17
TMS320C28346
,
TMS320C28345
,
TMS320C28344
TMS320C28343, TMS320C28342, TMS320C28341
www.ti.com.cn
ZHCSA18E –MARCH 2009–REVISED AUGUST 2018
Submit Documentation Feedback
Product Folder Links: TMS320C28346 TMS320C28345 TMS320C28344 TMS320C28343 TMS320C28342
TMS320C28341
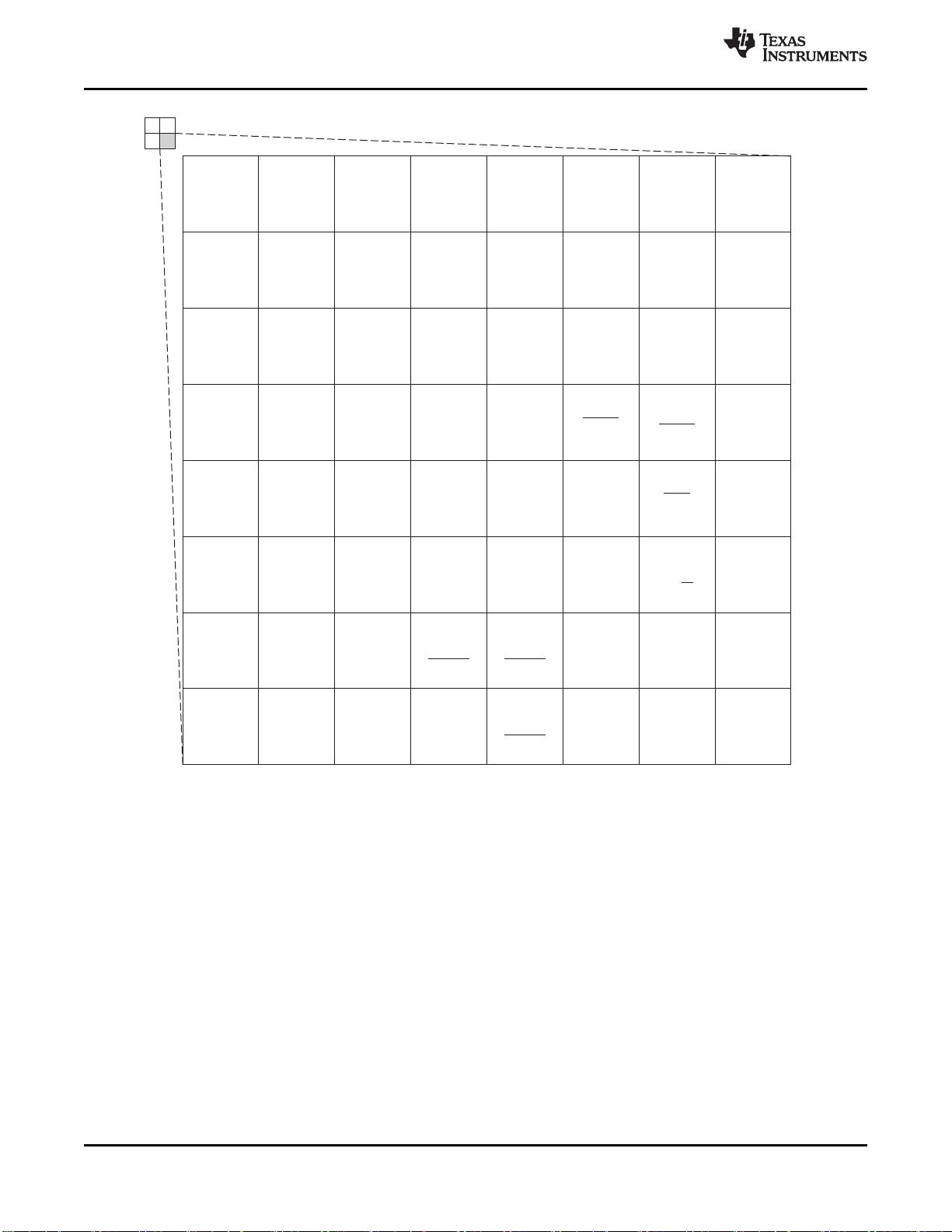
Terminal Configuration and FunctionsCopyright © 2009–2018, Texas Instruments Incorporated
4.2 Signal Descriptions
Table 4-1 describes the signals. The GPIO function (shown in Italics) is the default at reset. The peripheral
signals that are listed under them are alternate functions. Some peripheral functions may not be available
in all devices. See Table 3-1 for details. Inputs are not 5-V tolerant. All XINTF pins have a drive strength
of 4 mA (typical). All GPIO pins are I/O/Z, 4-mA drive typical and have an internal pullup, which can be
selectively enabled or disabled on a per-pin basis. This feature only applies to the GPIO pins. The pullups
on GPIO0–GPIO11 and GPIO58–GPIO63 pins are not enabled at reset. The pullups on GPIO12–GPIO57
and GPIO64–GPIO87 are enabled upon reset.
