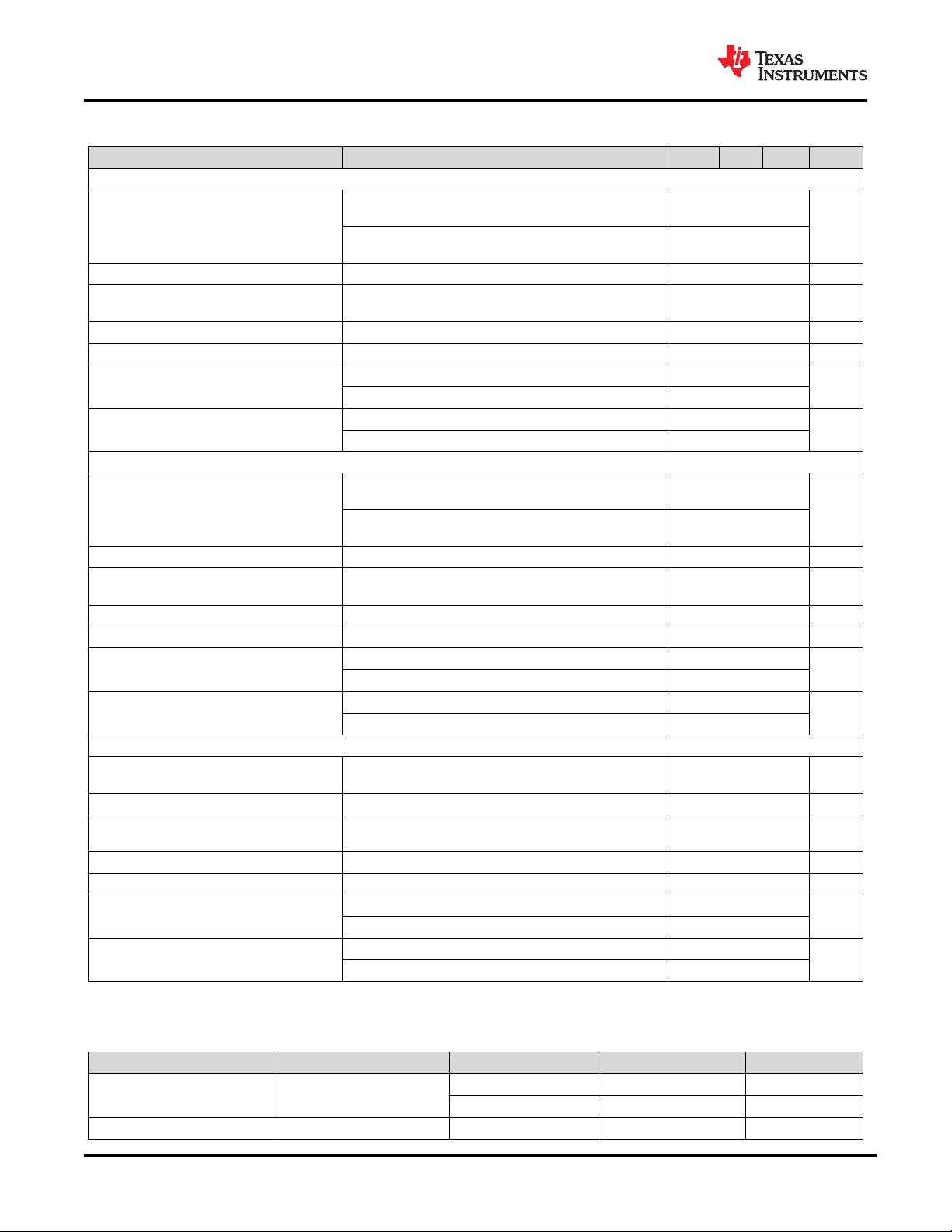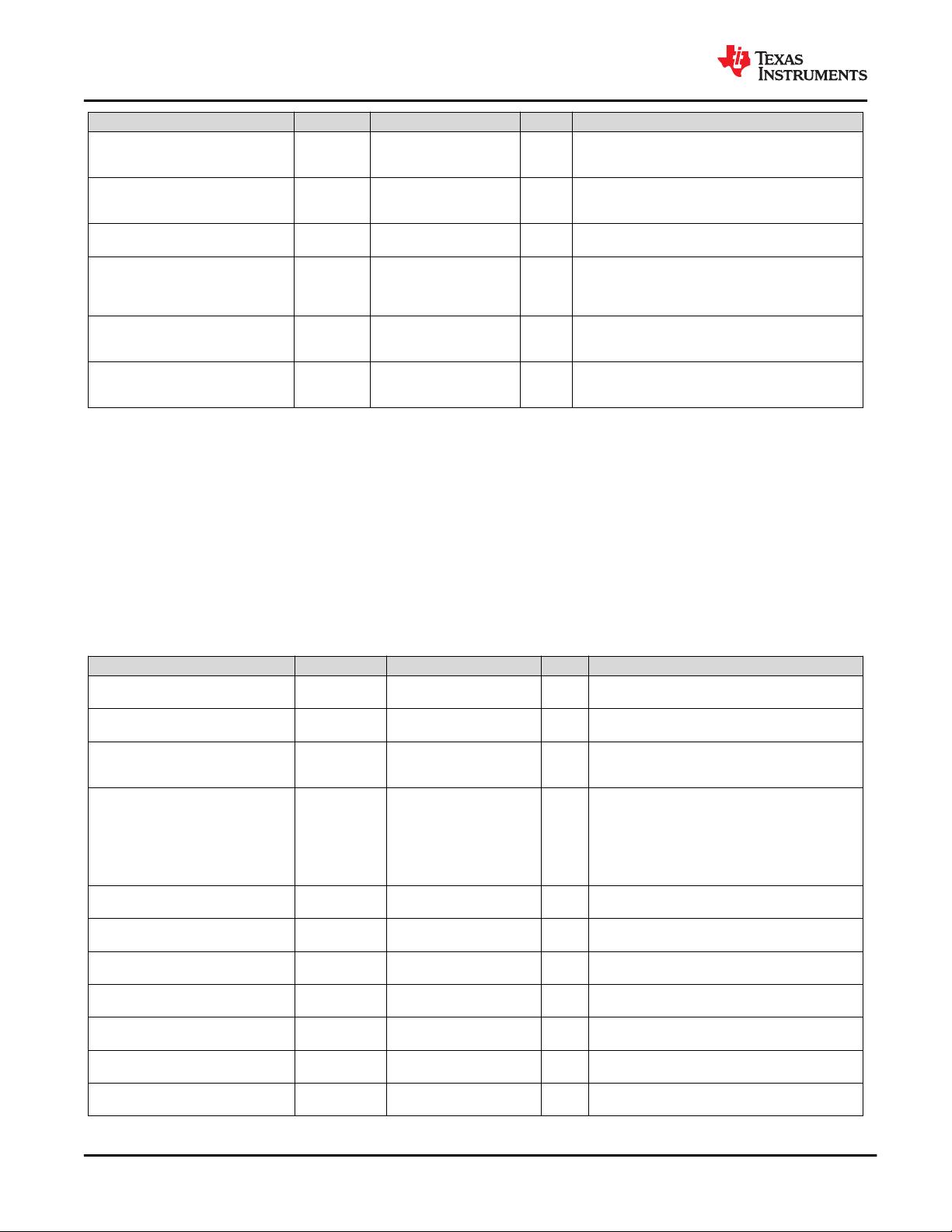
PARAMETER TERMINALS MIN NOM MAX UNIT COMMENTS
V
TX-IDLE-DIFF-AC-p
Electrical idle differential peak output
voltage
TXP, TXN 0 20 mV V
TX-IDLE-DIFFp
= |V
TXP-Idle
– V
TXN-Idle
| ≤ 20 mV
V
TX-RCV-DETECT
The amount of voltage change allowed
during receiver detection
TXP, TXN 600 mV
The total amount of voltage change that a transmitter can
apply to sense whether a low impedance receiver is
present.
T
TX-IDLE-MIN
Minimum time spent in electrical idle
TXP, TXN 20 ns Minimum time a transmitter must be in electrical idle.
