FEM Modeling and Simulation of a Layered SAW
device Based on ZnO/128° YX LiNbO
3
Zaid. T. Salim
School of Nano Electronic Engineering
University Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP)
Perlis, Malaysia
zaidtareq86@gmail.com
U. Hashim, and M. K. Md. Arshad
Institution of Nano Electronic Engineering
University Malaysia Perlis (UniMAP)
Perlis, Malaysia
uda@unimap.edu.my
mohd.khairuddin@unimap.edu.my
Abstract—In this paper, the modeling and simulation of a
layered surface acoustic wave device based on ZnO/128° YX
LiNbO
3
were conducted using Finite Element Method (FEM) in
COMSOL Multiphysics 4.3b platform. The SAWs propagation
characteristics were numerically investigated with variation in
the ZnO layer thickness. The results show that the SAW device
frequency response was varied with the ZnO layer thickness
from 166.1 MHz to 150.4 MHz. The free and metalized phase
velocities (
f
and
m
) were calculated and used to calculate the
electromechanical coupling coefficient (K
2
) of the structure. The
results show that a large coupling coefficient of 6.05% can be
obtained in 500 nm ZnO layer thickness which is in a good
agreement with the data published by Nakamura and
Hanamoka.
Keywords—FEM; SAW device; Surface acoustic wave; 128°
YX LiNbO
3
; ZnO
I. INTRODUCTION
Surface acoustic wave devices are used in many types of
electronic components such as filters, resonators and actuators
[1]. Recently, it were investigated both theoretically and
experimentally as gas sensor, pressure sensors, bio sensors and
many other applications such as humidity, magnetic field and
ultrasonic sensors [2-4].A large number of studies were
conducted to develop layered SAW devices by utilizing a
piezoelectric thin film over the substrate to modify the SAW
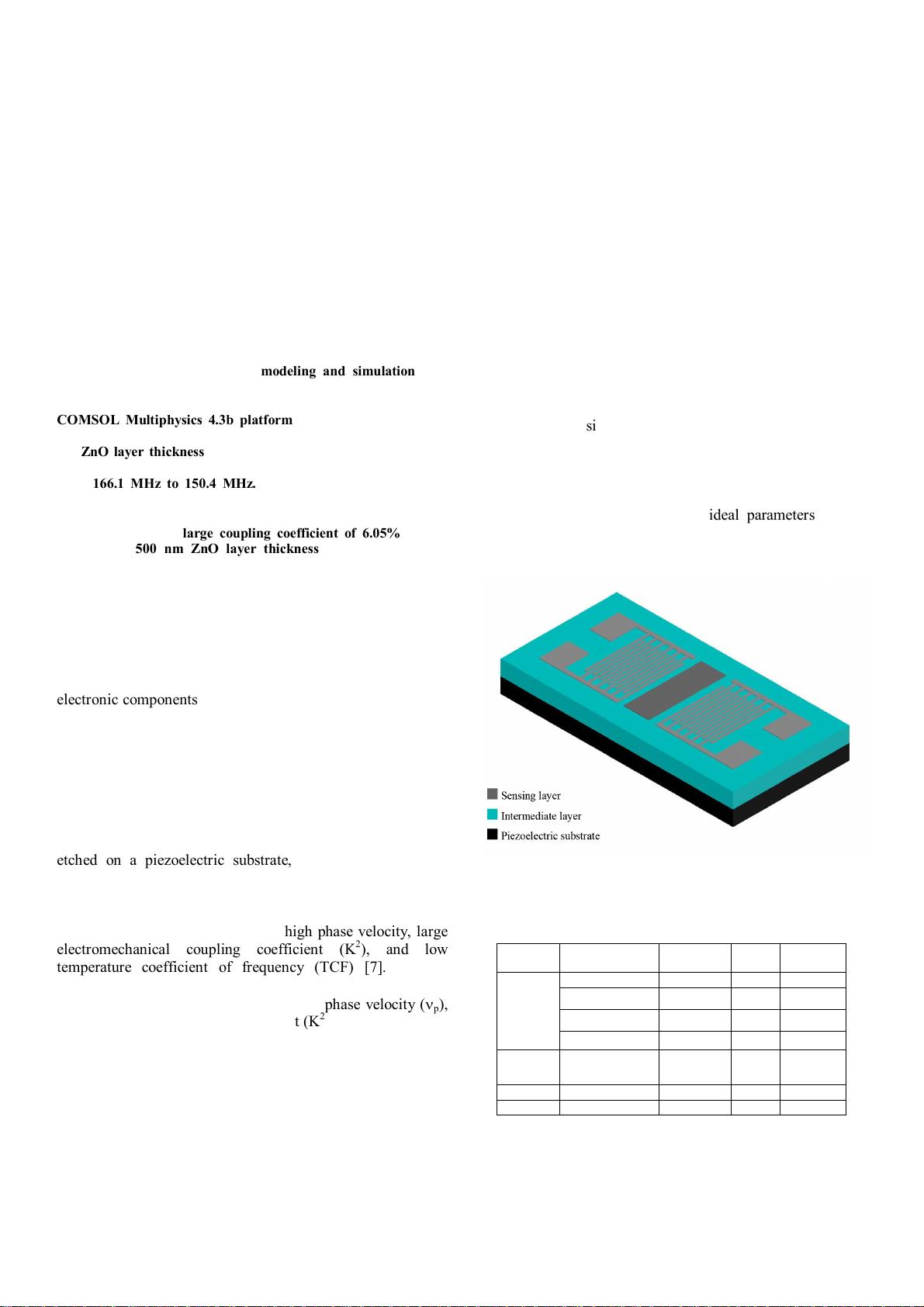
device performance [5]. A typical two-port layered SAW
device is consist of two interdigitated transducers (IDTs)
etched on a piezoelectric substrate, intermediate layer and
sensing layer [6] as illustrated in Fig. 1.