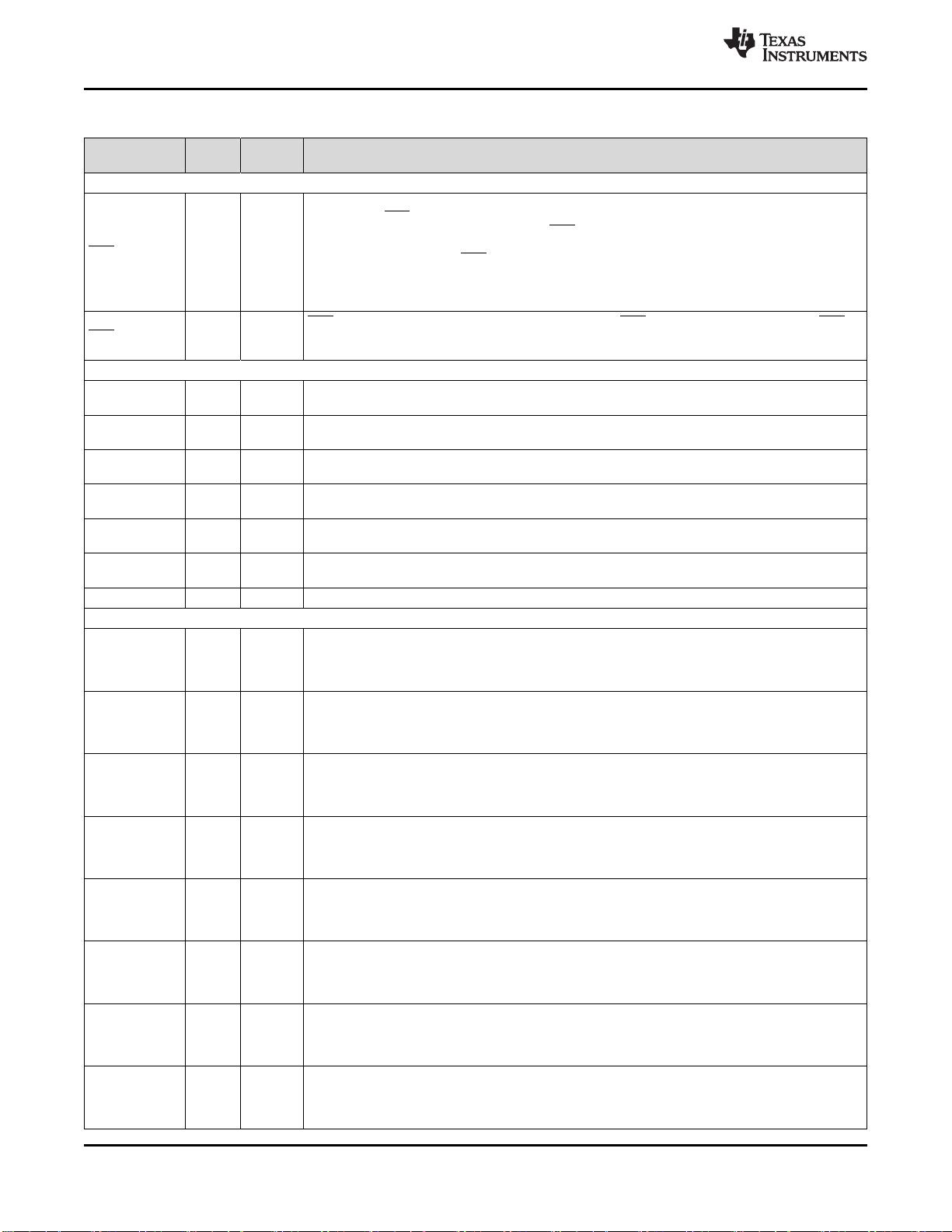
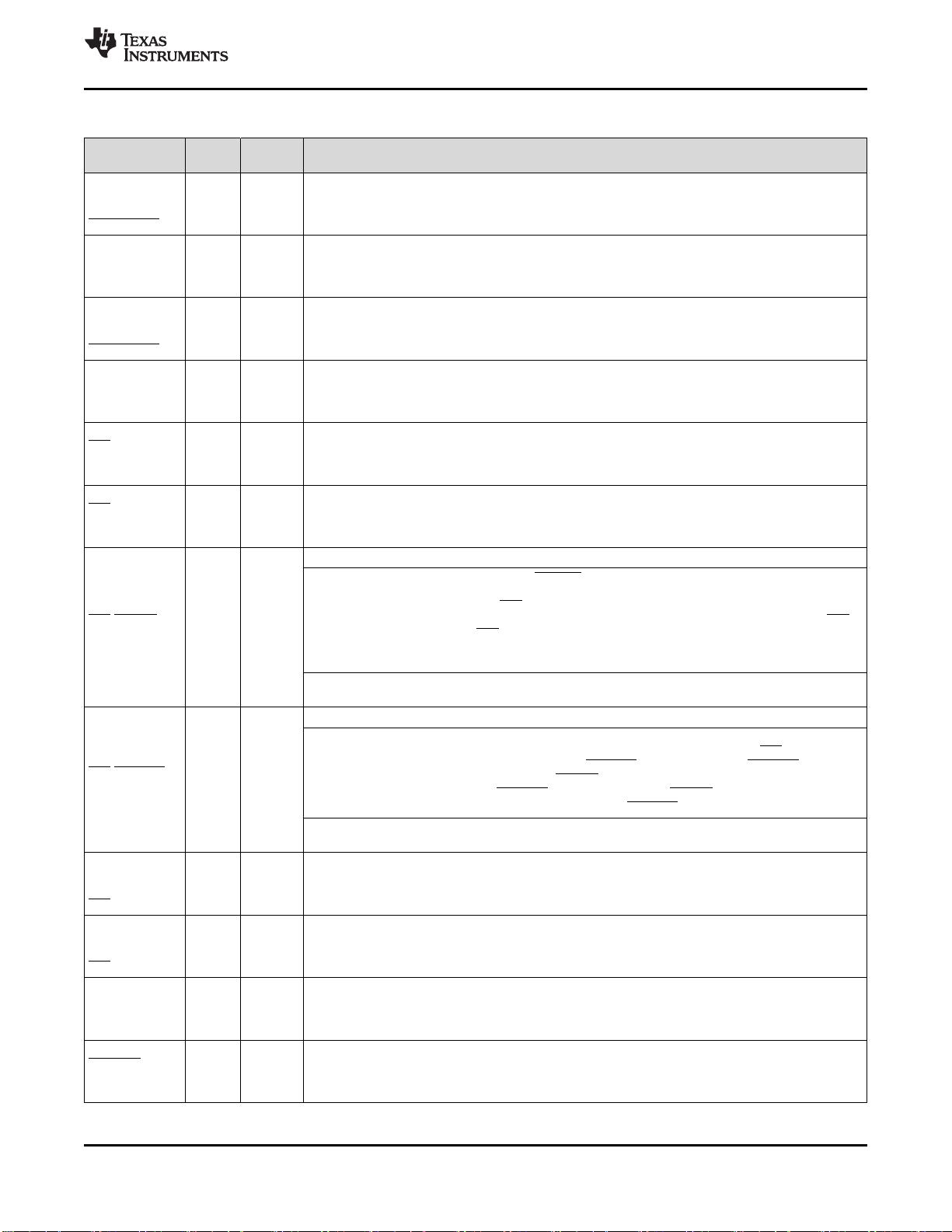
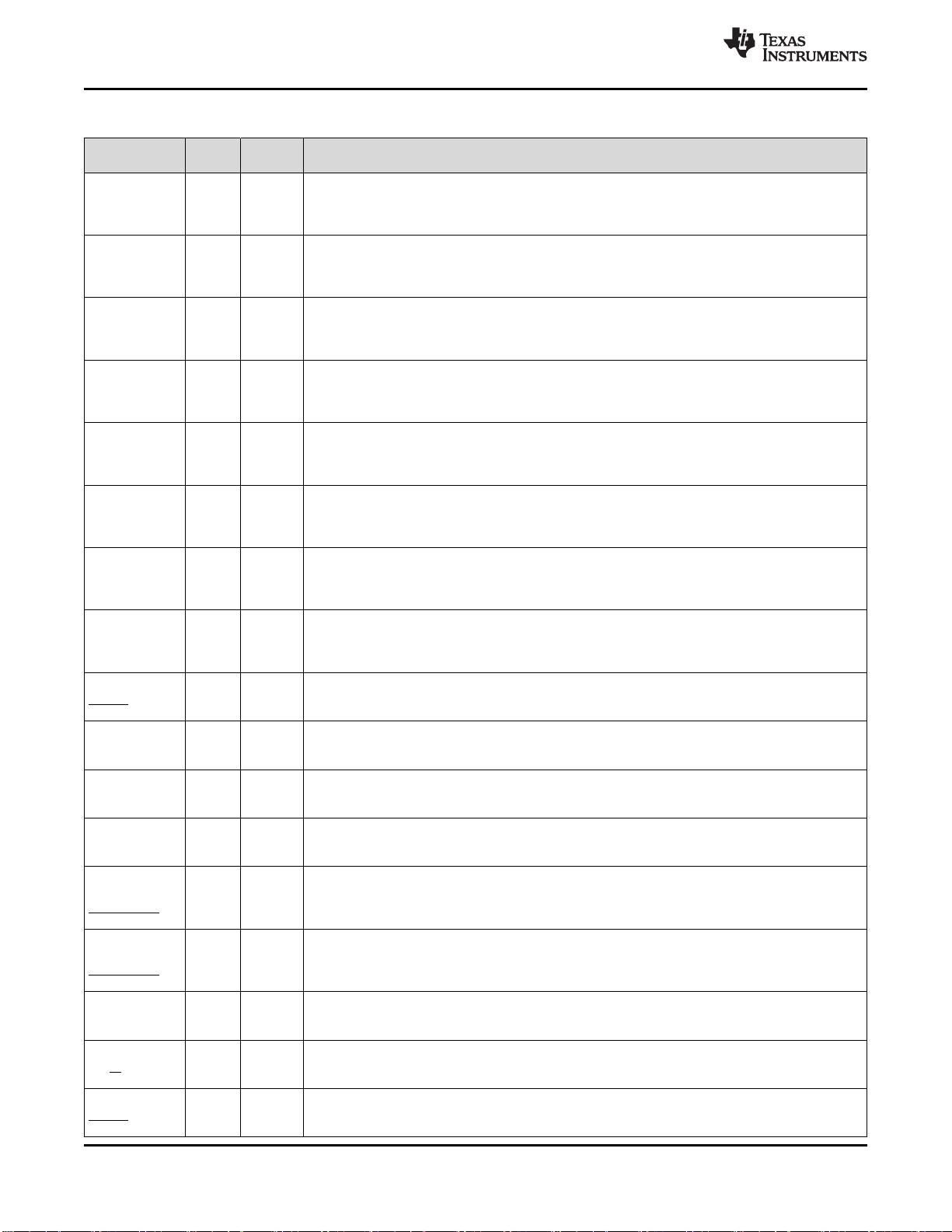
