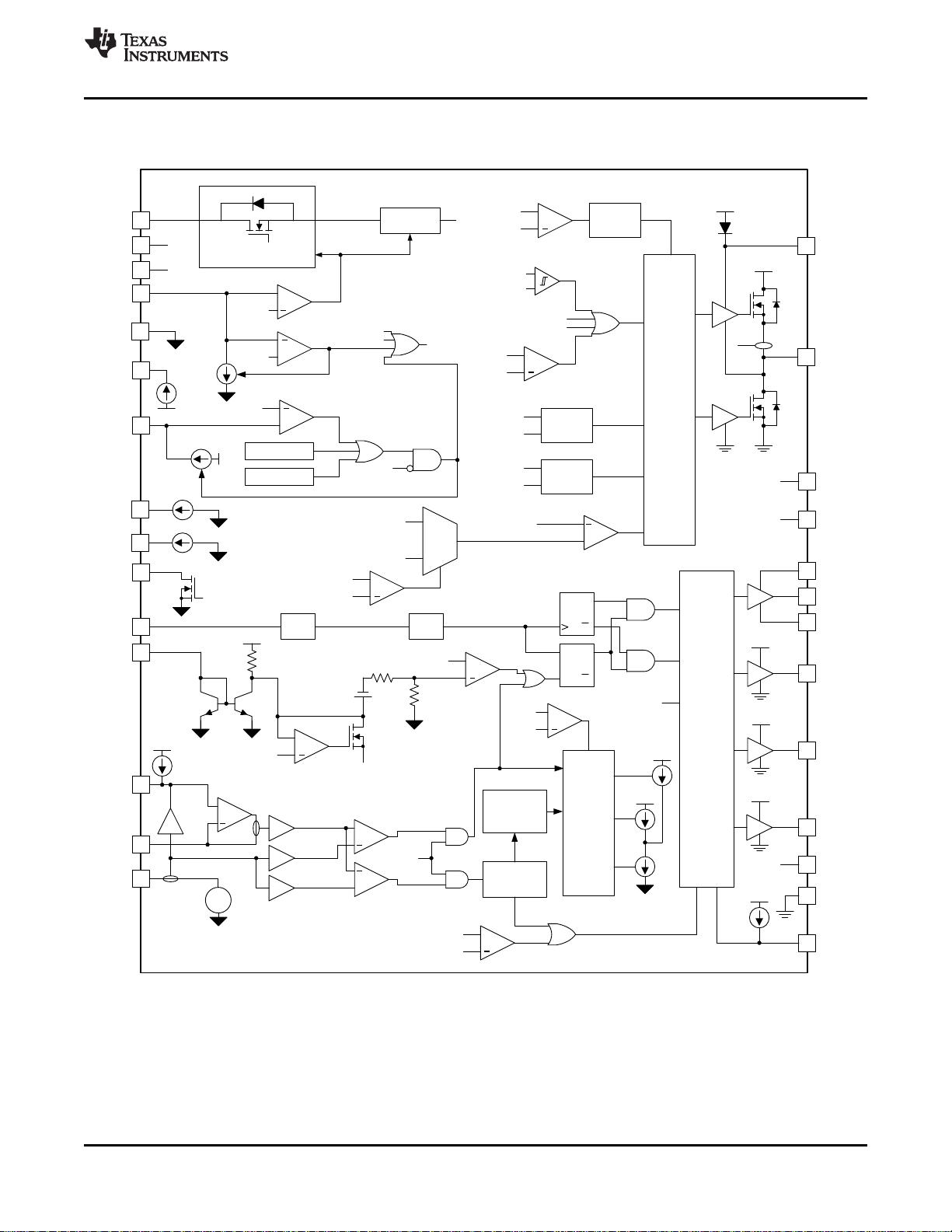
14
LM5036
ZHCSI27B –APRIL 2018–REVISED APRIL 2019
www.ti.com.cn
版权 © 2018–2019, Texas Instruments Incorporated
7.3 Feature Description
7.3.1 High-Voltage Start-Up Regulator
The LM5036 device contains a high-voltage VCC start-up regulator that allows the input pin (VIN) to be
connected directly to an input voltage up to 100-V. Higher input voltages can be accommodated by adding some
additional external parts, as described in Applications with V
IN
> 100-V. When the UVLO pin voltage is greater
than V
SD
(0.38-V typical), the start-up regulator is enabled to charge an external capacitor connected to the VCC
pin. The output voltage of the VCC regulator is regulated at V
CC
(7.8-V typical). The VCC regulator provides
power to the reference (REF) regulator. The regulator output at VCC is internally current limited to I
CC(Lim)
(81-mA
typical) . The value of the VCC capacitor depends on the total system design, and its start-up characteristics.
The recommended range of values for the VCC capacitor is 0.47-µF to 10-µF.
