978-1-5386-0462-5/17/$31.00 ©2017 IEEE. VCIP 2017, Dec. 10 – 13, 2017, St Petersburg, U.S.A.
Polar Square Projection for Panoramic Video
Yueming Wang, Ronggang Wang, Zhenyu Wang, Kui Fan
Shenzhen Graduate School, Peking University
Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
wymmail@foxmail.com, {rgwang,
wangzhenyu}@pkusz.edu.cn, kuifan@pku.edu.cn
Yufan Deng, Shensian SYU, Ming-Jong Jou
Shenzhen China Star Optoelectronics Semiconductor
Display Technology Co. Ltd.
Guangdong, China
{dengyufan, Valexsyu, mingjongjou}@tcl.com
Abstract—Panoramic video provides an immersive experience
by presenting a 360° spherical video content. Due to the limitations
of coding and storage technology, the spherical panoramic video
needs to be projected onto the two-dimensional plane for storage
and encoding. In this paper, we propose a polar square projection
scheme. We project the area near the poles of the sphere into two
square planes and a latitude circle on sphere is projected to a
square circle on squares plane, in addition, the rest of area on
sphere is projected into a rectangle by means of equal area
projection. Experimental results show our proposed projection
can obtain a gain of 11.63% BD-rate compared to the
equirectangular projection.
Keywords—virtual reality, panoramic video, spherical video
projection, aqui-angle projection, equal area projection
I. INTRODUCTION
Panoramic video is a typical content for virtual reality
applications, and panoramic video provides an immersive visual
experience by presenting a 360° video. Users usually watch
panorama video through head mounted displays (HMDs). HMD
simulates a sphere of real space, where the viewer is at the center
of the sphere, and HMD can track users head direction and
render corresponding video content to provide a sense of
immersion.
Unfortunately, existing encoding techniques do not support
the processing of spherical video. Therefore, the spherical
panoramic video needs to be projected onto the two-dimensional
plane for storage and encoding. And since panoramic video
provides 360 degrees of video content, panoramic video usually
requires a higher resolution than traditional video. With the
development of virtual reality video capture devices, the
resolution of panoramic video is increasing to 8k and even
higher-resolution. In order to address the above issues, Both
ISO/IEC MPEG and IEEE 1857 have setup adhoc workgroups
to standardize efficient panoramic video projections and coding
methods [6].
There are many projection methods to map a spherical
panoramic video onto a two-dimensional plane [1][2], and the
coding efficiency varies with different projection methods.
Equirectangular projection [3] (ERP) is one of the most basic
and common projection methods, and is widely used in
panoramic video. However, ERP has severe oversampling in
high latitude regions and the coding efficiency is low. In order
to improve the coding efficiency of panoramic image, many
projection methods were proposed. Cube projection is a typical
method, which projects the sphere onto the cube by perspective
projection [4]. Afterwards, octahedron projection (project the
sphere onto the octahedron by perspective projection) [5] and
icosahedron projection (ISP, project the sphere onto the
icosahedron by perspective projection) [6][7] were proposed to
obtain a better approximation of the sphere.
In [8], Yu et al proposed content adaptive representations of
omnidirectional videos, which divide video of equirectangular
format into tiles, then the tiles are down-sampled based on the
content of the video. Moreover, Yu et al obtains an average
division and down sampling configuration according to the test
data set.
In [9], a novel tile segmentation projection was proposed,
according to latitude, the author divides the sphere into 3 or 5
pieces then the polar pieces are projected into circles, and other
pieces are projected into rectangles.
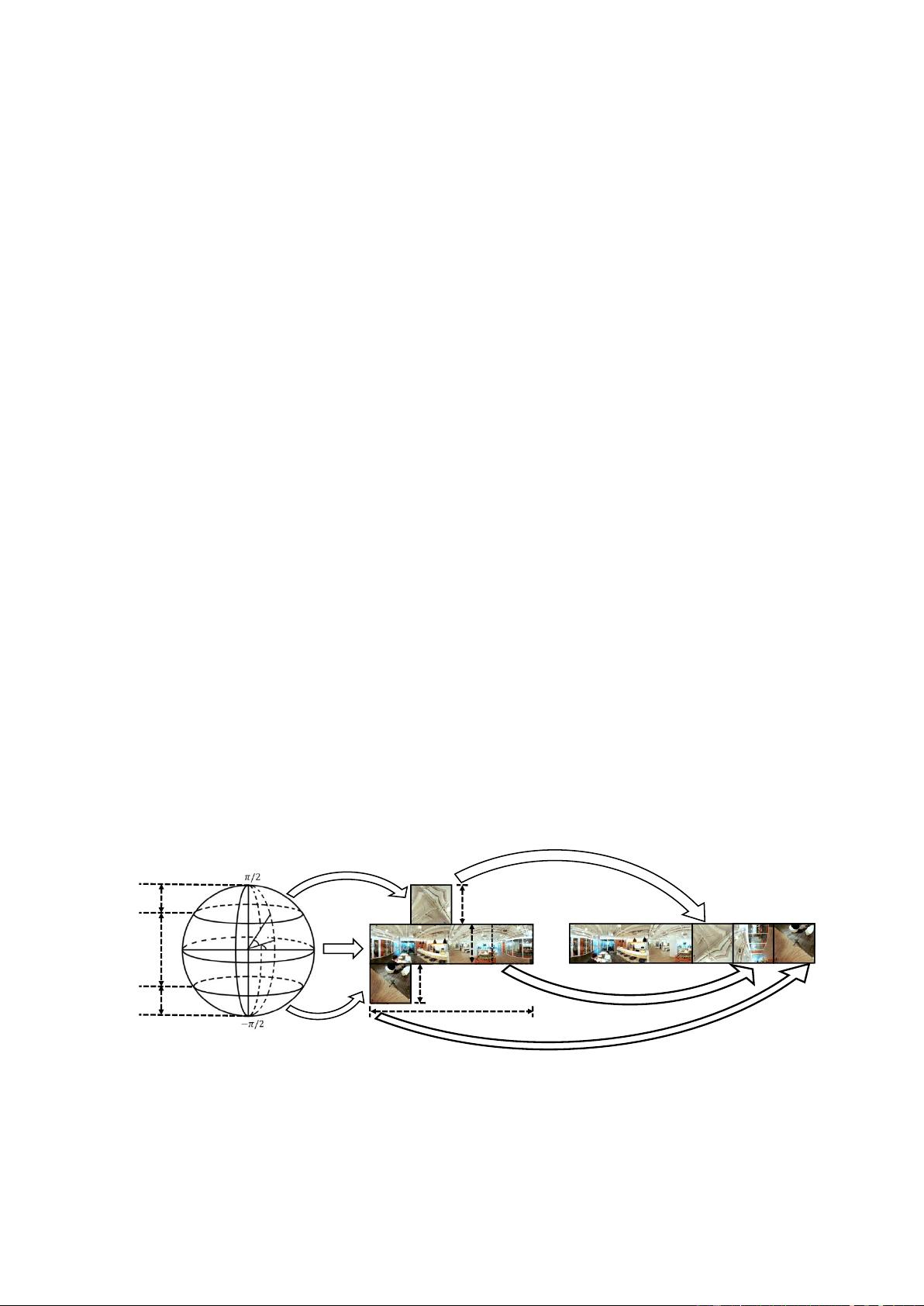
(a) (b) (c)
Fig.1 The schematic diagram of our proposed projection method in this paper