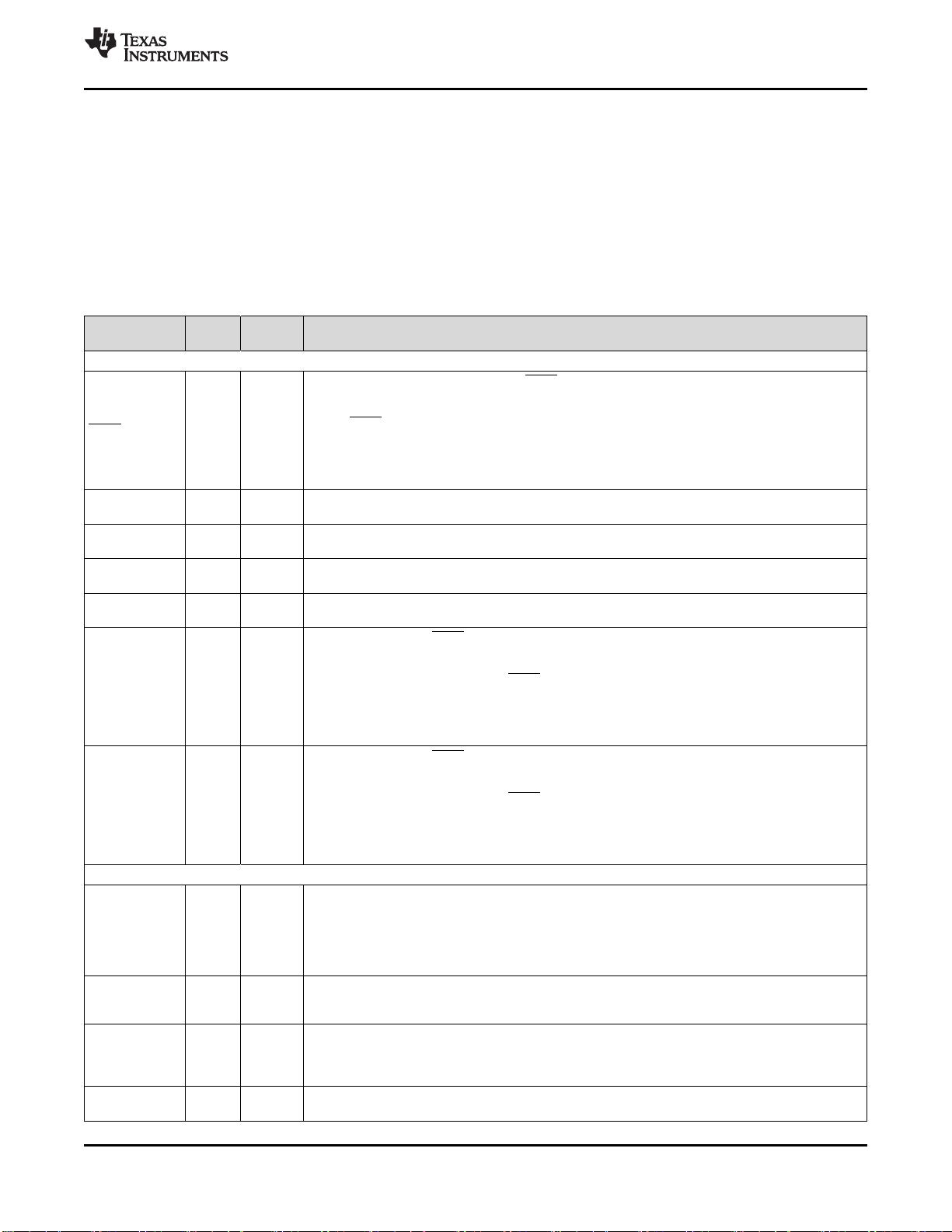
Table 4-1. Signal Descriptions
NAME
ZHH
BALL #
ZFE
BALL #
DESCRIPTION
JTAG
TRST M7 R8
JTAG test reset with internal pulldown. TRST, when driven high, gives the scan system control of
the operations of the device. If this signal is not connected or driven low, the device operates in its
functional mode, and the test reset signals are ignored.
