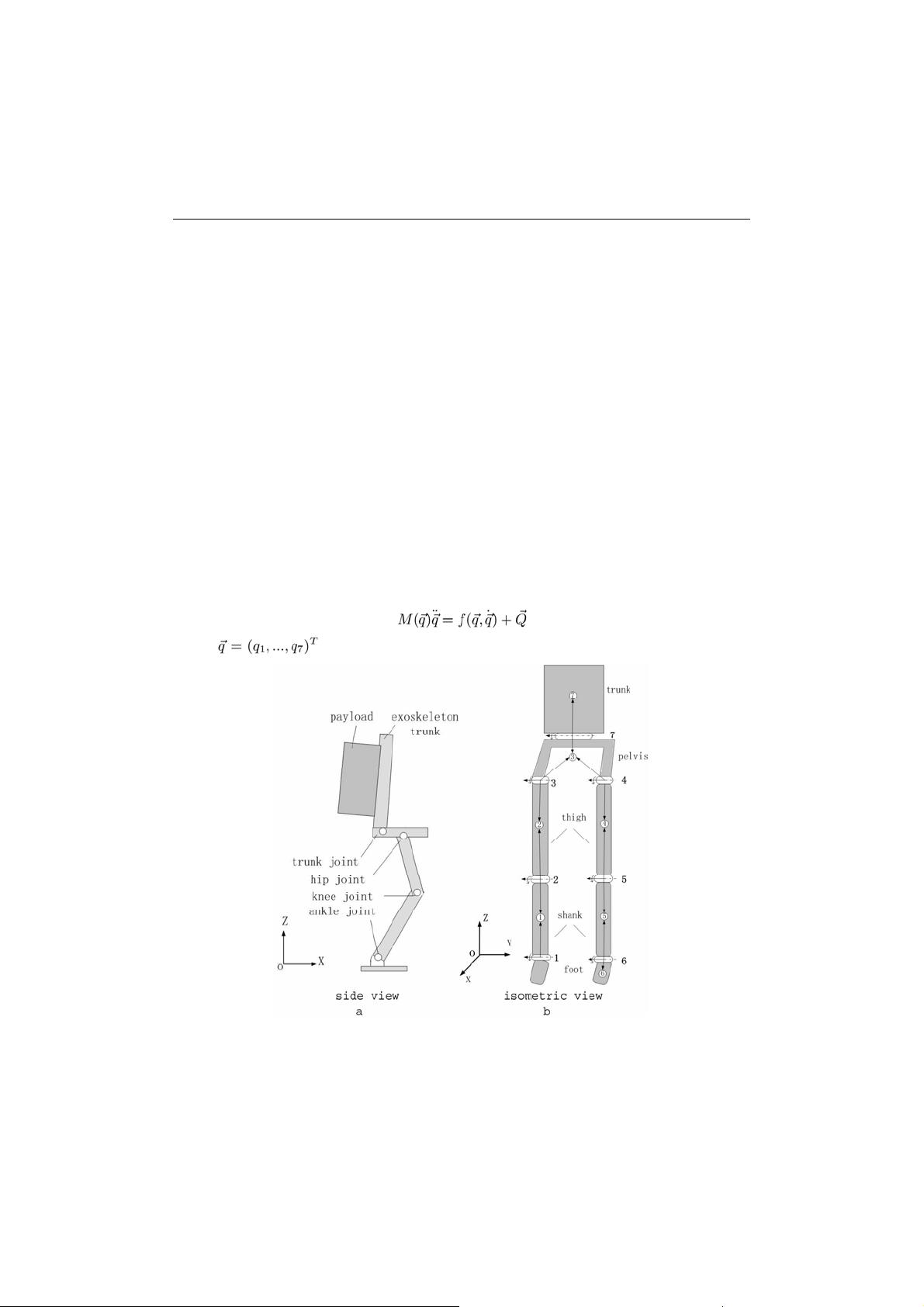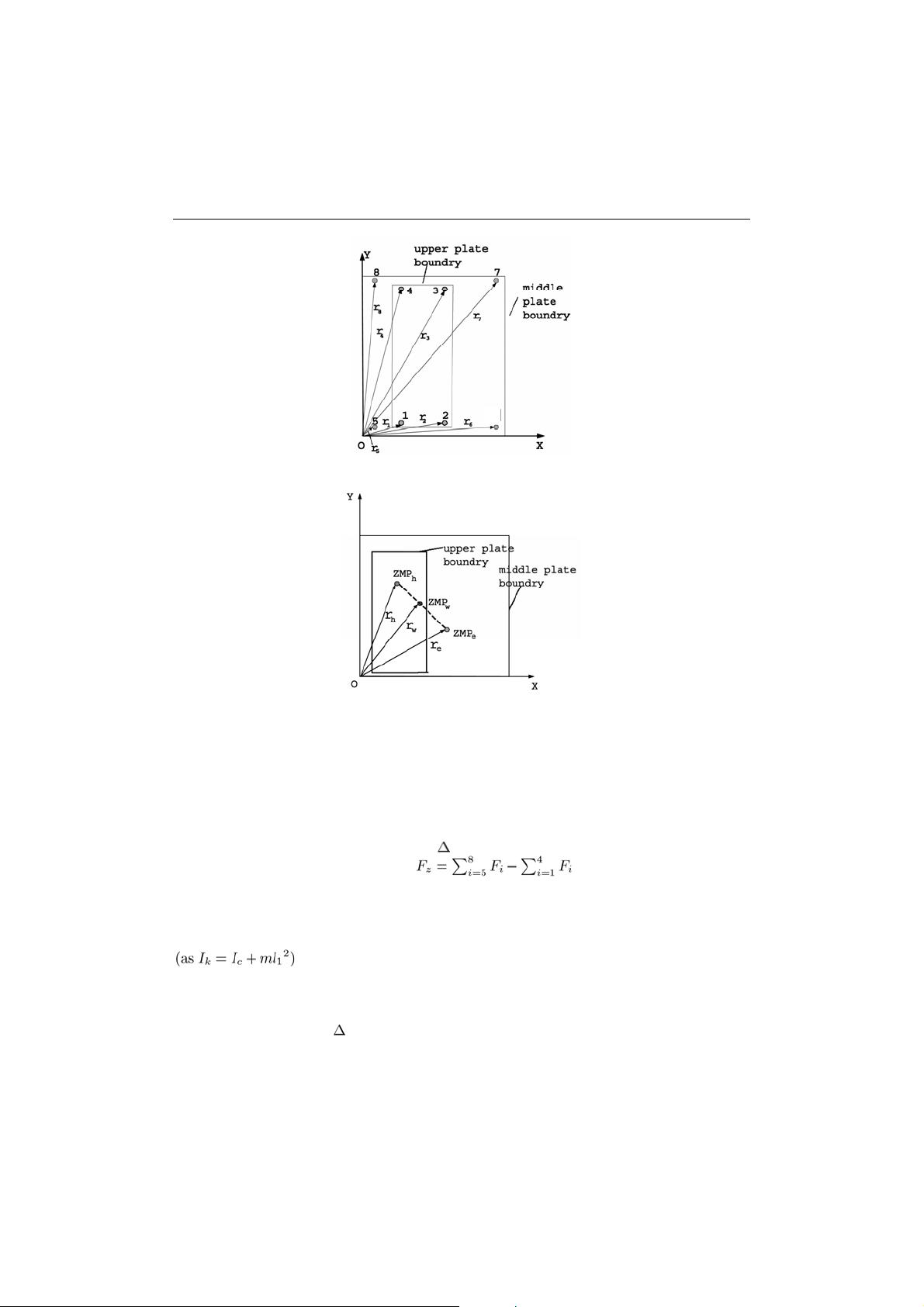
Design of an Assistive Gait Device for Strength Endurance and Rehabilitation
7
The matrix function
takes into account the mass distribution, and the vector function
describes the effect of both inertial and gravity forces. The elements of the vector
are generalized forces applied to the system, while the dots denote the time derivatives.
