A High PSR SOI Current-mode Bandgap Reference
Sheng Junli
1
, Jiang Bingjian
2
, Tang Zhangwen*
ASIC & System State Key Laboratory, Fudan University, Shanghai 201203, China
* Email:zwtang@fudan.edu.cn
Abstract
This paper presents a high PSR current mode bandgap
references. The circuits are designed with adopting
GSMC 130 nm SOI process. The bandgap’s output
voltage value is 0.528V and current value is 10.2μA. It is
tapped out that the temperature coefficient of voltage
reference is 115 ppm/°C from -40°C to 125°C and
current reference is less than 59.4 ppm/°C , power
consumption is 173 μW, the PSR is 95.8 dB at 100kHz,
and adjusting output resistance can realize other output
voltage value with no variation on temperature
coefficient.
Keys:Bandgap,SOI ,Temperature coefficient,PSR
Introduction
Reference source is an important module in analog and
mixed-signal circuits such as data converters. The
reference source should not have variation following
temperature, power voltage and process. Bandgap
reference is a common method which have two classic
mode[1]: voltage mode and current mode. In addition to
that, there is a mode named reverse bandgap[2].
As scaling down, it is uneasy to use voltage mode to
design bandgap voltage reference to generate a output at
about 1.25V by using power lower than 1.2V, not to
mention generating a current reference[3]. Lower power
supply may be more sensitive with disturbance from
environment, so designing a bandgap with low PSR have
the necessity.
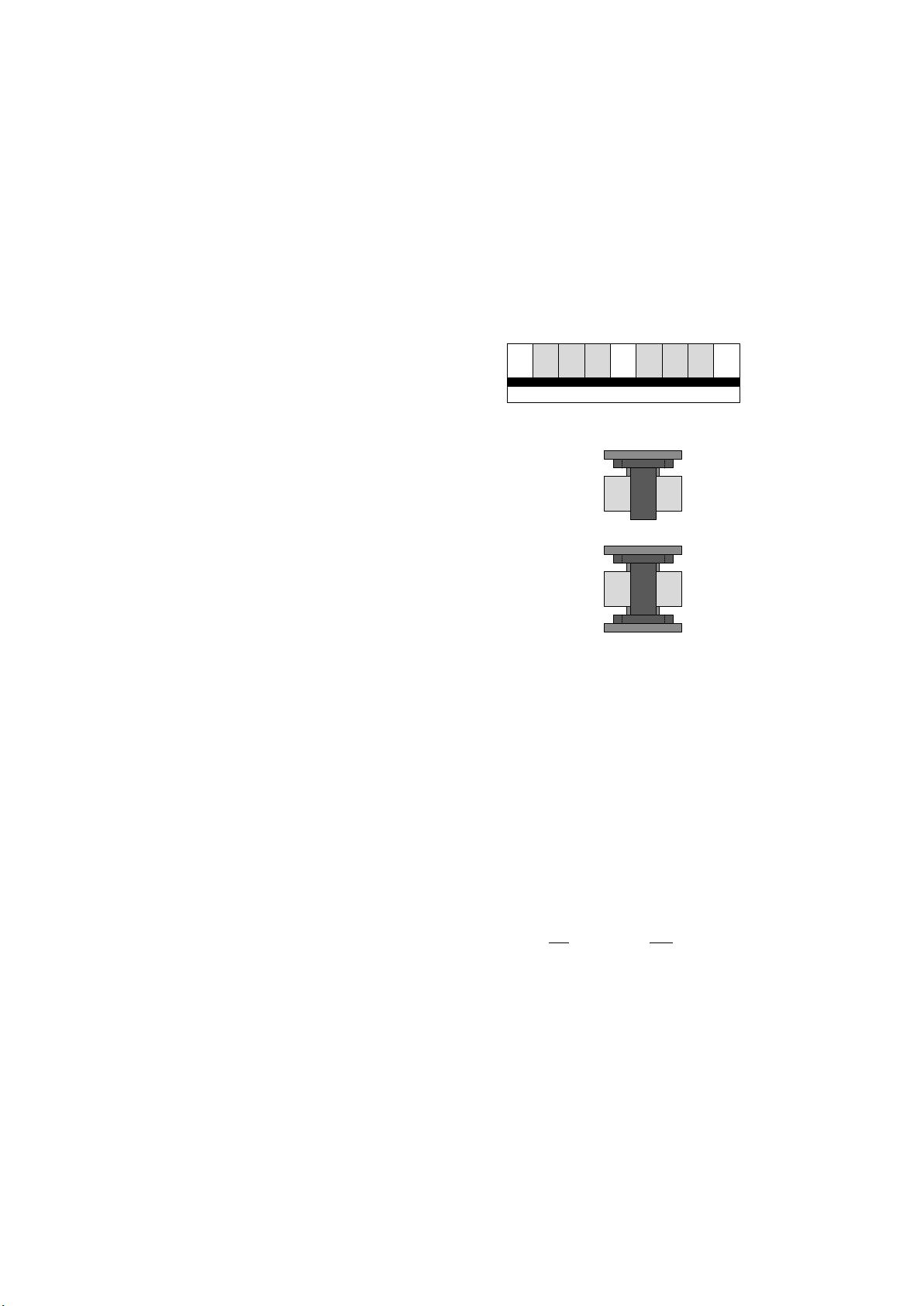
Different from normal body silicon, SOI forms a
semiconductor film on an insulator, which cross-section
drawn is in Figure 1 .So it eliminates the parasitic latch
effect which can be in body silicon CMOS circuit
completely. The drain and source are no longer like a
small well in body silicon, so they have smaller parasitic
capacitance and less noise from substrate. It also proofs
radiation. Then SOI could be applied in the area of
high-speed circuits and irradiation circuits. Furthermore,
as is shown in Figure 2 , the body which is the active
area under poly gate is connected over the poly, so it has
no effect on voltage difference between source and drain
* Project supported by the National Science Funding of China (No.
61376036), ASIC & System State-Key Laboratory Funding, China (No.
2015MS010).
as it is fairly connected by one side or two sides of
source and drain. All these provide a better power
restraint than body silicon.
S G
D
S G
D
OXOX OX
oxide
substrate
Figure 1.The cross-section drawn of SOI
S G
D
B
B
Figure 2. The layout of T-mode and H-mode SOI
2. Circuit realization
The target is to design a reference source to supply a
voltage reference of about 0.525V and a current
reference of about 10μA. The design is taken most view
on temperature coefficient, PSR, and output voltage.
Figure 3 shows a current mode bandgap with output
voltage value of 0.528V and current value of 10.2μA.
2.1 Current mode bandgap core
In Figure 3, resisters R1~3 and diodes D1~2 generate a
current I1 that has less relation with temperature if we
neglect the temperature character of resistance.
3
11
1 ln( )
13
TD
I N V V
RR
(1)
In Figure 3, R1 and D1 and D2 generate PTAT current,
R1 and D2 generate CTAT current. A is the error
amplifier. Usually, we can also use a MOS which works
at the sub-threshold state[4] and use a MOS which is
diode-connected[5] instead of a common diode. Usually,
we use a bipolar which is diode-connected for senior
978-1-4799-8484-8/15/$31.00 ©2015 IEEE









