26 27
20th anniversary edition
2017 Global Customer Experience Benchmarking Report
20th anniversary edition
2017 Global Customer Experience Benchmarking Report
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
70.9
34.1
32.3
31.5
31.3
30.5
26.9
11.6
9.1
7.6
5.5
4.4
Sales revenues or profits
Customer advocacy or loyalty (e.g. NPS)
Customer experience
First contact resolutions (right first time)
Complaint levels (service quality)
Productivity and cost to serve
Employee engagement
Customer effort scores (ease of doing business)
Other
Migration to digital assisted services
Security systems or services
Migration to fully automated services
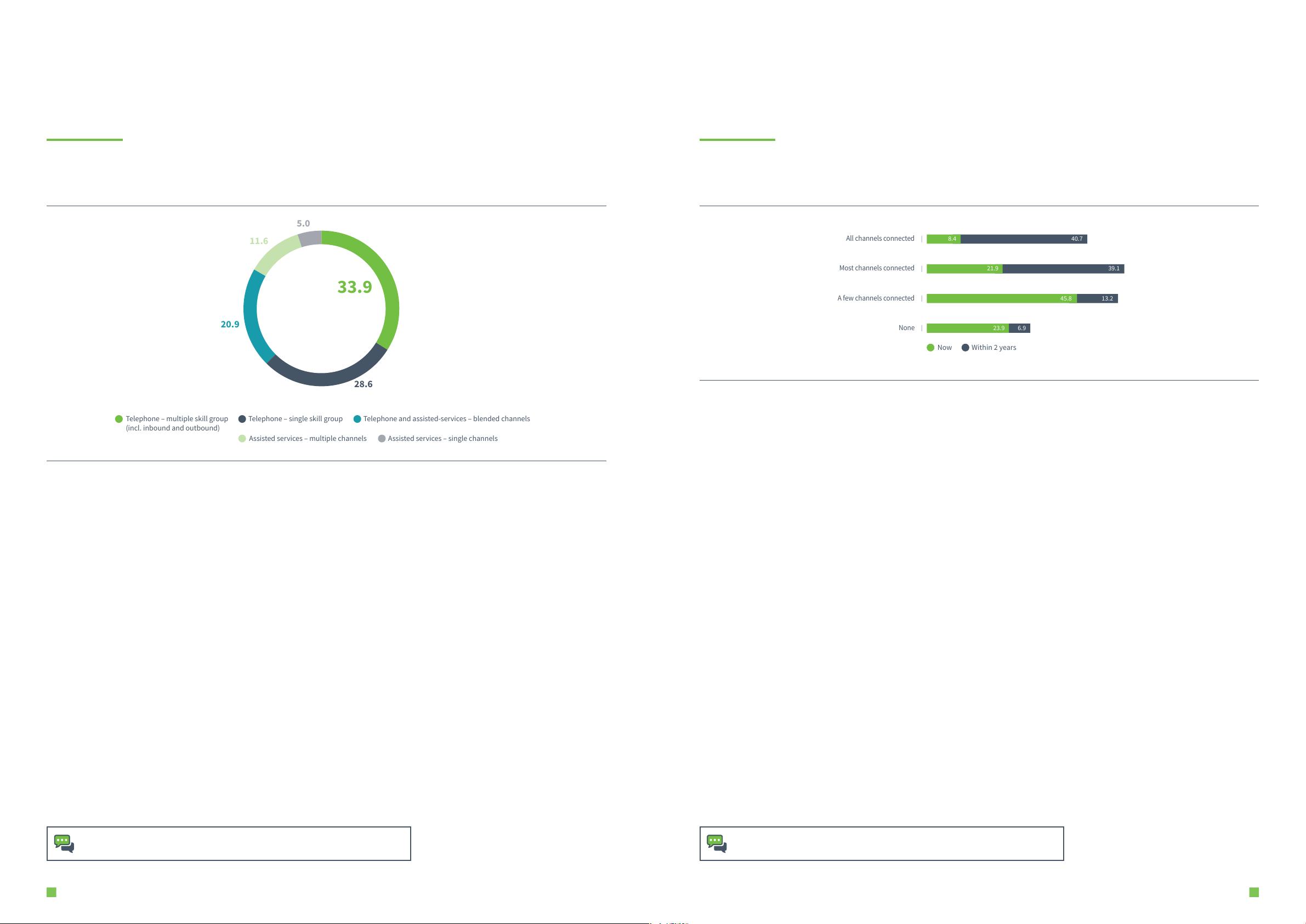
Figure 1.5: What are the top challenges for establishing a full omnichannel strategy?
