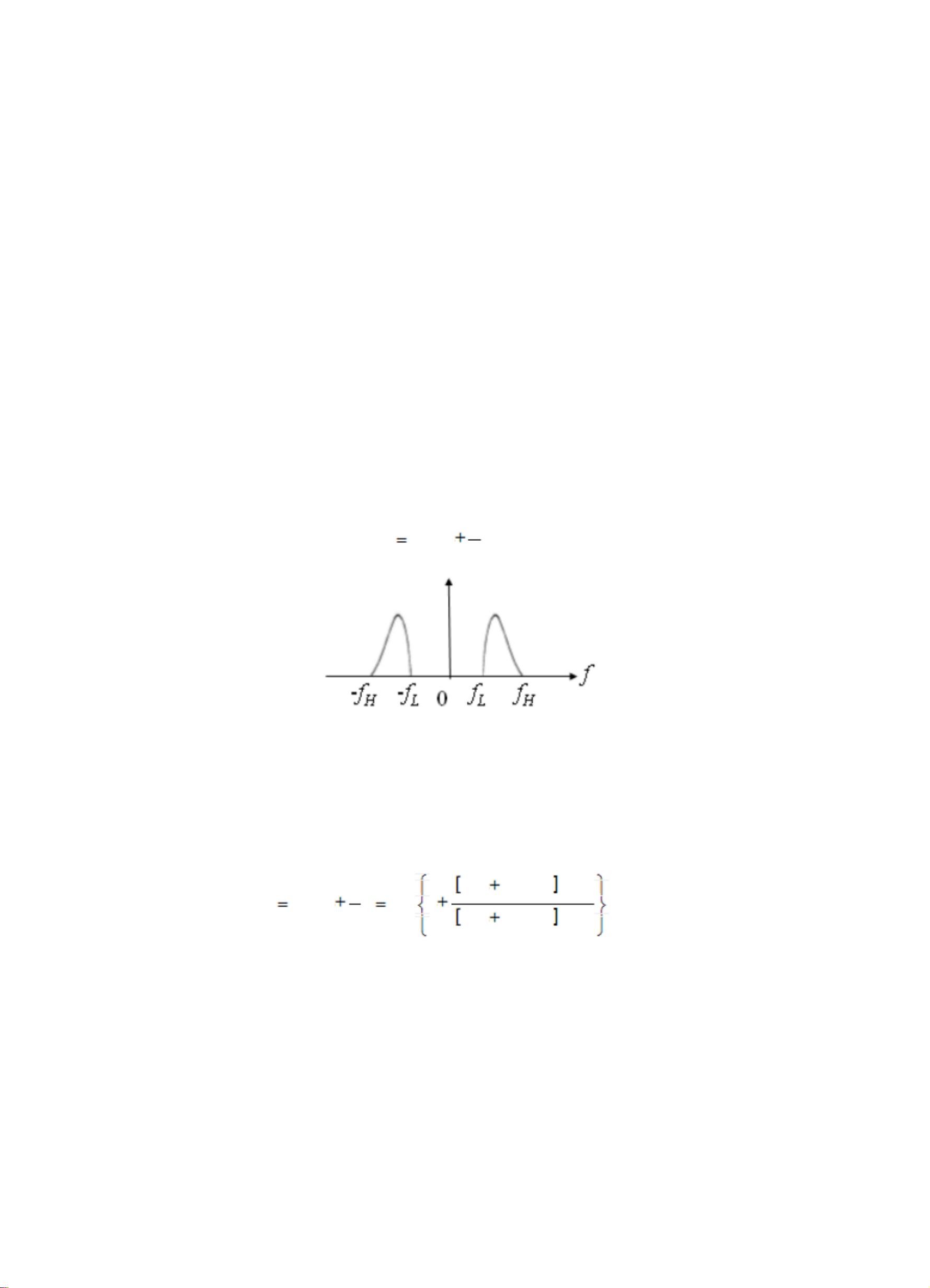"深入理解PCM编码原理及优势——数字信号传输技术简介"
版权申诉
PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) is a fundamental method used in digital communication to transmit signals in the form of digital data. With the advancement of microelectronics and computer technology, the advantages of digital transmission have become increasingly apparent. Digital communication offers strong resistance to interference, minimal distortion, stable transmission characteristics, noise immunity over long distances, and efficient encoding, decoding, and encryption capabilities to enhance the effectiveness, reliability, and security of communication systems. Additionally, digital communication allows for storage, time-scale transformation, complex computation processing, among other functionalities.