Various factors must be considered in the selection of the
piezoelectric materials used in the SAW device. The
piezoelectric materials must have a high phase velocity, large
electromechanical coupling coefficient (K
2
), and low
temperature coefficient of frequency (TCF) [7]. Table I
summarize the properties of the most common piezoelectric
materials. Choi et al [8] reported that the phase velocity (
p
),
electromechanical coupling coefficient (K
2
) and the sensitivity
can be modified by utilizing a dielectric intermediate layer to
the SAW device structure. Furthermore, Armstrong et al. [9]
reported that when using a piezoelectric thin film over a
piezoelectric substrate, more efficient SAWs can be obtained.
ZnO is a commonly used piezoelectric material due to its
electrical, structural and optical properties. ZnO thin films
were used to generate SAWs over a non-piezoelectric
substrate such as silicon glass and diamond [10-12]. Kalantar-
Zadeh et al. [13] reported that using a ZnO thin film can
increase the SAW device sensitivity compared to SiO
2
in
study using ST-quarts substrate. We can conclude that a pre-
fabrication simulation can help us to investigate the SAW
device performance and select the ideal parameters for the
required application by gaining a better understanding about
the propagation characteristics of the structure.
Fig. 1. Schematic of a typical two-port layered SAW device.
TABLE I. THE MOST COMMON PIEZOELECTRIC MATERIALS USED IN SAW
DEVICES.
Material Orientation/cut
(m/s)
K
2
(%)
TCD
(ppm)/ºC
LiNbO
3
Y-Z 3488 4.5 94
41º Y-X 4751 11.3 50
64º Y-X 4478 17.2 70
128º Y-X 3996 5.5 75
LiTaO
3
77.1º Y-Z
112º X-Y
3254
3300
0.72
0.70
35
18
ZnO
(11-20) 2700 1.1 59-42
SiO
2
47.5º Y-X(ST) 3158 0.11 0
IEEE-ICSE2016 Proc. 2016, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia
978-1-5090-2383-7/16/$31.00 ©2016 IEEE
好的基
片材料
必须要
包含三
个特
点:1:
高的相
位速
度,2:
大的机
电耦合
系数,
3:低的
频率温
度系数
在一般的基片无法满足一
个滤波器需要的三个要求
时,我们可以使用一个中
间的介电层来改变一个基
片的系数三种基本的系数