T
TX-IDLE-SET-TO-IDLE
Maximum time to transition to a valid
electrical idle after sending an EIOS
TXP, TXN 8 ns
After sending the required number of EIOSs, the
transmitter must meet all electrical idle specifications
within this time. This is measured from the end of the last
EIOS to the transmitter in electrical idle.
T
TX-IDLE-TO-DIFF-DATA
Maximum time to transition to a valid diff
signaling after leaving electrical idle
TXP, TXN 8 ns
Maximum time to transistion to valid diff signaling after
leaving electrical idle. This is considered a debounce time
to the Tx.
C
TX
AC coupling capacitor
TXP, TXN 75 200 nF
All transmitters shall be AC coupled. The AC coupling is
required either within the media or within the transmitting
component itself.
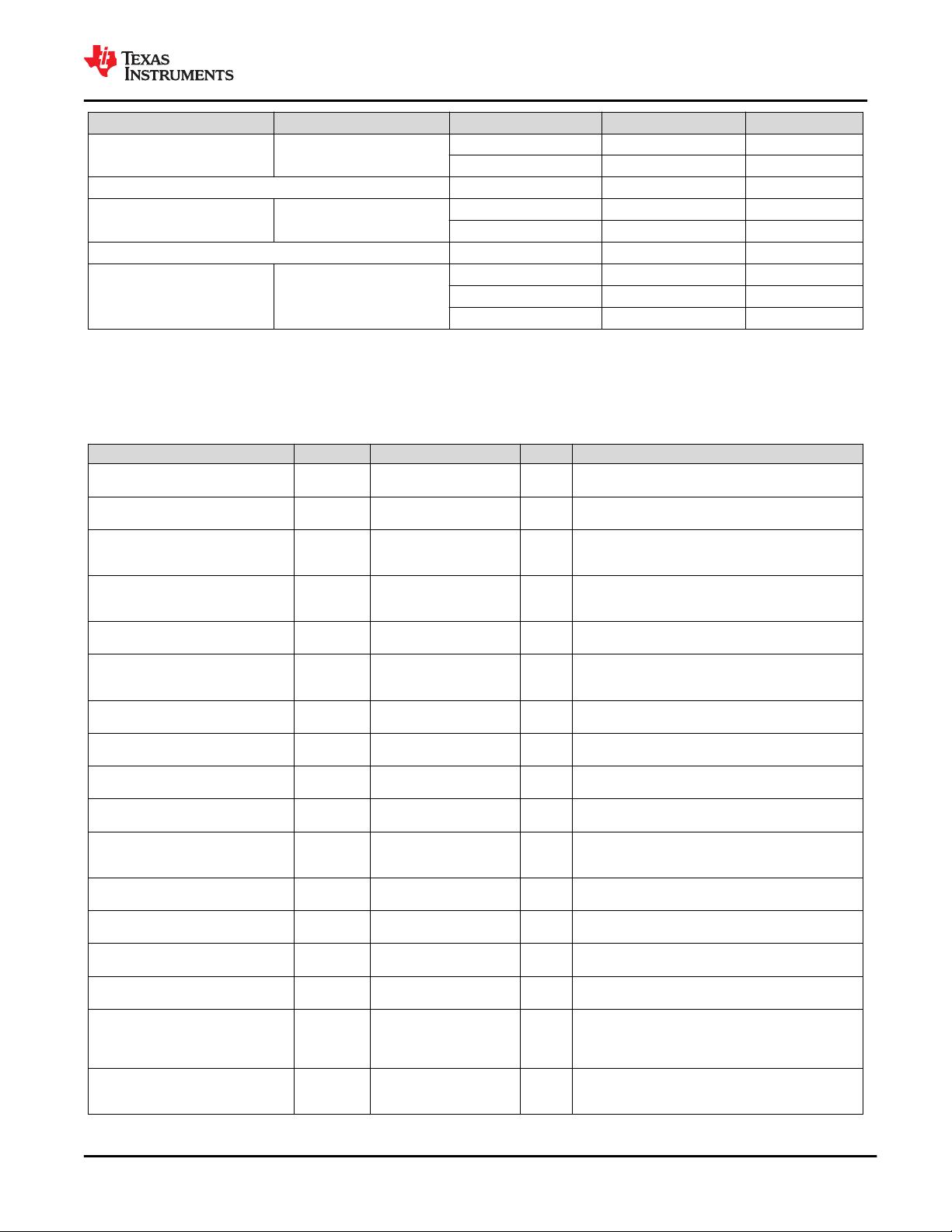
(1) SCC permits a 0, –5000 ppm modulation of the clock frequency at a modulation rate not to exceed 33 kHz.