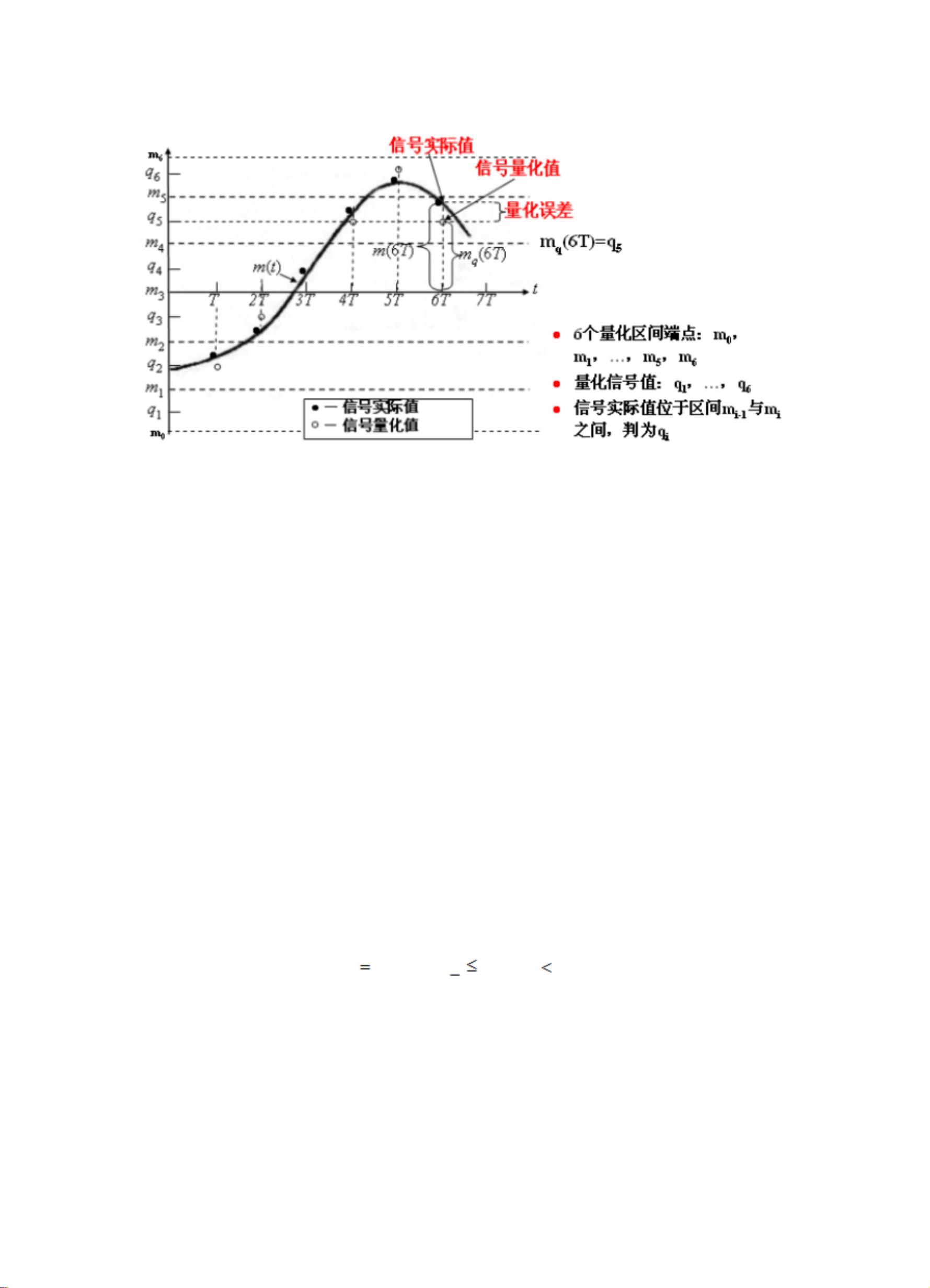
Analog-to-digital conversion falls within the scope of source coding, which includes processes such as parallel/serial conversion, encryption, and data compression. This paper focuses on discussing the basic method of analog signal digitization - Pulse Code Modulation. The process of analog signal digitization, which involves sampling, quantization, and encoding, is essential for obtaining digital signals. This study provides a brief introduction to PCM (Pulse Code Modulation) and elaborates on the principles of PCM coding. It delves into the various stages of PCM, such as baseband sampling, bandpass sampling, 13-segment quantization, PCM encoding, and PCM decoding, providing detailed explanations for each process.
Furthermore, simulations of these processes were conducted using MATLAB 7.0, comparing the results of uniform quantization and non-uniform quantization for speech signals. The findings suggest that non-uniform quantization has advantages over uniform quantization. This study sheds light on the importance of PCM in digital communication and highlights the significance of efficient signal processing techniques for enhancing communication systems.
Keywords: Pulse Code Modulation, Sampling, Non-uniform Quantization, Encoding, Decoding.
2009-08-24 上传
点击了解资源详情
点击了解资源详情
2023-05-11 上传
2021-10-30 上传
2021-06-01 上传
月亮677
- 粉丝: 9
- 资源: 17万+
最新资源
- Angular实现MarcHayek简历展示应用教程
- Crossbow Spot最新更新 - 获取Chrome扩展新闻
- 量子管道网络优化与Python实现
- Debian系统中APT缓存维护工具的使用方法与实践
- Python模块AccessControl的Windows64位安装文件介绍
- 掌握最新*** Fisher资讯,使用Google Chrome扩展
- Ember应用程序开发流程与环境配置指南
- EZPCOpenSDK_v5.1.2_build***版本更新详情
- Postcode-Finder:利用JavaScript和Google Geocode API实现
- AWS商业交易监控器:航线行为分析与营销策略制定
- AccessControl-4.0b6压缩包详细使用教程
- Python编程实践与技巧汇总
- 使用Sikuli和Python打造颜色求解器项目
- .Net基础视频教程:掌握GDI绘图技术
- 深入理解数据结构与JavaScript实践项目
- 双子座在线裁判系统:提高编程竞赛效率