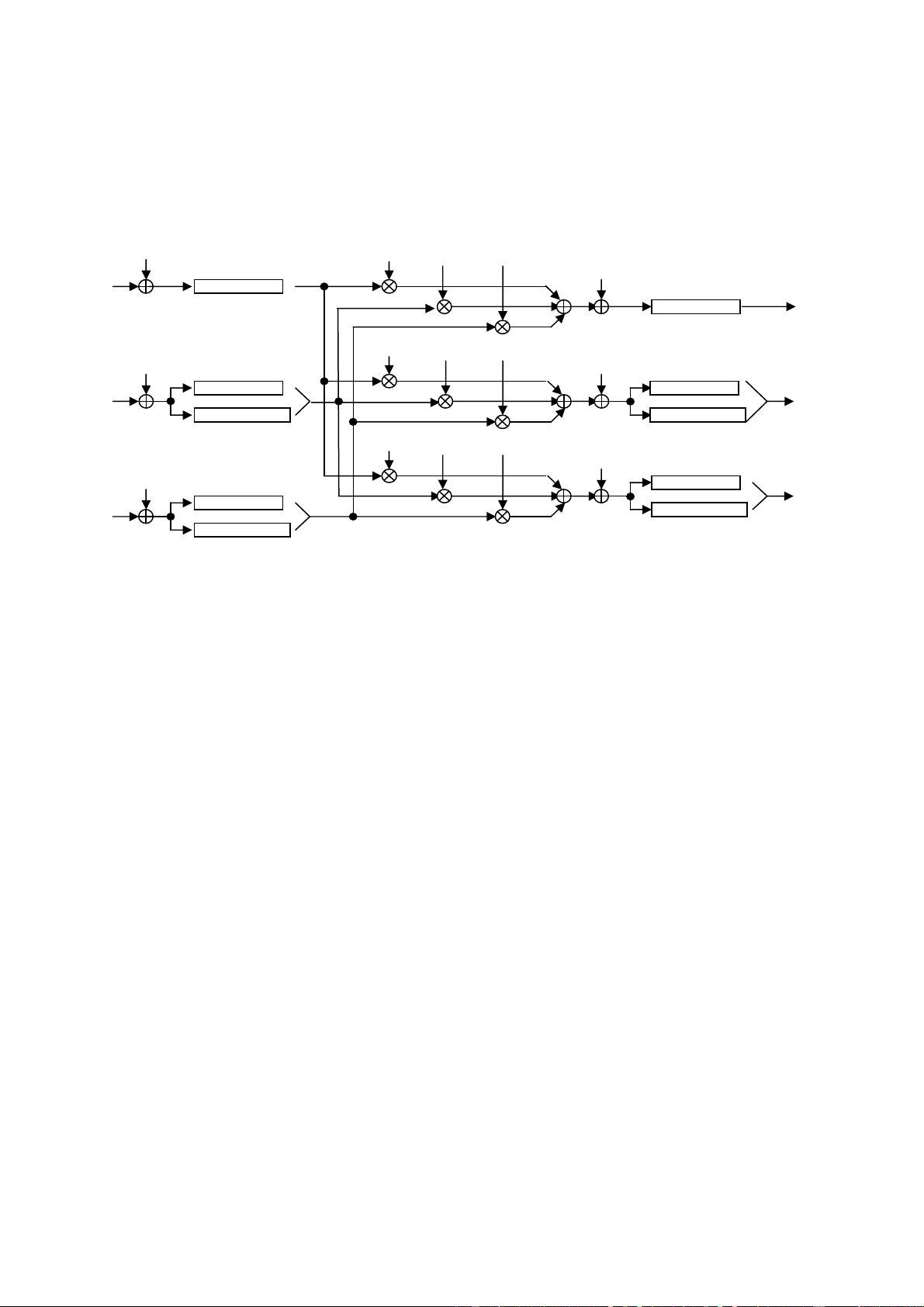
The median filter has a 3-tap order-statistic filter which outputs median values within its window. It can be used to reduce
impulse noises on the luminance component of the input video. The chrominance component bypasses the median filter
without any filtering. The median filter is enabled by the register front_median_flt_on.
The FIR filter has 15 taps for luminance and 7 taps for chrominance and their coefficients are programmable for any type
of FIR filters such as a low pass filter for high frequency noise reduction. The FIR filters for luminance and chrominance
are enabled by the registers front_nr_y_flt_on and front_nt_c_flt_on respectively. The FIR filter, alternatively, can be
used as an anti-aliasing filter. When the input video is scaled down in the horizontal direction, the FIR filter can be used
as a low pass filter to avoid aliasing.
The difference between input and output of the median filter is stored in front_median_flt_diff register and the
difference between input and output of the FIR low pass filter is stored in front_nr_flt_diff register. The difference
valuses are used in post noise reduction to reduce artifacts caused by noise, and user can select which result to be used
by setting front_nr_flt_diff_sel register.