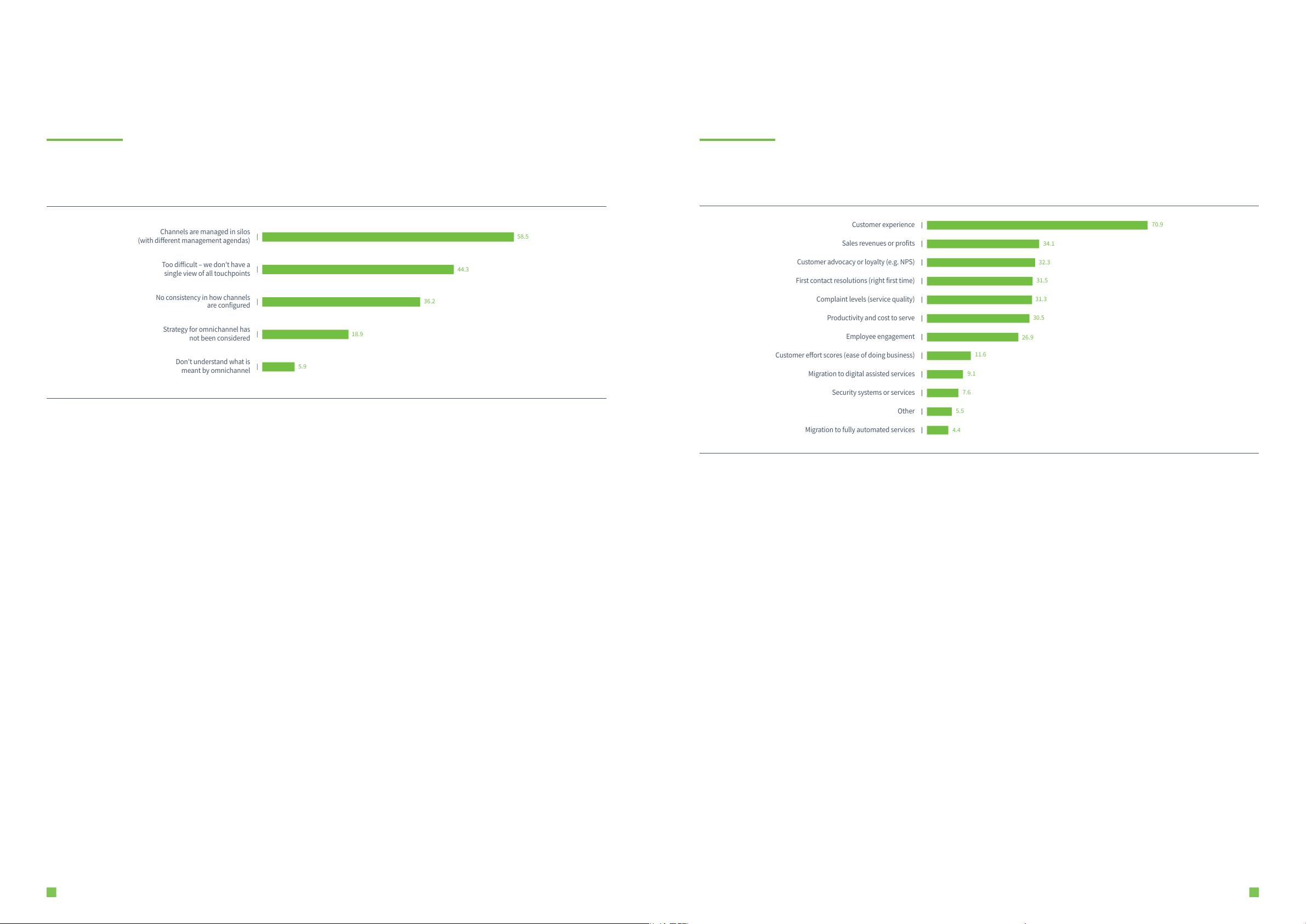
Figure 1.6: What are the top three performance measurements according to your company’s board or executive team?
n | 1110
n | 1345
Strategy Strategy
0 10 20 30 40 50 60
58.5
44.3
36.2
18.9
5.9
Channels are managed in silos
(with different management agendas)
Too difficult – we don't have a
single view of all touchpoints
No consistency in how channels
are configured
Don't understand what is
meant by omnichannel
Strategy for omnichannel has
not been considered
Disparate management is the biggest threat to omnichannel.
