COL 10(Suppl.), S13201(2012) CHINESE OPTICS LETTERS June 30, 2012
Analysis on the characteristics of animal tissues based on
the Terahertz time domain spectroscopy system
Chengzhen Lu (
©©©
«««
)
1
, Chen Liu (
444
)
1
, Erliang Cui (
www
)
1
,
Jia Li (
ooo
ZZZ
)
1
, Wei Liu (
444
)
1∗
, and Ping Sun (
±±±
)
2
1
Key Laboratory of Terahertz Optoelectronics, Ministry of Education, Department of Physics,
Capital Normal University, Beijing 100048, China
2
Beijing Normal University, Beijing Area Major Laboratory of Applied Optics,
Department of Physics, Beijing 100875, China
∗
Corresponding author: lwei263@263.net
Received August 17, 2011; accepted October 27, 2011; posted online April 18, 2012
THz spectral properties of several of fresh animal tissues are investigated based on the time domain
system. Terahertz pulse transmission spectra of different animal tissues slices with different thickness
are obtained, and the refractive index, the absorption coefficient, and the extinction coefficient of these
tissues are analyzed and discussed. According to the double Debye model, tissue parameters are simulated
and calculated. The theoretical and experimental results are matched. These studies are helpful to make
further research of the THz spectral performances of human tissues and cancers.
OCIS codes: 320.7100, 320.7150.
doi: 10.3788/COL201210.S13201.
The terahertz spectroscopy has the advantages of non-
ionization and low average power, thus it is not thought
to be hazardous to the tissues of human. Furthermore,
the terahertz waves can excite the vibration mode and
rotation mode of macromolecules. Both amplitude and
phase information of materials which are detected and
then contrasted can be gotten. Compared with visible
light and infrared, it also has the advantage of low sc at-
tering, so the surface character and depth pattern of
samples can be acquired at the sa me time. Therefore, it
makes the terahertz detection in the field of biomedicine
possible to measure the tissue in vivo without any dam-
age.
In recent years, with the development of the tech-
nology o f the terahertz radiatio n source and detection
source, the technology of terahertz imaging is develop-
ing rapidly. Intermolecular transition models can be
detected by the tera hertz radiation. In addition, the vi-
bration frequency of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules
lie in terahertz wave band, and information of these
molecules can be detected c oherently using terahertz
radiation
[1,2]
. Terahertz imaging can detect skin inflam-
mation, such as dermatitis, eczema, and psoriasis, etc.
It is reported that human tissues can b e imaged in vivo
and vitro by the technology of terahertz radiation and
distinguish diseas e d
[3,4]
, normal and infla med tissue in
quality
[4−6]
. THz-CT imaging has the spatial resolution
of sub-millimeter, and it is possible to r e place X-CT with
THz-CT imaging
[2]
. In 2004 and 200 6, various cancer
types and organs were studied by Fitzgerald et al, which
means that THz imaging can be use d to give the tumor
margins in fres h tissues
[7−9]
. However, terahertz imaging
can analy z e the difference be tween tumour tissues a nd
normal tissues in quality at present.
In this letter, in order to distinguish normal tissues,
inflammation and tumor tissues, differe nt kinds of slices
with different thickness are tested and analyzed based
on THz-TDS (terahertz time domain spectrometer) sys -
tem in transmission geometry. The refractive index, the
extinction coefficient, and the absorption coefficient of
tissues are obtained to provide the proof of experiments
and theories for distinguishing different tissues in quan-
tification.