(2) Measurements at 2.5 GT/s require a scope with at least 6.2 GHz bandwidth. 2.5 GT/s may be measured within 200 mils of Tx device's
pins, although deconvolution is recommended.
(3) Transmitter jitter is measured by driving the transmitter under test with a low jitter "ideal" clock and connecting the DUT to a reference
board.
(4) Transmitter raw jitter data must be convolved with a filtering function that represents the worst case CDR tracking BW. After the
convolution process has been applied, the center of the resulting eye must be determined and used as a reference point for obtaining
eye voltage and margins.
(5) Measurement is made over at least 10 UI.
(6) The Tx PLL Bandwidth must lie between the min and max ranges given in the above table. PLL peaking must lie below the value listed
above. Note: the PLL B/W extends from zero up to the value(s) specified in the above table.
(7) A single combination of PLL BW and peaking is specified for 2.5 GT/s implemenations.
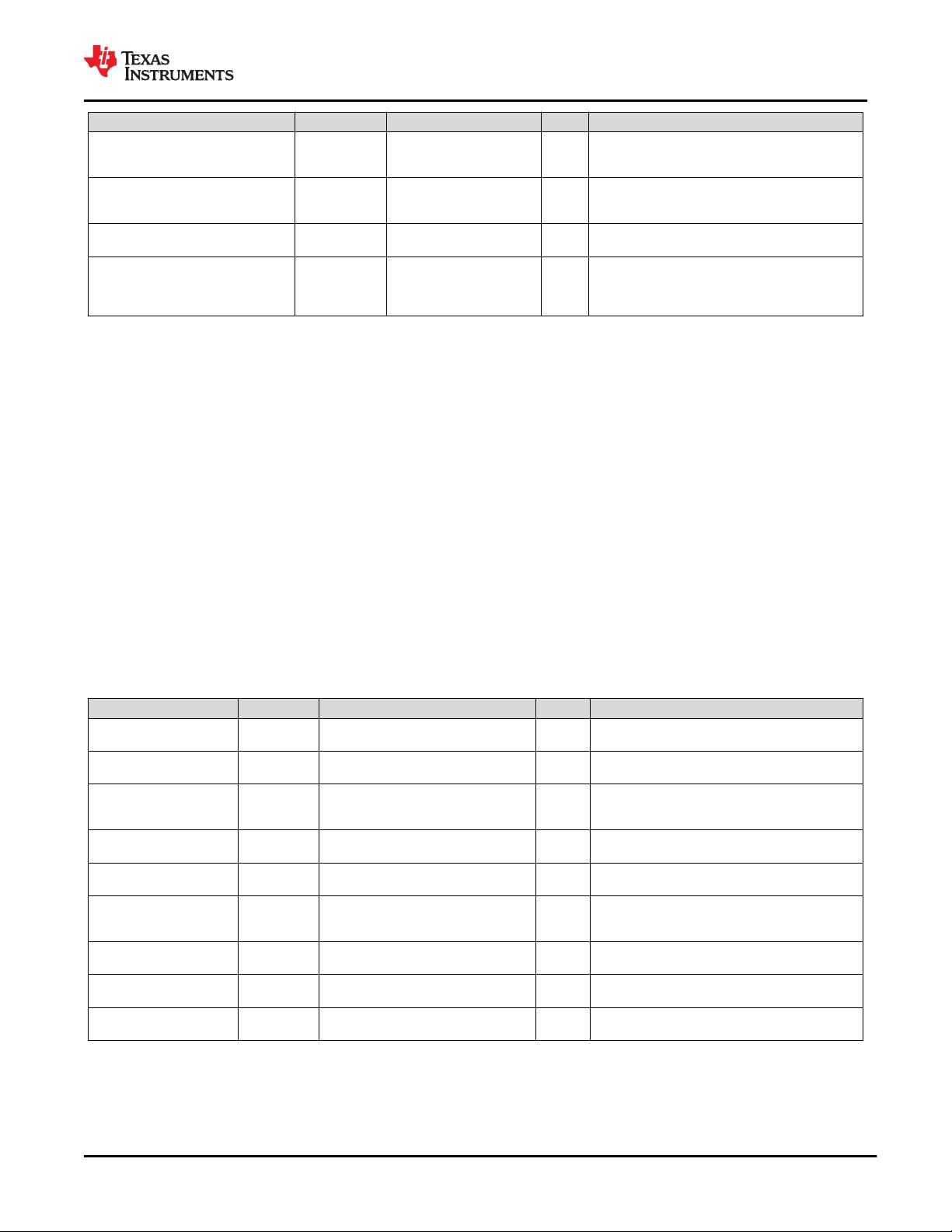
6.7 PCI Express Differential Receiver Input Ranges
PARAMETER
TERMINALS MIN NOM MAX UNIT COMMENTS
UI
(1)
Unit interval
RXP, RXN 399.88 400.12 ps
Each UI is 400 ps ±300 ppm. UI does not account for
SSC dictated variations.
V
RX-DIFF-PP-CC
(2)
Differential input peak-to-peak voltage
RXP, RXN 0.175 1.200 V V
RX-DIFFp-p
= 2*|V
RXP
– V
RXN
|
T
RX-EYE
(2)
(3)
Minimum receiver eye width
RXP, RXN 0.4 UI
The maximum interconnect media and transmitter jitter
that can be tolerated by the receiver is derived as T
RX-
MAX-JITTER
= 1 – T
