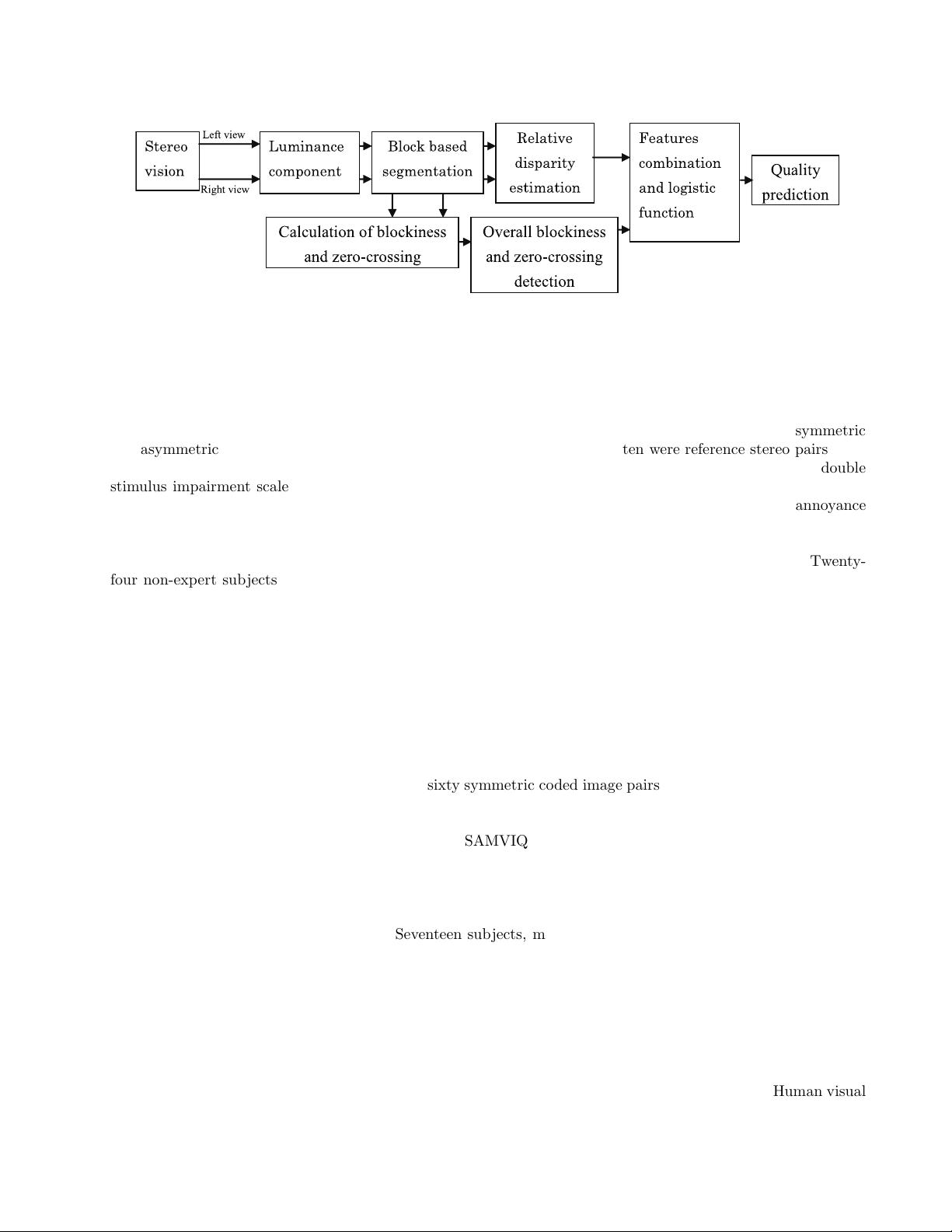
Figure 2. Proposed NR quality evaluation model.
2. THE SUBJECTIVE DATABASES
2.1 Toyama Database
The Media Information and Communication Technology (MICT) lab., University of Toyama conducted subjective
experiment on 24 bit/pixel RGB color stereoscopic images.
21
The database contained JPEG coded symmetric
and asymmetric 490 stereoscopic image pairs of size 640 × 480. Out of all, ten were reference stereo pairs. The
seven quality scales (QS: 10, 15, 27, 37, 55, 79, and reference) were selected for the JPEG coder. A double
stimulus impairment scale (DSIS) method was used in the subjective experiment. Both distorted and original
images were displayed sequentially . At the end of the presentation, the subject was asked to assess the annoyance
he/she felt over all perceptual quality on the distorted stereo image with respect to the reference stereo one. The
impairment scale contained five categories marked with adjectives and numbers as follows: “Imperceptible =5”,
“Perceptible but not annoying =4”, “Slightly annoying =3”, “Annoying =2” and “Very annoying =1”. Twenty-
four non-expert subjects (12 males and 12 females, age range: 19-32 years) were shown the database; most of
them were college/university student. A 10-inch auto stereoscopic, LCD (SANYO) display (resolution: 640 ×
480, image splitter technology) was used in this experiment to display the stereoscopic images and the subjects
were instructed about the limited horizontal viewing angle to perceive 3D image correctly. Mean opinion scores
(MOSs) were then computed for each stereo image after the screening of post-experiment results according to
ITU-R Rec. 500-10.
22
The MOS histogram and standard deviations of all MOSs of the database are shown in
Figure 1.
2.2 IRCCyN/IVC Database
The IRCCyN lab, university of Nantes conducted subjective experiment on 24 bit/pixel RGB color stereoscopic
images of size 512 × 448.
10
Six reference stereo images and their five degradation levels JPEG and JPEG2000
coded images were used in the database. Total sixty symmetric coded image pairs were consider in the database.
JPEG2000 compressions used bit rates ranging from 0.16 bits per pixel (bpp) to 0.71 bpp while JPEG compression
involved bit rates ranging from 0.24 bpp to 1.3 bpp. The subjective assessment methodology for video quality
(SAMVIQ) method was used in the experiment. The SAMVIQ method has possible to combine quality evaluation
capabilities and ability to discriminate similar levels of quality, using an implicit comparison process. The method
is based on a random access process to play sequence files. Subjects can start and stop the evaluation process
as they wish and can follow their own paces in rating, modifying grades, repeating play out when needed. Each
subject used a slider on a continuous scale graded from 0 to 100 defined by 5 linearly quality terms “bad”,
“poor”, “fair”, “good”, and “Excellent”. Seventeen subjects, mostly males familiar with subjective tests, with
an average age of 28.2 years took part in the test. A 21-inch Samsung SyncMaster 1100MB stereoscopic display
(resolution: 1024 × 768) was uses in the experiment. At the end of the test sessions, the difference mean opinion
score (DMOS) is computed as the difference between the MOS for the hidden reference and the MOS one relative
to the image. Details of the experiment was discussed in.
10
3. OBJECTIVE STEREOSCOPIC IMAGE QUALITY EVALUATION
It has already been established that the primary function of the human visual system (HVS) is to extract struc-
tural or edge information from the viewing field, and the HVS is highly adapted for this purpose.
23
Human visual
SPIE-IS&T/ Vol. 7524 75240T-3
Downloaded from SPIE Digital Library on 11 Aug 2010 to 210.32.178.105. Terms of Use: http://spiedl.org/terms