NOTE: TRST is an active high test pin and must be maintained low at all times during normal
device operation. An external pulldown resistor is recommended on this pin. The value of this
resistor should be based on drive strength of the debugger pods applicable to the design. A 2.2-kΩ
resistor generally offers adequate protection. Because this is application-specific, TI recommends
validating each target board for proper operation of the debugger and the application. (I, ↓)
TCK P9 T11
JTAG test clock. An external pullup resistor is required on this pin. A 2.2-kΩ resistor generally offers
adequate protection.(I)
TMS M8 P9
JTAG test-mode select (TMS) with internal pullup. This serial control input is clocked into the TAP
controller on the rising edge of TCK. (I, ↑)
TDI L6 T8
JTAG test data input (TDI) with internal pullup. TDI is clocked into the selected register (instruction
or data) on a rising edge of TCK. (I, ↑)
TDO N7 P8
JTAG scan out, test data output (TDO). The contents of the selected register (instruction or data)
are shifted out of TDO on the falling edge of TCK.
EMU0 N9 P10
Emulator pin 0. When TRST is driven high, this pin is used as an interrupt to or from the emulator
system and is defined as input/output through the JTAG scan. This pin is also used to put the
device into boundary-scan mode. With the EMU0 pin at a logic-high state and the EMU1 pin at a
logic-low state, a rising edge on the TRST pin would latch the device into boundary-scan mode.
NOTE: An external pullup resistor is recommended on this pin. The value of this resistor should be
based on the drive strength of the debugger pods applicable to the design. A 2.2-kΩ to 4.7-kΩ
resistor is generally adequate. Because this is application-specific, TI recommends validating each
each target board for proper operation of the debugger and the application.
EMU1 L9 R10
Emulator pin 1. When TRST is driven high, this pin is used as an interrupt to or from the emulator
system and is defined as input/output through the JTAG scan. This pin is also used to put the
device into boundary-scan mode. With the EMU0 pin at a logic-high state and the EMU1 pin at a
logic-low state, a rising edge on the TRST pin would latch the device into boundary-scan mode.
NOTE: An external pullup resistor is recommended on this pin. The value of this resistor should be
based on the drive strength of the debugger pods applicable to the design. A 2.2-kΩ to 4.7-kΩ
resistor is generally adequate. Because this is application-specific, TI recommends validating each
target board for proper operation of the debugger and the application.
Clock
XCLKOUT B14 D16
Output clock derived from SYSCLKOUT. XCLKOUT is either the same frequency, one-half the
frequency, one-fourth the frequency, or one-eighth the frequency of SYSCLKOUT. This is controlled
by bit 19 (BY4CLKMODE), bits 18:16 (XTIMCLK), and bit 2 (CLKMODE) in the XINTCNF2 register.
At reset, XCLKOUT = SYSCLKOUT/8. The XCLKOUT signal can be turned off by setting
XINTCNF2[CLKOFF] to 1. Unlike other GPIO pins, the XCLKOUT pin is not placed in high-
impedance state during a reset.
XCLKIN D9 A12
External Oscillator Input. This pin is to feed a clock from an external 3.3-V oscillator. In this case,
the X1 pin must be tied to V
SSK
. If a crystal/resonator is used (or if an external 1.8-V oscillator is
used to feed clock to X1 pin), this pin must be tied to V
SS
. (I)
X1 C8 A7
Internal/External Oscillator Input. To use the internal oscillator, a quartz crystal may be connected
across X1 and X2. The X1 pin is referenced to the 1.8-V core digital power supply. A 1.8-V external
oscillator may be connected to the X1 pin. In this case, the XCLKIN pin must be connected to V
SS
.
If a 3.3-V external oscillator is used with the XCLKIN pin, X1 must be tied to V
SSK
. (I)
X2 A8 A9
Internal Oscillator Output. A quartz crystal may be connected across X1 and X2. If X2 is not used it
must be left unconnected. (O)