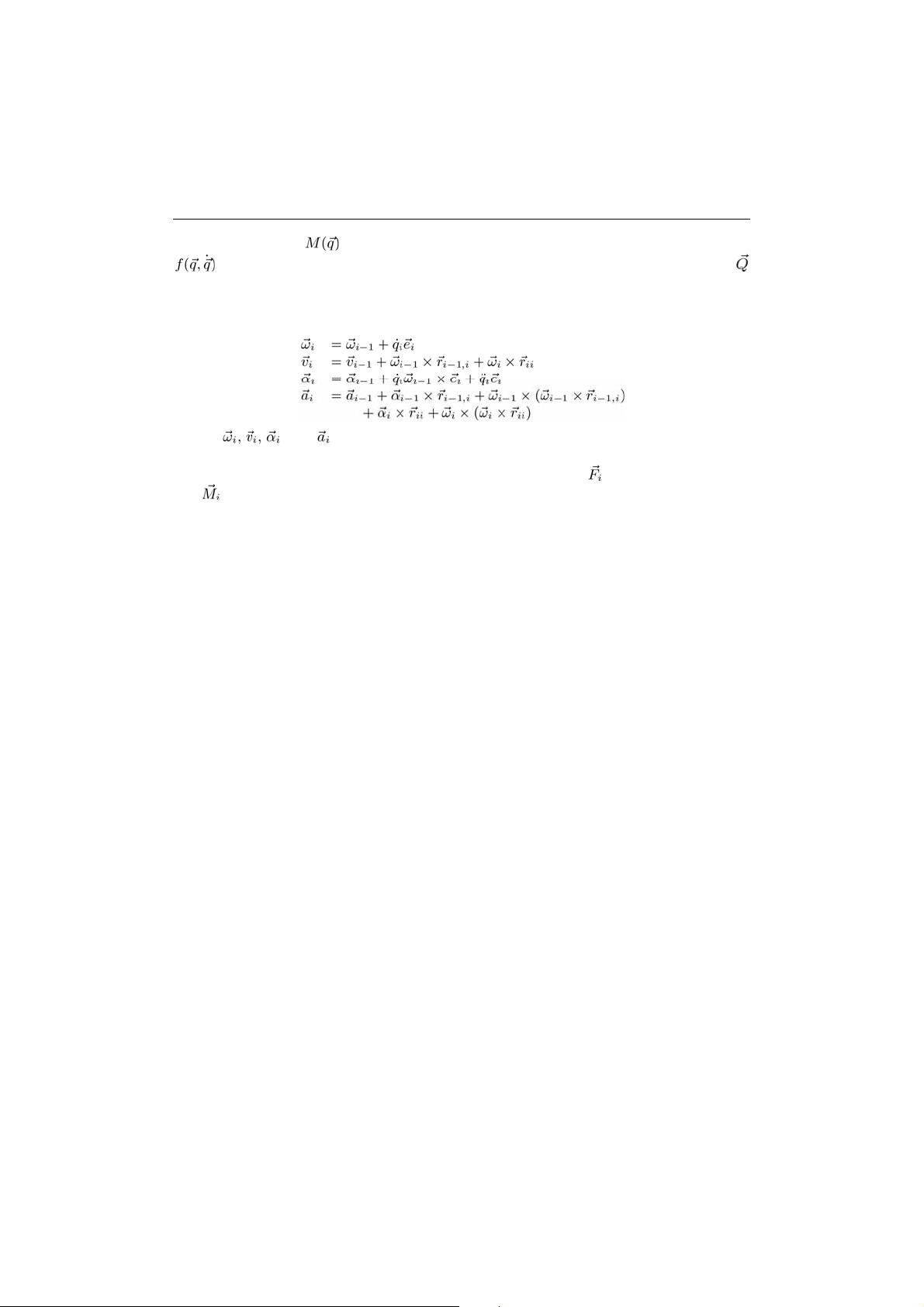
Applying the basic theorems of rigid body kinematics, we obtain the following recursive
(Low et al., 2006):
(2)
where
and are the angular velocity, linear velocity of the center of mass,
angular acceleration, and linear acceleration of the center of mass of the i-th link,
respectively. The inertial force of the center of mass of the i-th link
and moment of the i-th
link can then be obtained by using Newton-Euler equations, respectively,
iii
amF
&
&
=
(3)
iiiiii
IIM
ωωα
×+=
(4)
4. Control Strategy of the Exoskeleton System
An important feature of the exoskeleton system, which is also the main difference between
exoskeleton and biped robot, is the participation role of human in the process of control and
decision-making. By introducing human as part of the control system, some intractable tasks
for robots such as navigation, path planning, obstacle crossing and gait selection can be
easily undertaken by the pilot instead of robot's complex artificial controller and vision
system. However, two problems remain for the exoskeleton controller to solve: how to
transfer the pilot's intention to the exoskeleton and how to keep the stability of the
exoskeleton. Accordingly, the proposed control strategy can be divided into two parts,
namely Locomotion control and ZMP control.
4.1 Locomotion Control
During the single support phase, the trajectory of the swinging foot determines the gait
parameters such as step length, step height, etc. To ensure that the exoskeleton and the
wearer can walk together, the trajectory of the exoskeleton's swing foot should trace that of
the user in time. To do that, a mechanical linkage named inner exoskeleton is attached to the
wearer operator (Low et al., 2006). Accordingly, the exoskeleton that is controllable and
carrying payloads is named outer exoskeleton. The inner exoskeleton equipped with encoders
is to capture the joint information of the pilot.
4.2 Control of the ZMP
If the ZMP of the exoskeleton is within the support area, it implies that the exoskeleton can
keep the stability only by using the ground reaction force without adding any force to the
user. In other words, the user will not feel any extra burden from the exoskeleton. Hence the