A third cite inconsistency in design as a key challenge, and approaching half (44%) say it’s ‘just too hard’.
CX remains a top strategic measurement for organisational performance, and is voted so by more than
twice that of any other metric.
The migration of traic to automated or digital services is permeated by service benchmarks being
accomplished, as opposed to cost savings.
Key findings
Organisations understand the CX benefits created by an omnichannel approach and they
believe in the value CX presents to the organisational objectives. Yet so many still struggle
to deliver on areas receiving so much attention. The biggest blockage point is caused by the
58.5% of organisations who are managing their contact channels via individual silos.
Design, build and review processes (as evidenced in figure 2.7 and 7.7 of our review) are
also a significant threat to ease of resolution and frictionless customer journeys facilitated
by omnichannel system strategies. Over one third (36.2%) of CX operations highlight an
absence of consistency in how channels are configured, indicating flaws in the project
implementation phase - even prior to live deployments.
Omnichannel solutions may not be necessary for every type of provider, although such
scenarios are likely to be an exception. 44.3% of organisations simply state that it’s too diicult,
and may need some help on how to overcome what may not be a sustainable position.
Why it matters: The role and value of omnichannel enablement is strategically well
understood by organisations. The results show that management of channels by siloes
stops visibility, management control, focus, education and enrolment in a broader CX
strategy. Organisational change is required, which is an uncomfortable truth.
Key findings
CX performance has firmly cemented itself by some margin, and for the fih year in
succession, as the top most important performance indicator for boardroom and/or
executive teams. It’s a consistent theme across every region, sector, operation size or type.
There’s just one exception: sales revenues and profits relegate CX to second place when
viewing sales-only ‘service-type’ operations.
Customer advocacy or loyalty (e.g. net promoter score) has jumped a couple of positions
and established itself as the third most important executive level KPI. This wider
consideration of the end-to-end customer experience and business value pertaining to the
interaction, has led to first contact resolution dropping from second place last year to fourth
priority in 2017. It remains a significant focus to directly influence ease of resolution - the
consumer’s top rated impact of CX.
In the 2016 benchmarking report, we commented on executive commitments towards CX
being further evidenced by the fact that cost focus had dropped from second to sixth spot in
one year. We’re encouraged that this has been maintained. Conversely, we’re disheartened to
see the attention on employee engagement drop three positions to seventh place in 2017.
Why it matters: Executive commitment towards CX continues to increase, which is a real
shi from five years ago when focus was predominantly on cost reduction. CX, revenue,
profit growth, customer advocacy and first contact resolution represent the correct metrics
to positively steer and influence strategic customer growth throughout the organisation.
Accelerate your journey
Basic: The first challenge as already
mentioned is ensuring that an organisation
has its own clearly defined ‘single truth’ of
what omnichannel optimisation means, and
is able to articulate this across the entire
business to ensure consistent thinking.
Intermediate: Adapting traditional
organisational silo-based structures to
mitigate functional inconsistency and friction
is something that many organisations are
struggling to achieve even though they
recognise the barriers it causes to CX.
Designing and delivering in a function-based
approach oen leads to delivering a fractured
experience, rather than creating a seamless
and consistent customer experience.
Advanced: With a clear omnichannel
definition and defined cross-functional
collaboration and ownership, organisations
that are succeeding in omnichannel have a
clear set of design principles and maximise
the use of customer journey mapping.
At the same time, they maintain clear
tracking and measurement of actionable
insight at all points in these journeys to
remain adaptive and innovative.
Accelerate your journey
Basic: Simply measuring the outcomes of an
organisation’s CX eorts is not enough. It’s vital
to understand what elements are impacting the
overall CX metric.
Intermediate: Measuring the component parts
of the CX and business eiciency in delivering it,
should be tracked across, and used to improve,
all channels and it should be visible from the
front line to the board room. Ideally you should
measure performance with the minimum time
lag possible and focus on ‘what customers say
and what they did recently’.
Advanced: Use advanced data analytics and
multiple customer satisfaction/sentiment tools
and business metrics to establish a real-time
view of ‘what customers are doing and what
they think about it’, and create a view of CX
eectiveness that spans the entire organisation.
Top strategic performance measures
Omnichannel strategy challenges