RX-EYE
= 0.6 UI
T
RX-EYE-MEDIAN-to-MAX-JITTER
(2)
(3)
Maximum time between the jitter median
and maximum deviation from the median
RXP, RXN 0.3 UI
Jitter is defined as the measurement variation of the
crossing points (V
RX-DIFFp-p
= 0 V) in relation to
recovered TX UI. A recovered TX UI is calculated over
3500 consecutive UIs of sample data. Jitter is
measured using all edges of the 250 consecutive UIs in
the center of the 3500 UIs used for calculating the TX
UI.
BW
RX-PLL-HI
(6)
Maximum Rx PLL bandwidth
RXP, RXN 22 MHz Second order PLL jitter transfer bounding function.
BW
RX-PLL-LO-3DB
(6)
Minimum Rx PLL for 3 dB peaking
RXP, RXN 1.5 MHz Second order PLL jitter transfer bounding function.
V
RX-CM-AC-P
(2)
AC peak common mode input voltage
RXP, RXN 150 mV
V
RX-CM-AC-P
= RMS(|V
RXP
+ V
RXN
|/2 – V
RX-CM-DC
)
V
RX-CM-DC
= DC
(avg)
of |V
RXP
+ V
RXN
|/2.
RL
RX-DIFF
(4)
Differential return loss
RXP, RXN 10 dB
Measured over 50 MHz to 1.25 GHz with the P and N
lines biased at +300 mV and –300 mV, respectively.
RL
RX-CM
(4)
Common mode return loss
RXP, RXN 6 dB
Measured over 50 MHz to 1.25 GHz with the P and N
lines biased at +300 mV and –300 mV, respectively.
Z
RX-DIFF-DC
(5)
DC differential input impedance
RXP, RXN 80 120 Ω RX dc differential mode impedance
Z
RX-DC
(4)
(5)
DC input impedance
RXP, RXN 40 60 Ω
Required RXP as well as RXN dc impedance (50 Ω
±20% tolerance).
XIO2001
SCPS212J – MAY 2009 – REVISED JANUARY 2021
www.ti.com
18 Submit Document Feedback
Copyright © 2021 Texas Instruments Incorporated
Product Folder Links: XIO2001