PDF: 9709604409/Source: 2594706000 Aptina reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
MT9M413_DS - Rev. B 9/10 EN
8 ©2008 Aptina Imaging Corporation. All rights reserved.
MT9M413: 1.3Mp CMOS Digital Image Sensor
External Control Sequence
External Control Sequence
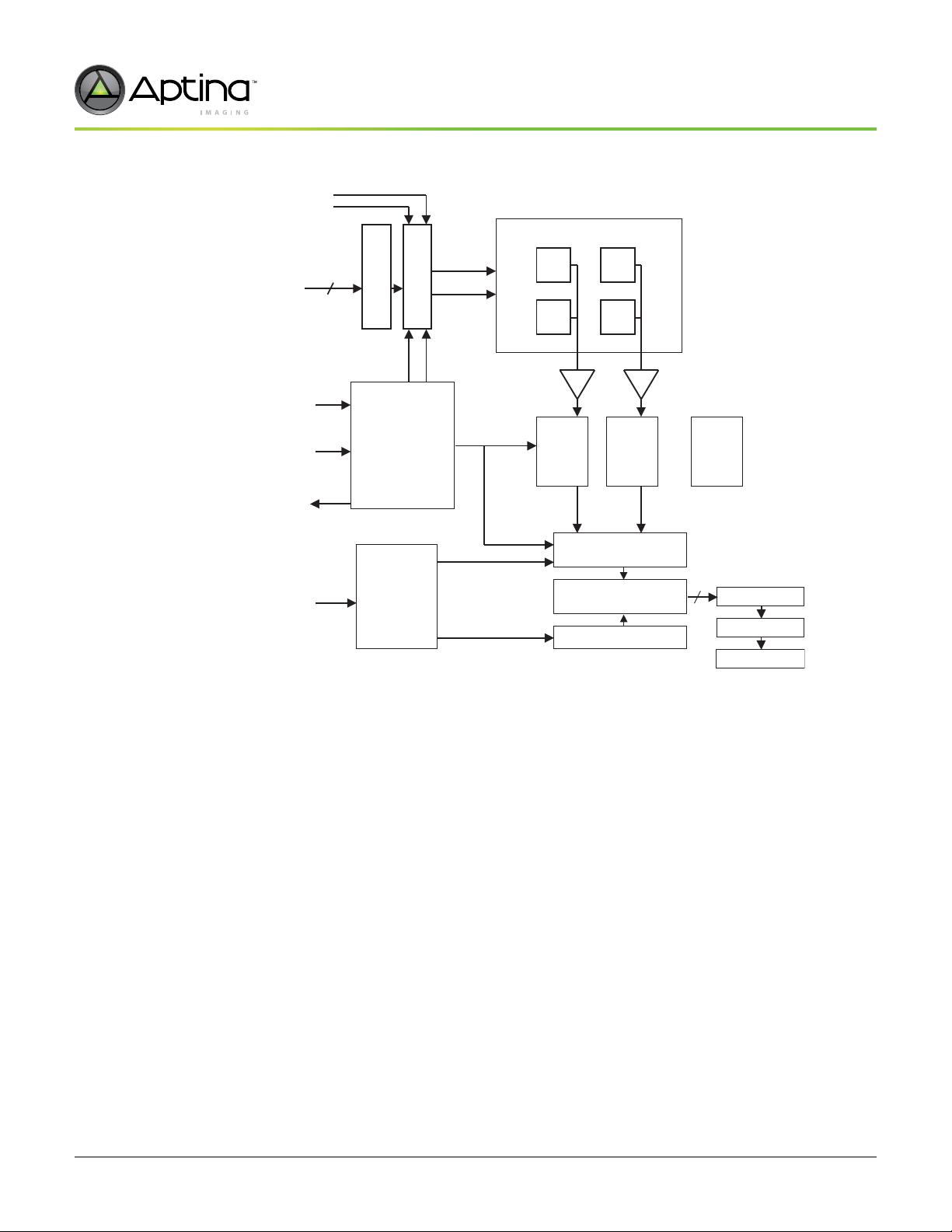
The MT9M413 includes on-chip timing and control circuitry to control most of the pixel,
ADC, and output multiplexing operations. However, the sensor still requires a controller
(FPGA, CPLD, ASIC) to guide it through the full sequence of its operation.
With the TrueSNAP freeze-frame electronic shutter, signal charges are integrated in all
pixels in parallel. The charges are then sampled into pixel analog memories (one
memory per pixel) and subsequently, row by row, are digitized and read out of the
sensor.
The integration of the photosignal is controlled by two control signals:
•PG_N
•TX_N
To clear pixels and start new integration, PG_N is LOW. To transfer the data into pixel
memory, TX_N is LOW. The time difference between the two procedures is the exposure
time. It should be noted that neither the PG_N or TX_N pulses clear the pixel analog
memory. Pixel memory can be cleared during the previous readout (that is, the readout
process resets the pixel analog memory), or by applying PG_N and TX_N together
(clearing both pixel and pixel memory at the same time).
With the TrueSNAP freeze-frame electronic shutter, the sensor can operate in either
simultaneous or sequential mode, generating continuous video output. In simultaneous
mode, as a series of frames is being captured, the PG_N and TX_N signals are exercised
while the previous frame is being read out of the sensor. In simultaneous mode, the end
of integration occurs in the last row of the frame (row #1023) or in the last row of the
window of interest. The position of the start integration is then calculated from the
desired integration time. In sequential mode, the PG_N and TX_N signals are exercised
to control the integration time, and then digitization and readout of the frame take
place. Alternatively, the sensor can run in single frame or snapshot mode in which one
image is captured.
The sensor has a column-parallel ADC architecture that allows the array of 1,280 ADCs
on the chip to digitize the analog data from an entire pixel row simultaneously. Table 3
shows the input signals utilized to control the conversion and readout process.
The 10-bit ROW_ADDR (row address) input bus selects the pixel row to be read for each
readout cycle. The ROW_STRT_N signal starts the process of reading the analog data
from the pixel row, the ADC, and the storage of the digital values in the ADC registers.
When these actions are completed, the sensor sends a response back to the system
controller using the ROW_DONE_N. Row address must be valid for the first half of the
row processing time (the period between ROW_START_N and ROW_DONE_N).
The MT9M413 contains a pipeline style memory array, which is used to store the data
after digitization. This memory also allows the data from the previous row conversion
cycle to be read while a new conversion is taking place.
Table 3: Conversion and Readout Process
Signal Name Description Input Bus Width
ROW_ADDR Row address 10-bit
ROW_STRT_N Row start 1-bit
LD_SHFT_N Load shift register 1-bit
DATA_READ_EN_N Data read enable 1-bit