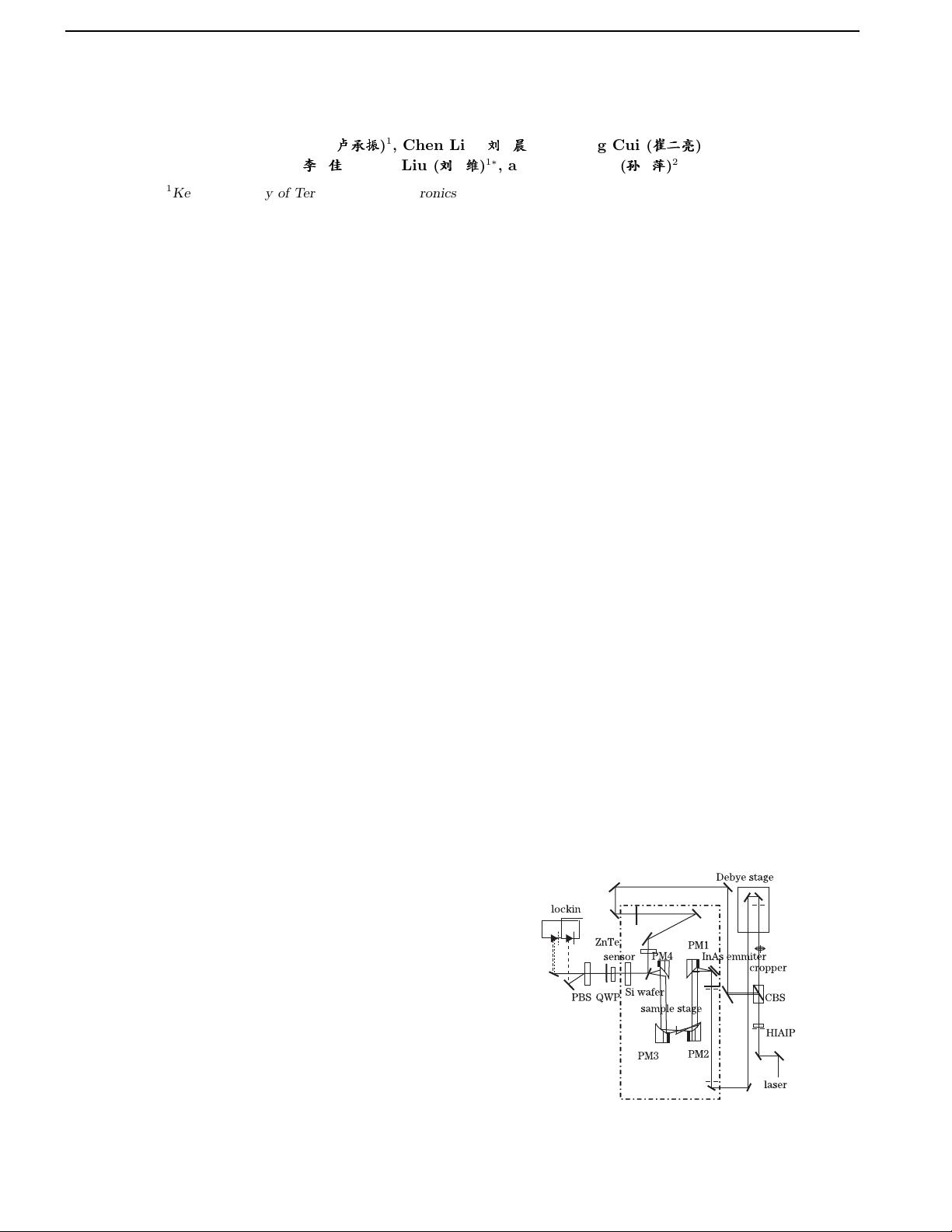
Based on the Z-3 THz-TDS system working in trans-
mission geometry, the blo ck diagram of elements is shown
in Fig. 1, in which the mode-locked Mai-Tai laser gener-
ates femtosecond pulse with 800 nm center wavelength,
pulse width less than 120 fs and pulse power 1 W. The
mechanism of THz beam emission is that femtosecond
laser illuminates InAs wafer to produce the photoinduced
Dember electric field with the carrier accelerated by addi-
tional bias voltage. The Terahertz detection mechanism
is linear electro-optic Pockels effect. A polarizer, quar-
ter wave plate and a Wollaston Prism separate the light
into two orthogonal polarized lights. Then the change
in polarization is detected by the balanced photodiodes.
The delay line with the 200 Hz sawtooth oscillating scans
the entire THz pulse in order to obtain the THz field as a
Fig. 1. Block diagram of THz elements.
1671-7694/2012/SS13201(4) S13201-1
c
2012 Chinese Optics Letters