LM5036 can power itself using its internal high-voltage start-up linear regulator, but internal power dissipation
can be reduced by powering VCC from an auxiliary switched mode supply. LM5036 device integrates all of the
functions needed to implement a low-cost and easy-to-design isolated fly-buck auxiliary supply based on the
constant-on-time (COT) control scheme. The primary output V
AUX1
of the auxiliary supply must be connected
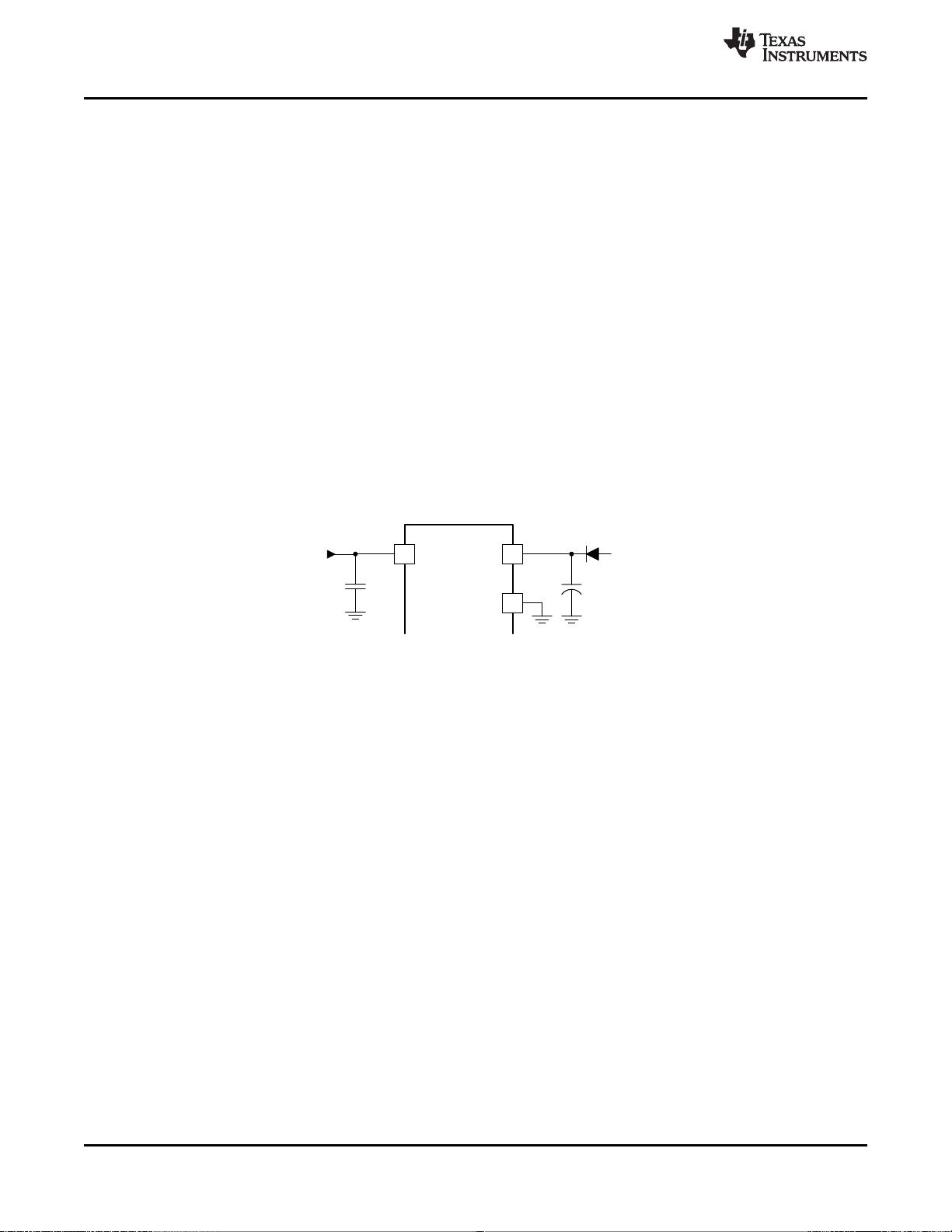
through a diode to the VCC pin, as shown in 图 12. The auxiliary supply must raise the VCC voltage above the
internally generated V
CC
voltage in order to shut off the internal start-up regulator. Powering VCC from an
auxiliary switched mode supply improves efficiency while reducing the power dissipation of the controller IC. The
VCC under-voltage (UV) circuit will still function in this mode, requiring that VCC never falls below its UV
threshold during the start-up sequence. The VCC regulator series pass transistor includes a diode between VCC
and VIN that should not be forward biased in normal operation. Therefore, the auxiliary VCC voltage should
never exceed the V
IN
voltage.
图图 12. External VCC Bias Supply Connection
7.3.2 Undervoltage Lockout (UVLO)
The LM5036 device contains a three-level under-voltage lockout circuit. When the UVLO pin voltage is below
V
SD
(0.38-V typical), the controller is in a low current shutdown mode where the functional circuit blocks are not
enabled including VCC startup regulator, auxiliary supply and the main half-bridge control logic and gate drive
circuitry, etc.
When UVLO pin voltage is above V
SD
, the VCC and REF regulators become active.
When the VCC and REF outputs exceed their respective UV thresholds and the input voltage V
IN
rises above
V
AUX_UVLO
(15-V typical), the auxiliary supply is enabled.
When UVLO pin voltage rises above V
UVLO
(1.25-V typical) and VCC and REF voltage are above their respective
UV thresholds, the control logic of the main half-bridge converter is enabled. The soft-start capacitor is released
and normal operation begins. An external set-point voltage divider from V
IN
to GND can be used to set the
minimum operating voltage of the half-bridge converter. The divider must be designed such that the voltage at
the UVLO pin is greater than V
UVLO
when V
IN
enters the desired operating range. UVLO hysteresis is
accomplished with an internal current sink I
UVLO
(20-µA typical) that is switched on or off into the impedance of
the external set-point divider. When the UVLO pin voltage threshold of V
UVLO
is exceeded, the current sink is
deactivated to quickly raise the voltage at the UVLO pin. When the UVLO pin voltage falls below the V
UVLO
threshold, the current sink is enabled causing the voltage at the UVLO pin to quickly fall. See 表 1 for more detail
on functional modes of LM5036.